При установке пакетов из официальных или сторонних репозиториев вы можете столкнуться с проблемой неудовлетворенные зависимости Ubuntu. Чтобы понять причину возникновения этой ошибки сначала надо разобраться как работают пакетные менеджеры в Linux. Здесь всё компоненты системы, библиотеки и сами программы разделены на пакеты. И если какой-либо программе нужна определенная библиотека, она не поставляется вместе с этой библиотекой, а ожидает, что эта библиотека будет уже установлена в системе.
Установкой библиотек и других компонентов занимается пакетный менеджер, отсюда у каждой программы есть ряд зависимостей которые должны быть удовлетворены чтобы программа смогла заработать.
По английски наша ошибка ещё может писаться как the following packages have unmet dependencies. Она может возникнуть в нескольких случаях, давайте сначала рассмотрим основные из них:
- Вы используете dpkg для установки deb пакета. Эта утилита не занимается установкой зависимостей. Вместо неё надо использовать apt install или потом просто установить недостающие зависимости с помощью apt, как это делается описано ниже;
- Вы используете старую версию дистрибутива — в старых версиях могло что-то изменится в репозитории и часть пакетов была удалена или переименована. С LTS версиями такое случается редко, но с обычными релизами вполне может произойти;
- Вы пытаетесь установить программу не от своего дистрибутива — несмотря на родство всех дистрибутивов семейства Debian, не желательно использовать программы из других дистрибутивов, так, как они могут требовать пакеты, которые в этом дистрибутиве называются по другому;
- У вас установлен устаревший пакет, который не позволяет обновить некоторые зависимости — случается, когда в системе уже есть какой-нибудь пакет старый пакет, требующий старую версию библиотеки, а новая программа, которую вы собираетесь установить уже хочет более новую версию и не позволяет её обновить. Эта проблема не очень типична для Ubuntu, так как здесь большинство версий программ в репозиториях заморожено, но часто встречается при использовании дистрибутивов с системой роллинг релизов.
1. Обновление и исправление зависимостей
Самое первое что надо сделать при проблемах с зависимостями, это хоть как-нибудь их исправить, потому что иначе пакетный менеджер работать не будет. В некоторых случаях, если списки репозиториев давно не обновлялись их обновление может помочь:
sudo apt update
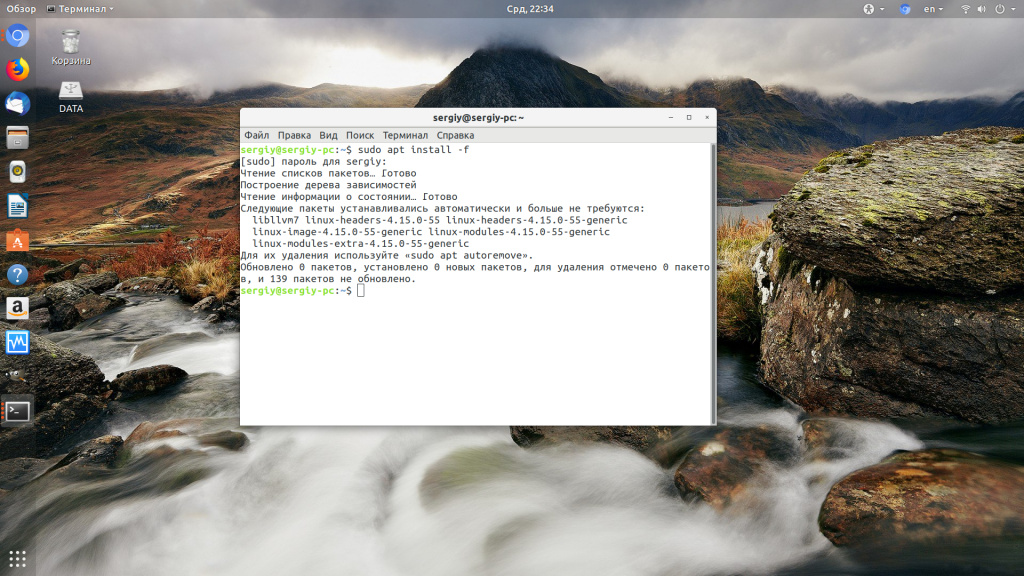
Далее выполните:
sudo apt install -f
Эта команда установит зависимости, которые есть во официальных репозиториях (поможет при использовании dpkg) и если это не решит проблему, то удалит пакеты, для которых зависимости удовлетворить не удалось. Также после этого можно выполнить:
sudo dpkg --configure -a
А потом повторить предыдущую команду. Следующим шагом можно попробовать обновить систему до самой последней версии. Это тоже может помочь если вы пытаетесь установить пакет из официальных репозиториев и при этом возникает проблема с зависимостями:
sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt full-upgrade
Если причиной вашей проблемы стал устаревший пакет надо его удалить или придумать для него замену. Например, если у вас установлена старая версия php, могут возникнуть проблемы с установкой новой версии, потому что будут конфликтовать версии библиотек, от которых зависит программа. Однако можно найти PPA со специально подготовленной старой версией php, которая ни с кем конфликтовать не будет.
