This blog post is a complete revised Step-by-step SCCM Installation Guide. It covers every aspect of the SCCM Installation. From the server prerequisites to the SQL installation, the Sccm installation itself and all configuration and site server installation. Following this guide, you should have a functional SCCM server in a couple of hours.
We already did a guide in the past when SCCM 1511 was released but it’s was time for a 2020 refresh.
Since our first guide, more than 12 SCCM version has been released… and the product even changed its name to Microsoft Endpoint Manager. (MEM or MEMCM).
SCCM installation has never been an easy process and the product itself can be complex for inexperienced administrators. With this blog post, our goal is to bring it a bit further, explaining concepts and best practices rather than just guide the user through the installation process.
If you’re not familiar with SCCM Current Branch Features, you can visit this Microsoft Docs article which covers it all.
If you’re still running SCCM 2012 (!) and plans to migrate, stop reading this guide. You do not need to do a complete new installation. See our blog post on how to upgrade to SCCM Current Branch instead.
We hope this guide brings all the information you need and that you’ll appreciate administering it.
The PDF file is a 162 pages document that contains all informations to install and configure SCCM Current Branch. Use our products page or use the button below to download it .
Download
SCCM Current Branch Installation and Configuration Guide
Important Info
This post is HUGE, use this table of content to navigate easily through the SCCM Installation guide sections.
- Part 1 | Design Recommendation and Installation Prerequisites
- Part 2 | SQL Installation and Configuration
- Part 3 | SCCM Installation
- Part 4 | Application Catalog Web Service Point Installation
- Part 5 | Application Catalog Website Point Installation
- Part 6 | Asset Intelligence Synchronization Point Installation
- Part 7 | Certificate Registration Point Installation
- Part 8 | Distribution Point Installation