Также подобная проблема может возникать при использовании PPA. Эти репозитории поддерживаются сторонними разработчиками, и могут содержать проблемы, если это ваш вариант, то, лучше поискать альтернативные способы установки необходимой программы.
2. Установка зависимостей
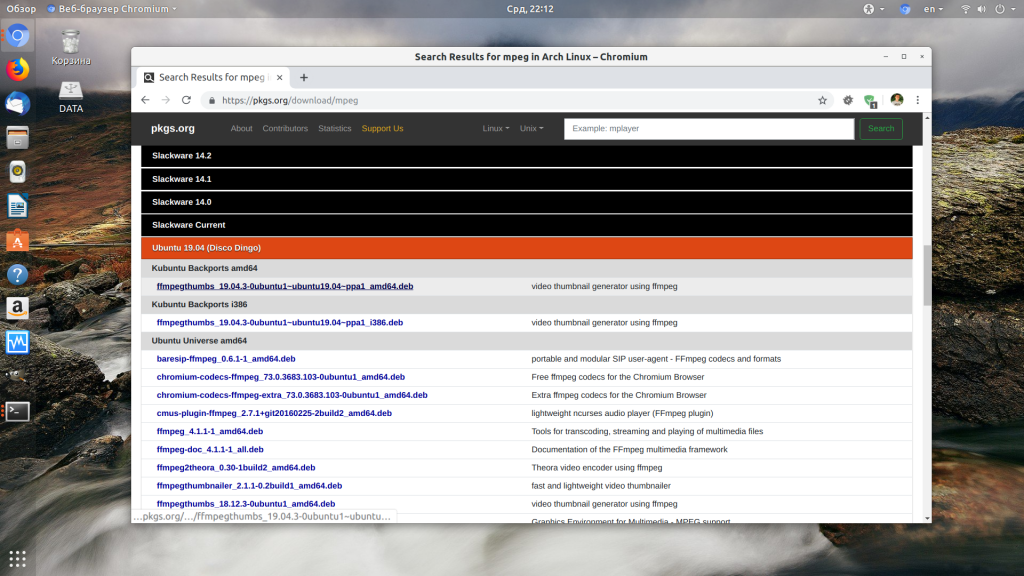
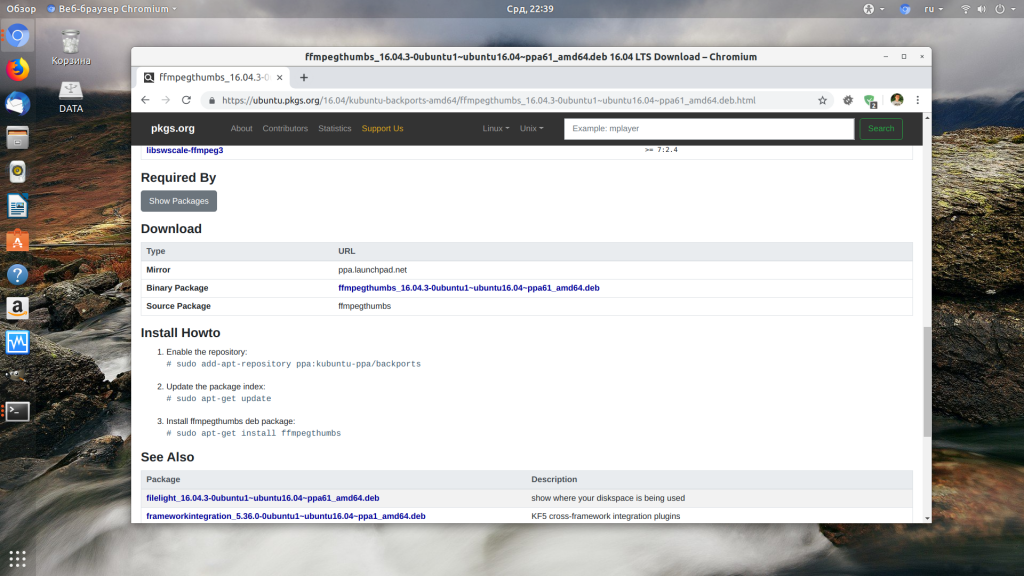
Дальше установка зависимостей Ubuntu. Следующий этап, если вы скачали пакет в интернете, например, от другого дистрибутива с таким же пакетным менеджером, можно попытаться установить таким же способом библиотеки, которые он просит. Это может сработать особенно, если вы пытаетесь установить программу из старой версии дистрибутива. Пакеты можно искать прямо в google или на сайте pkgs.org:
Здесь собрано огромное количество пакетов от различных дистрибутивов, в том числе и от Ubuntu и Debian. Просто выберите нужную версию пакета для вашей архитектуры. Скачать файл можно чуть ниже на странице пакета:
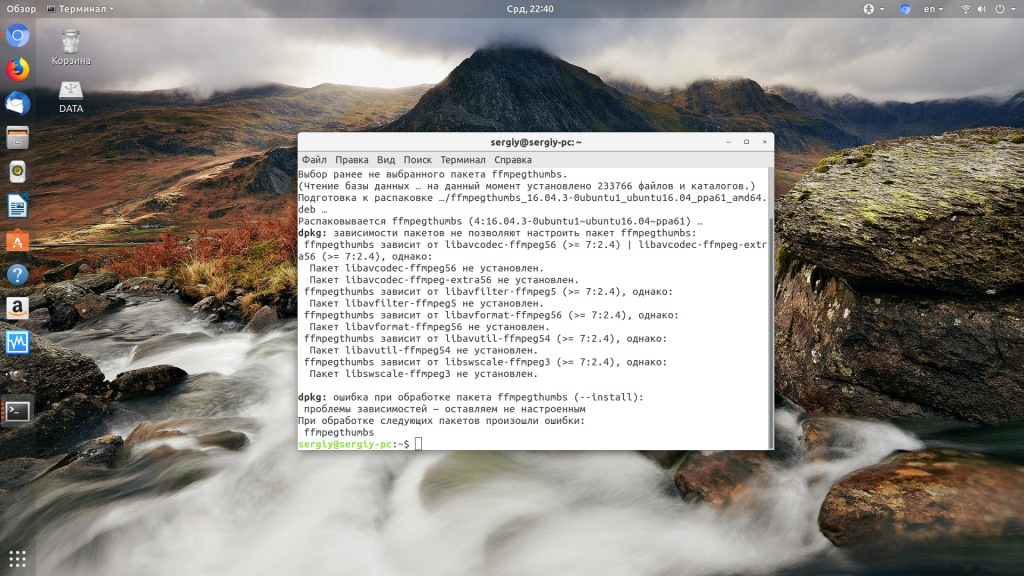
После загрузки пакета с сайта его можно установить через тот же dpkg:
sudo dpkg -i ffmpegthumbs_19.04.3-0ubuntu1~ubuntu19.04~ppa1_amd64.deb
После этого можно снова попробовать установить свой пакет. Но устанавливаемая библиотека может потребовать свои неудовлетворенные зависимости, а та ещё свои, поэтому тянуть программы из других дистрибутивов таким образом не рационально.
3. Удаление зависимостей
Если у вас есть скачанный пакет, и он говорит, что он зависит о версии библиотеки, которой в вашей системе нет, но вы уверены, что ему подойдет и другая версия, то можно просто убрать эту зависимость из пакета. Но для этого надо его перепаковать. Такая ситуация была когда-то с популярным менеджером Viber. Рассмотрим на примере того же вайбера.