- Part 9 | Endpoint Protection Point Installation
- Part 10 | Enrollment Point Installation
- Part 11 | Enrollment Proxy Point Installation
- Part 12 | Fallback Status Point Installation
- Part 13 | Management Point Installation
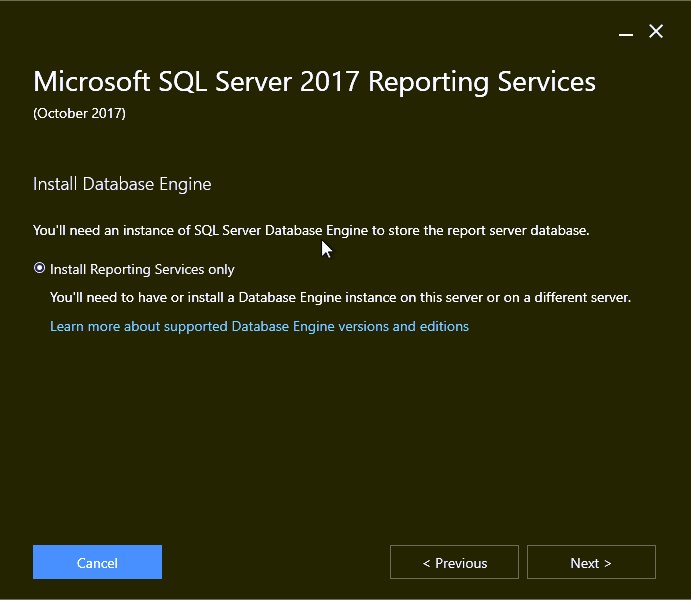
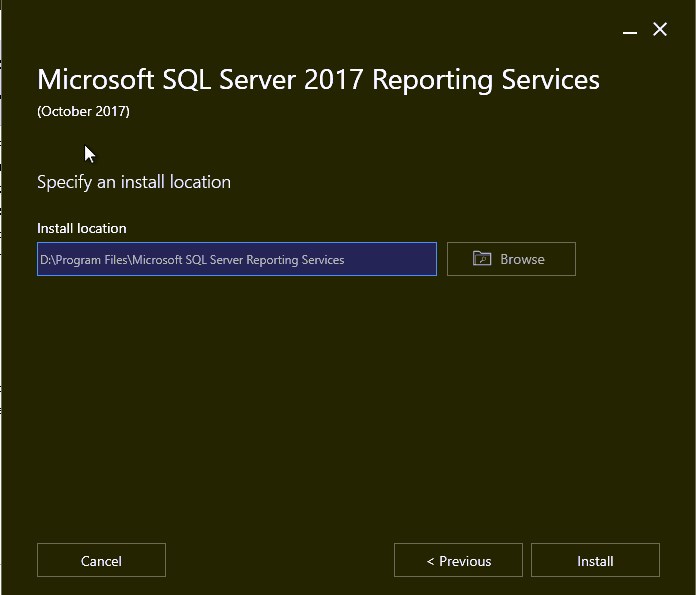
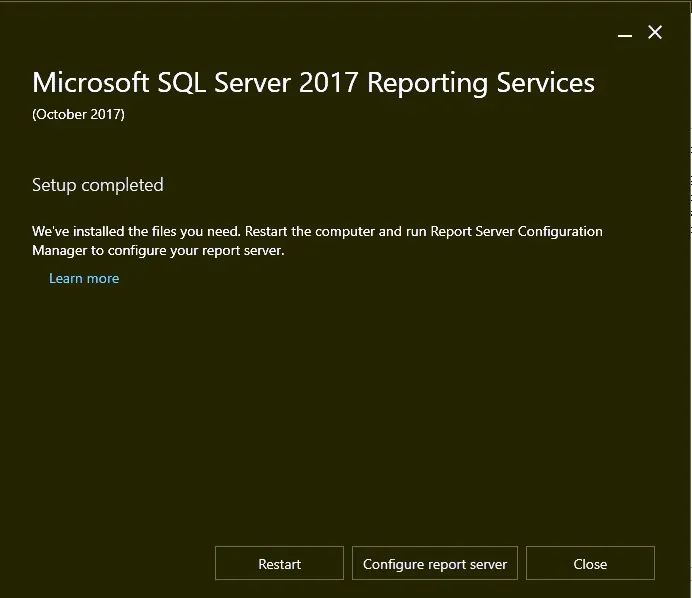
- Part 14 | Reporting Services Point Installation
- Part 15 | Software Update Point Installation
- Part 16 | State Migration Point Installation
- Part 17 | System Health Validator Point Installation