Сначала распакуйте пакет в подпапку package командой:
dpkg-deb -x ./viber.deb package
Затем туда же извлеките метаданные пакета:
dpkg-deb --control viber.deb package/DEBIAN
В файле package/DEBIAN есть строчка Depends, где перечислены все библиотеки, от которых зависит пакет и их версии. Просто удалите проблемную библиотеку или измените её версию на ту, которая есть в системе.
vi package/DEBIAN
Затем останется только собрать пакет обратно:
dpkg -b viber package.deb
И можете устанавливать, теперь с зависимостями будет всё верно:
sudo dpkg -i package.deb
Но такое исправление зависимостей Ubuntu следует использовать только для пакетов, которые точно неверно собраны. Важно понимать, что пакетный менеджер вам не враг, а помощник, и то что вы отключите зависимости и установите программу ещё не значит, что она потом будет работать.
4. Распаковать пакет
Следующий способ подойдет, если программа которую вы устанавливаете это библиотека, например, веб-драйвер для Selenium. Пакет можно распаковать и просто разложить исполняемые файлы из него по файловой системе в соответствии с папками внутри архива. Только желательно использовать не корневую файловую систему, а каталог /usr/local/ он как раз создан для этих целей.
5. Использовать snap пакеты
Самый простой способ обойти проблемы с зависимостями — использовать новый формат установщика программ, в котором программа содержит все зависимости в установочном архиве и они устанавливаются аналогично Windows в одну папку. Установка такой программы будет дольше, но зато такие там вы точно не получите проблем с зависимостями Ubuntu. Всё программы, которые поддерживают этот формат есть в центре приложений Ubuntu:
Выводы
В этой статье мы разобрали как исправить проблемы с зависимостями Ubuntu. Некоторые из способов довольно сложные, а другие проще. Но сама эта система, согласно которого пакеты зависят от других, а те ещё от других очень сложная и не удивительно, что время от времени в ней возникают ошибки. А какие способы решения этой проблемы вы знаете? Напишите в комментариях?
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
Note: All commands asked to be run must be run in the terminal, which can be opened by either Ctrl+Alt+T or searching for terminal in the dash.
Is it really broken?
Try running the following command and try to reinstall the software you were trying to install
sudo apt-get update
Pre-Perfomance Steps
Backing up
Back up the following files:
/etc/apt/sources.list/var/lib/dpkg/status
To do so, use these commands
sudo cp /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.original
and
sudo cp /var/lib/dpkg/status /var/lib/dpkg/status.original
Clearing your apt-cache
apt keeps a cache of recently downloaded packages to save bandwidth when it is required to be installed. This can be counter-productive in some cases
Now, to clean it, you have two options
sudo apt-get clean
This will remove all cached packages belonging to the folder /var/cache/apt/archives/ and /var/cache/apt/archives/partial except the .lock files. This is recommended
sudo apt-get autoclean
This scans the folders /var/cache/apt/archives/ and /var/cache/apt/archives/partial and checks if the package is still in the repositories and removes the ones that aren’t
Fixing dependencies
Using apt’s fix-broken mode
sudo apt-get -f install
This will cause apt to scan for missing dependencies and fix them from the repositories
If the output states that nothing new was installed or upgraded, it has failed.
Checking if all required sources are enabled
Type gksu software-properties-gtk and you’ll get this window
Make sure all sources are enabled.