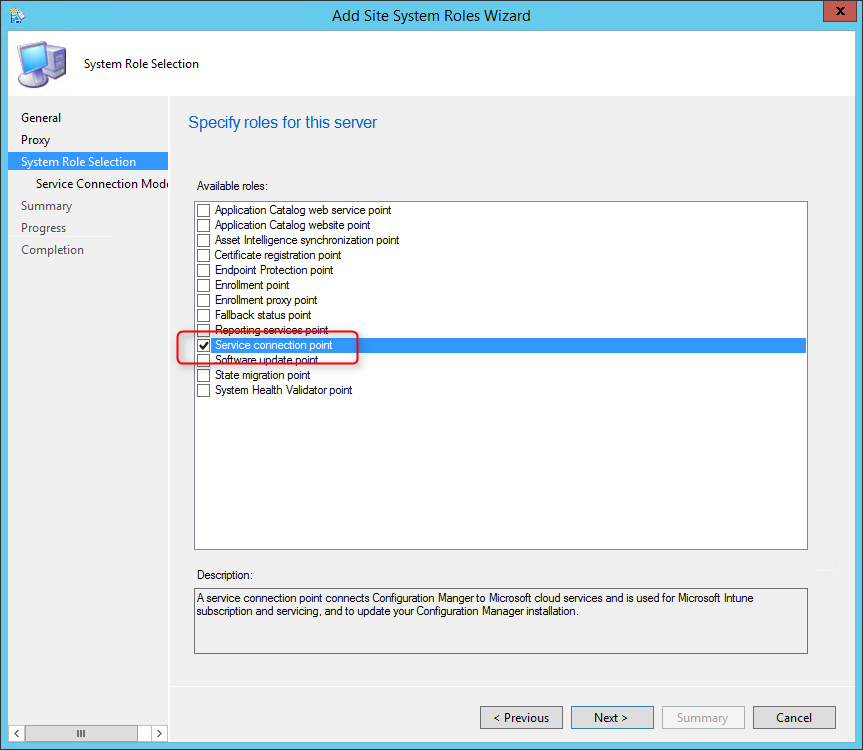
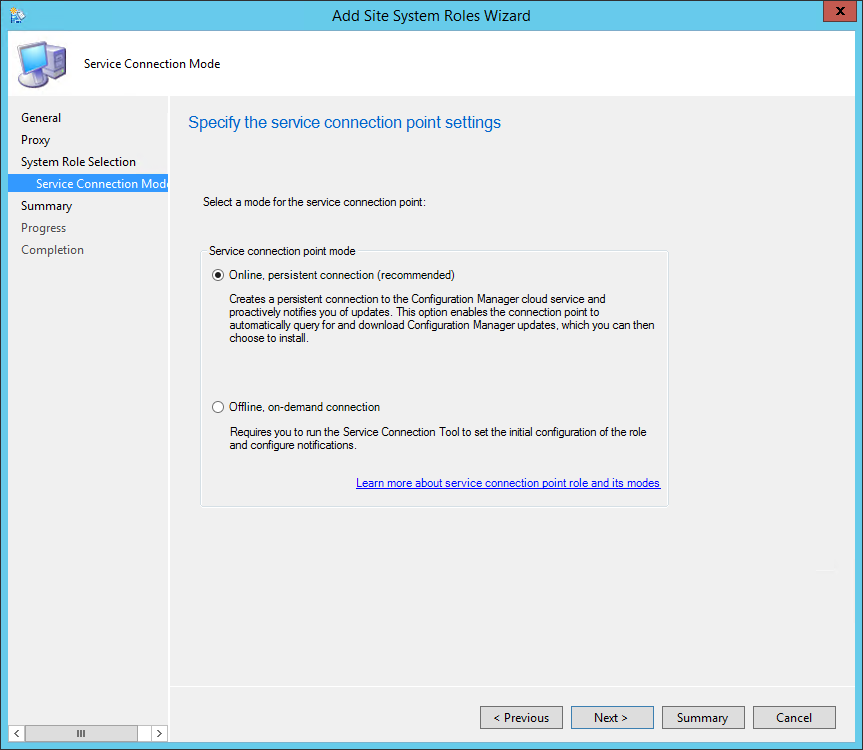
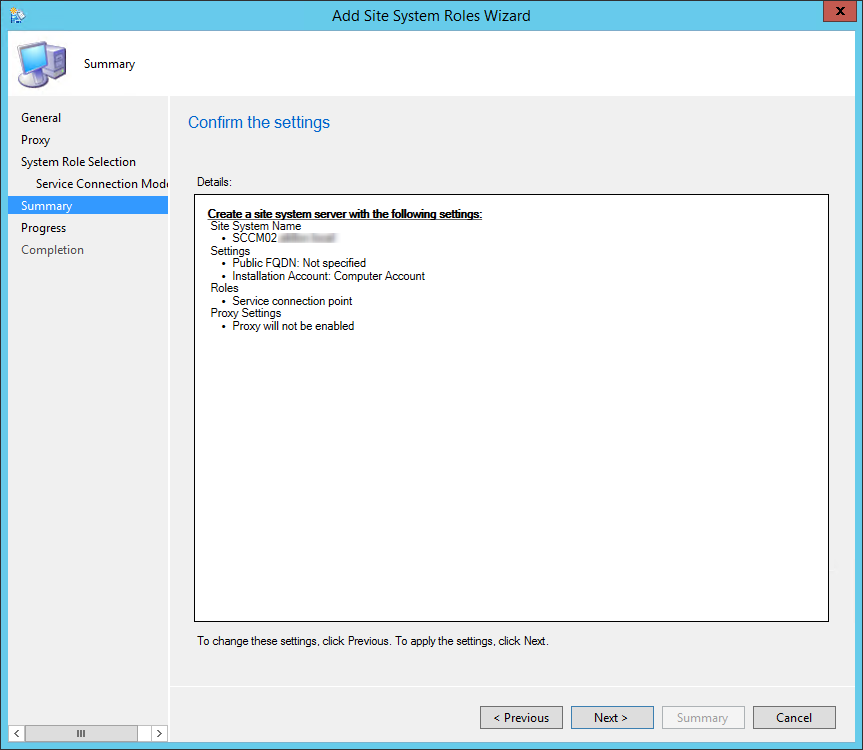
- Part 18 | Service Connection Point Installation
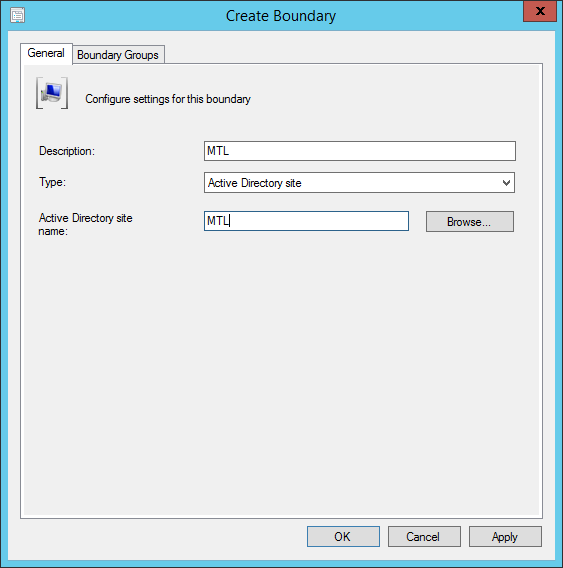
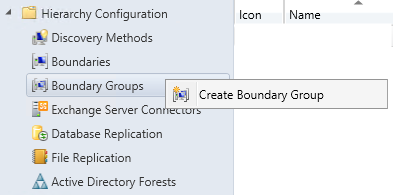
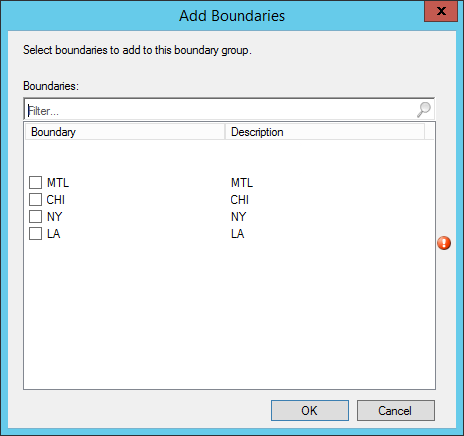
- Part 19 | Boundaries Configuration
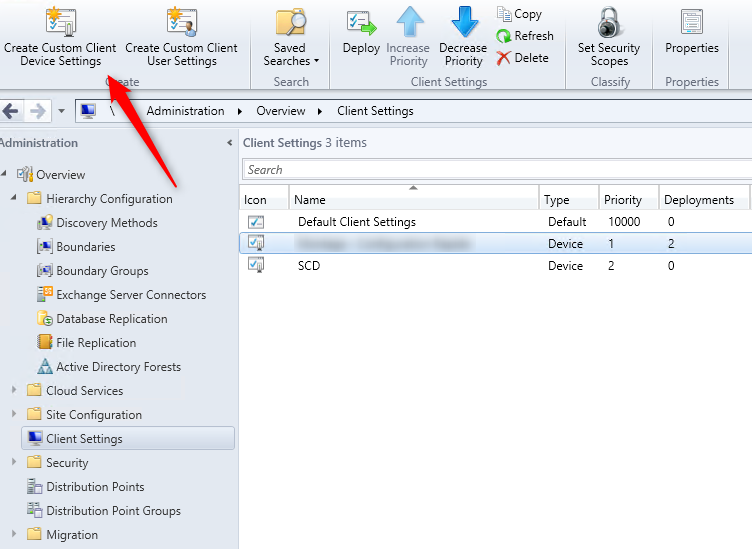
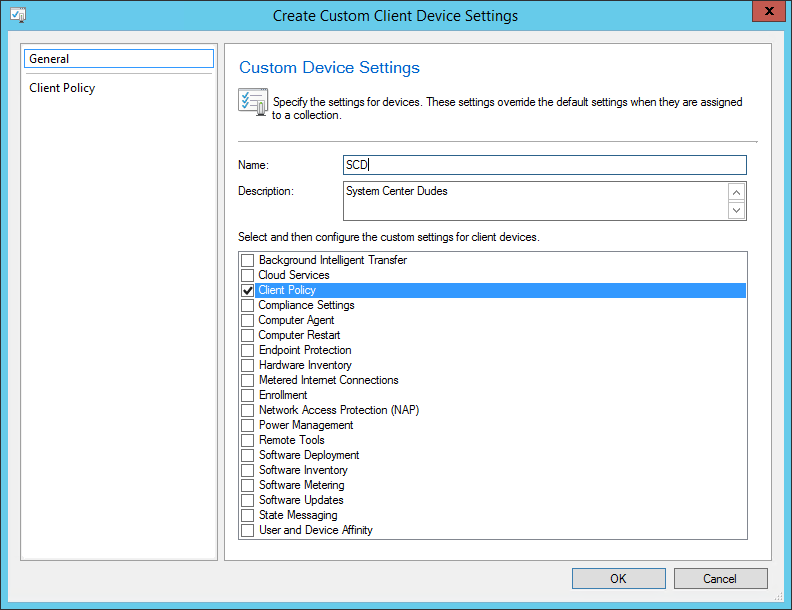
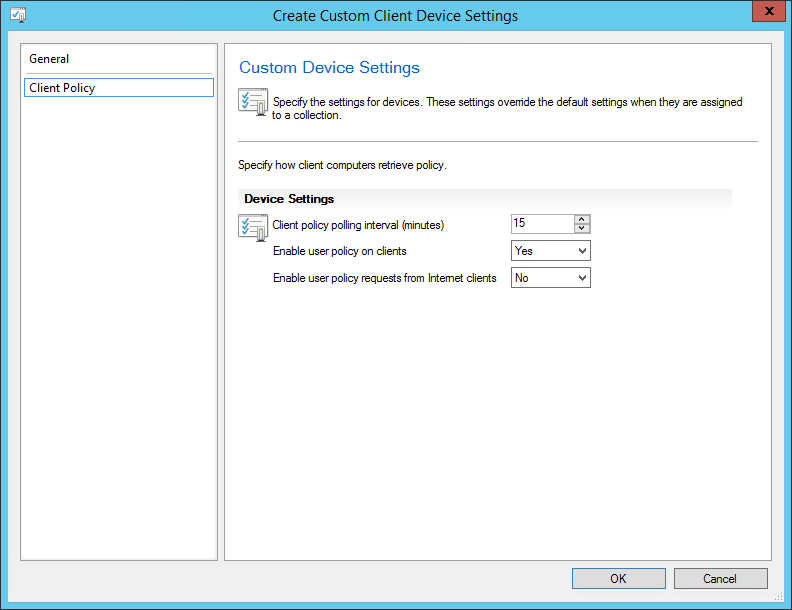
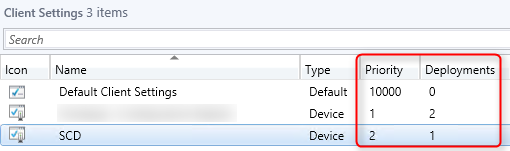