next, go to the Other software tab and check if the required PPAs for the software to be installed are there and are enabled. Also, try disabling some PPAs which might be having broken packages
now, run sudo apt-get update
Try installing the software now
Selecting a better server to download from
Type gksu software-properties-gtk and you’ll get this window
Click the Download from the Dropdown box and select other
Click Select Best Server
Run sudo apt-get update
Try installing the software
also, try using sudo apt-get install -f
PPA Purge
This is a tool used to purge broken/unwanted ppa’s and their applications along with it
To install it, run
sudo apt-get install ppa-purge
But, Considering the question apt is broken so the above command will fail. So use this command
mkdir ppa-purge && cd ppa-purge && wget http://mirror.pnl.gov/ubuntu/pool/universe/p/ppa-purge/ppa-purge_0.2.8+bzr56_all.deb && wget http://mirror.pnl.gov/ubuntu//pool/main/a/aptitude/aptitude_0.6.6-1ubuntu1_i386.deb && sudo dpkg -i ./*.deb
Now use ppa purge
sudo ppa-purge ppa:someppa/ppa
Y-PPA Manager
Y-PPA Manager is a gui app that helps you manage PPA’s and various problems assosiated with it
To install it
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/y-ppa-manager
and
sudo apt-get update
and
sudo apt-get install y-ppa-manager
Considering the question, apt is broken so, use these command instead
sudo su
and
32 Bit:
mkdir y-ppa-manager && cd y-ppa-manager && wget https://launchpad.net/~webupd8team/+archive/y-ppa-manager/+files/launchpad-getkeys_0.3.2-1~webupd8~oneiric_all.deb && wget https://launchpad.net/~webupd8team/+archive/y-ppa-manager/+files/y-ppa-manager_0.0.8.6-1~webupd8~precise_all.deb && wget https://launchpad.net/~webupd8team/+archive/y-ppa-manager/+files/yad_0.17.1.1-1~webupd8~precise_i386.deb && dpkg -i ./*.deb
64 Bit:
mkdir y-ppa-manager && cd y-ppa-manager && wget https://launchpad.net/~webupd8team/+archive/y-ppa-manager/+files/launchpad-getkeys_0.3.2-1~webupd8~oneiric_all.deb && wget https://launchpad.net/~webupd8team/+archive/y-ppa-manager/+files/y-ppa-manager_0.0.8.6-1~webupd8~precise_all.deb && wget https://launchpad.net/~webupd8team/+archive/y-ppa-manager/+files/yad_0.17.1.1-1~webupd8~precise_amd64.deb && dpkg -i ./*.deb
Now type in y-ppa-manager
You’ll be presented with this window
Double click on advanced, and you’ll get this window
Do the following Tasks outlined in black
Prevention is better than cure
It is better to prevent than to search for this question on AskUbuntu 
So, here are the guidelines to keep you safe
Keep your system up-to-date
always run the following command regularly
sudo apt-get update&&sudo apt-get upgrade
or, you can always use Update Manager with this command
gksu update-manager
Using only trusted PPA’s
Only use PPA’s meant to be used on Ubuntu also, only use PPA’s with trusted sources. Infact, the package might already be in the ubuntu repositories
Backing up when things are good and restoring it later
For this you need Y-PPA-Manager. The steps to install it are given above.
Run this command to open Y-PPA-Manager
y-ppa-manager
You’ll be presented with this window
Double click on advanced, and you’ll get this window
Run this:
You’ll be asked to save a tar.gz file with a dialog similar to the one below. Save it in another partition or a safe place
Later, when you need to restore it again, follow similar steps and when you get to the advanced dialog,Click on this:
You’ll be asked to restore from the previous backup which you saved before with a dialog similar to the one below
Still not working?
Package dependency errors are not always generic and depends on the package to be installed.
If following all the steps given to fix the error does not work for you, you can always ask on Ask Ubuntu
Here are some commands which you need to post the output of
sudo apt-get install packagename
and
cat /etc/apt/sources.list
and
cat /etc/apt/sources.list.d/*
(Thanks to Basharat Sial)
There are also other files/commands that you need the output of that might be error specific, and users will probably prompt you in the comments to post the file/command.
First of all try this
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get clean
sudo apt-get autoremove
If error still persists then do this
sudo apt --fix-broken install
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo dpkg --configure -a
sudo apt-get install -f
Afterwards try this again:
sudo apt-get install npm
But if it still couldn’t resolve issues check for the dependencies using sudo dpkg --configure -a and remove them one-by-one . Let’s say dependencies are on npm then go for this ,
sudo apt-get remove nodejs
sudo apt-get remove npm
Then go to /etc/apt/sources.list.d and remove any node list if you have. Then do a
sudo apt-get update
Then check for the dependencies problem again using sudo dpkg --configure -a and if it’s all clear then you are done .
Later on install npm again using this
v=8 # set to 4, 5, 6, ... as needed
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_$v.x | sudo -E bash -
Then install the Node.js package.
sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
The answer above will work for general cases also(for dependencies on other packages like django ,etc) just after first two processes use the same process for the package you are facing dependency with.
Error The following packages have unmet dependencies has plagued Ubuntu users for a while now, and there are more and more sightings of the error on various versions of Ubuntu. The APT package management system is easy to use, but in some occasions, such as when you’re mixing in third-party dependencies, you might get this error from apt-get.
This happens when you try to install something with the apt system via a terminal, and the installation fails with no obvious problem whatsoever. This issue isn’t limited to any one particular program, but it might happen with quite a few of them. This is because the issue lies in the apt system, and not in the program you’re installing.
There are fortunately quite a few solutions for this, some of which are easier to do, and others more difficult, but if you follow the instructions in the methods below, you will get rid of the error in no time.
Note: Before proceeding with any of the methods, it is advisable that you back up configurations files such as so you can revert back any changes in case something goes wrong. This is done by using the following steps:
- Press simultaneously the Alt, Ctrl and T on your keyboard to open a Terminal.
- Type in
and press Enter.
- When the previous command finishes running, type in sudo cp /var/lib/dpkg/status /var/lib/dpkg/status.original and press Enter again.
Method 1: Use the -f parameter
This is the easiest one to try, and only requires adding two more letters to the command that you’re typing. Instead of using sudo apt-get install PACKAGENAME, where PACKAGENAME is the package you’re trying to install with the apt system, use sudo apt-get install -f. The -f parameter will attempt to correct a system which has broken dependencies, after which you’ll be able to install the package in question.
- Open a Terminal by pressing Ctrl, Alt and T simultaneously on your keyboard.
- Type in sudo apt-get install -f and press Enter to execute it.
- Once it’s done, type in sudo dpkg –configure -a, press Enter to run it, and run the command from step 2 once more.
Method 2: Use Aptitude
Aptitude is an alternative of apt-get which you can use as a higher-level package manager. You can use it to try and install your package with it, instead of apt-get, but first you need to install aptitude.
- Press simultaneously the Ctrl, Alt, and T keys on your keyboard to open a
- Type in sudo apt-get install aptitude and press Enter to execute the command.
- Type in sudo aptitude install PACKAGENAME, where PACKAGENAME is the package you’re installing, and press Enter to execute it. This will try to install the package via aptitude instead of apt-get, which should potentially fix the unmet dependencies issue.
Method 3: Make sure that the restricted and universe repositories are enabled and try a better server
- Press simultaneously Alt and F2 on your computer, type in software-properties-gtk and press
- In the Ubuntu Software tab, make sure that all the repositories (main, universe, restricted, multiverse) are enabled.
- Click the list of servers where it says Download from, and choose
- Click Select Best Server.
- Press Alt, Ctrl and T simultaneously to open a Terminal, and type in sudo apt-get update, then press Once it’s done running, try installing the software again.
Method 4: Clean the package database
A corrupted package database is a potential cause for unmet dependencies, as well as packages not installing properly. However, cleaning the package database can fix this, and you can do it with two commands, which I will explain below. First of all, however, press Ctrl, Alt and T to open a Terminal, and don’t forget to hit Enter after the command in order to run it.
- sudo apt-get clean will clean the local repository from all the retrieved package files (.deb). It will remove everything except the lock files from /var/cache/apt/archives, and /var/cache/apt/archives/partial/.
- sudo apt-get autoclean will also clean up the retrieved files, but unlike the previous command, this one only removes packages that you can no longer download and are pretty much useless.
Method 5: Eliminate any held packages
Held packages are actually held because there are dependency problems and conflicts which apt can’t solve. Eliminating such packages means that there won’t be any such conflicts, and may consequently fix your issue.
- Open a Terminal by pressing Ctrl, Alt and T
- Type in sudo apt-get -u dist-upgrade and press If there are any held packages, it will show them, and it is yours to eliminate them.
- First try running
sudo apt-get -o Debug::pkgProblemResolver=yes dist-upgrade
and see if it fixes the issue. If it exits with X not upgraded at the end, where X is the number of held packages, you will need to delete them one by one.
- To remove a held package, use sudo apt-get remove –dry-run PACKAGENAME (PACKAGENAME is the package you’re trying to remove). The –dry-run parameter makes sure you are informed of whatever happens next. When you’ve removed all packages, try installing the one that caused the problem in the first place, and see what happens.
Method 6: Purge/Remove/Disable PPAs
Personal Package Archives are repositories that are hosted on the Launchpad, and are used to upgrade or install packages that aren’t usually available in the official repositories of Ubuntu. They’re most commonly a cause of unmet dependencies, especially when they’re used to upgrade an existing package from the Ubuntu repository. You can either disable, remove or purge them.
Disable means that packages installed from that PPA will no longer get updates.
- Press simultaneously Alt and F2, and run software-properties-gtk.
- From the Other Software tab, you will find two lines for every PPA, where one is for the source, and another for the compiled package. To disable a PPA, you should uncheck both lines.
Purge means that all packages in the selected PPA will be downgraded to the version in the official repositories, and will also disable the PPA. To install PPA Purge, you could use sudo apt-get install ppa-purge, but considering that the apt is broken, you should use this command in the Terminal (Alt, Ctrl and T simultaneously, then Enter to run):
mkdir ppa-purge && cd ppa-purge && wget http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/universe/p/ppa-purge/ppa-purge_0.2.8+bzr56_all.deb && wget https://ftp.u-picardie.fr/mirror/ubuntu/ubuntu/pool/main/a/aptitude/aptitude_0.8.10-6ubuntu1_i386.deb && sudo dpkg -i ./*.deb
Next, run sudo ppa-purge ppa:someppa/ppa in order to purge the selected PPA. However, since PPA Purge still doesn’t remove a PPA, you can use the commands below to remove the PPA. Ignore the first one if your intentions don’t include removing the installed package.
- sudo apt-get autoremove –purge PACKAGENAME
- sudo add-apt-repository –remove ppa:someppa/ppa
- sudo apt-get autoclean
You should be able to install the necessary package afterwards.
Even though there are quite a few methods above, you should also know that it’s always better to prevent such issues. You should keep your system up-to-date, only use trusted PPAs, and back up when everything is working properly so you can restore later. However, if you’ve forgotten to do these things, use the methods above to fix your issue, and use the prevention methods to make sure you don’
Kevin Arrows
Kevin Arrows is a highly experienced and knowledgeable technology specialist with over a decade of industry experience. He holds a Microsoft Certified Technology Specialist (MCTS) certification and has a deep passion for staying up-to-date on the latest tech developments. Kevin has written extensively on a wide range of tech-related topics, showcasing his expertise and knowledge in areas such as software development, cybersecurity, and cloud computing. His contributions to the tech field have been widely recognized and respected by his peers, and he is highly regarded for his ability to explain complex technical concepts in a clear and concise manner.
I have no idea if it is still relevant for you to get help on this, but here is a summary of the things one could do to help in such situation
(from here at Appuals (appuals.com)) :
Method 1: Use the -f parameter (I know you already did that, but I gather everything here altogether)
sudo apt-get install -f
sudo dpkg --configure -a
sudo apt-get install -f
Method 2: Use Aptitude
sudo aptitude install PACKAGENAMEwhere PACKAGENAME is the package you’re installing,
and press Enter to execute it. This will try to install the package via aptitude instead of apt-get, which should potentially fix the unmet dependencies issue.
Method 3: Make sure that the restricted and universe repositories are enabled and try a better server
software-properties-gtk
- In the Ubuntu Software tab, make sure that all the repositories (main, universe, restricted, multiverse) are enabled.
- Click the list of servers where it says “Download from”, and choose
- Click “Select Best Server”.
-
Press Alt, Ctrl and T simultaneously to open a Terminal, and type in
sudo apt-get updatethen press
Once it’s done running, try installing the software again.
Method 4: Clean the package database
sudo apt-get clean
sudo apt-get autoclean
Method 5: Eliminate any held packages
sudo apt-get -u dist-upgrade
then (if pb):
sudo apt-get -o Debug::pkgProblemResolver=yes dist-upgrade
and see if it fixes the issue. If it exits with X not upgraded at the end, where X is the number of held packages, you will need to delete them one by one.
To remove a held package,
sudo apt-get remove --dry-run PACKAGENAME(PACKAGENAME is the package you’re trying to remove). The --dry-run parameter makes sure you are informed of whatever happens next. When you’ve removed all packages, try installing the one that caused the problem in the first place, and see what happens.
Method 6: Purge/Remove/Disable PPAs
Personal Package Archives are repositories that are hosted on the Launchpad, and are used to upgrade or install packages that aren’t usually available in the official repositories of Ubuntu. They’re most commonly a cause of unmet dependencies, especially when they’re used to upgrade an existing package from the Ubuntu repository. You can either disable, remove or purge them.
Then if they still show some dependency issues, let’s purge them:
apt purge packageXX packageYY packageZZetc.
until everything is clean
Some say also to edit /var/lib/dpkg/status and remove blocs which have not complete installation but I doubt this really solves problems, it is just hiding it under the carpet.