- Part 20 | Client Settings Configuration
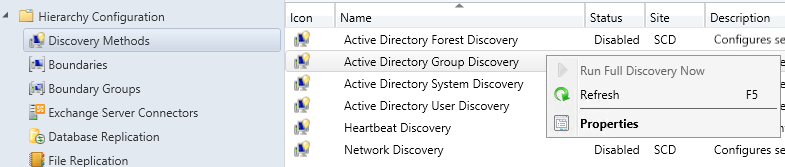
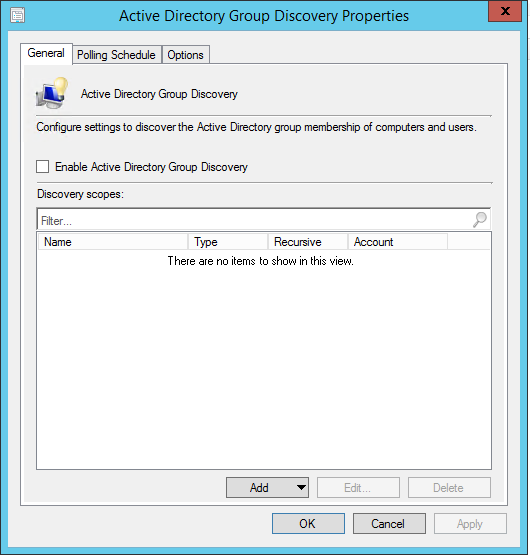
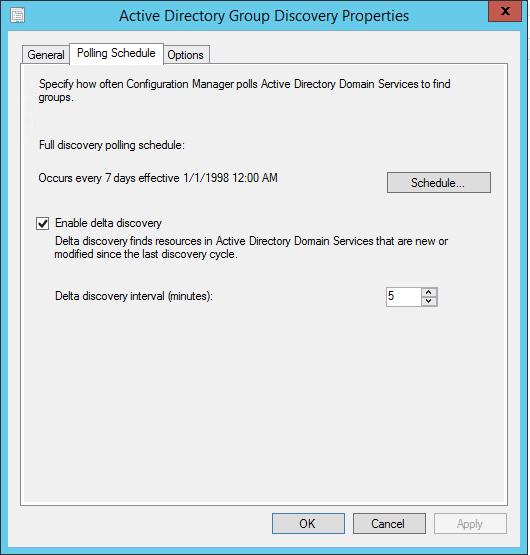
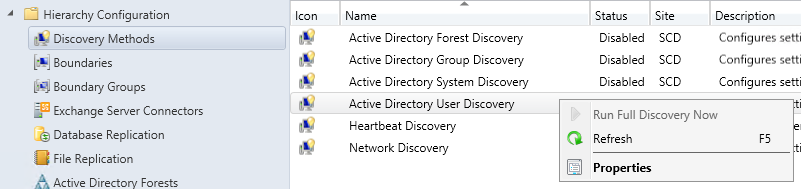
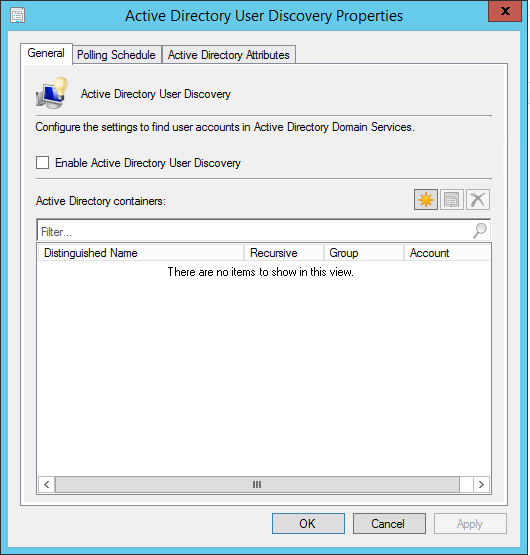
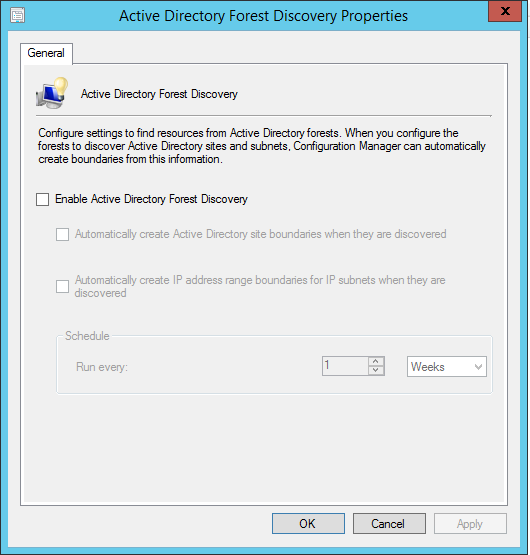
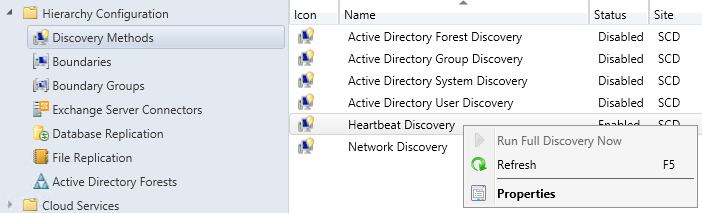
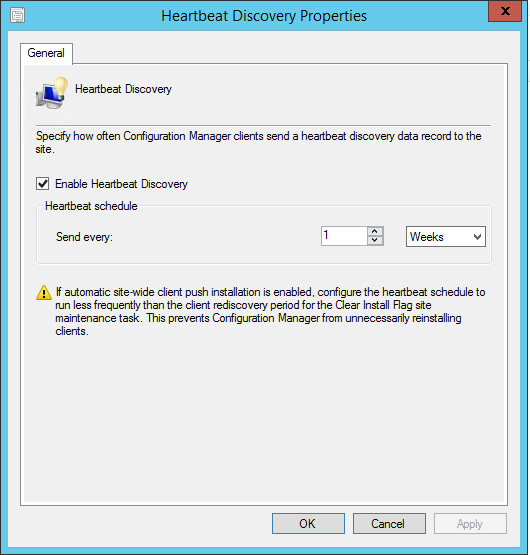
- Part 21 | Discovery Methods Configuration
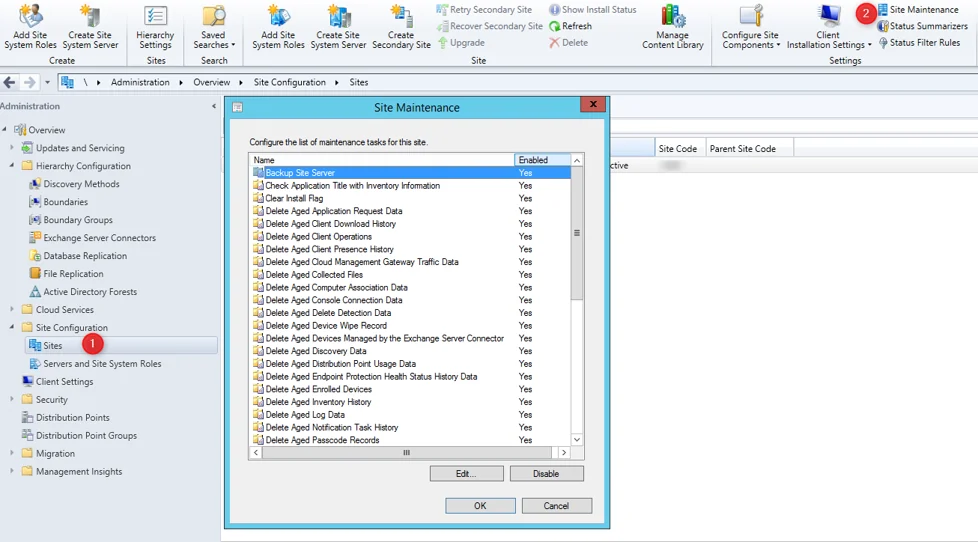
- Part 22 | Maintenance Task Configuration
- Part 23 | Backup and Restore
- Part 24 | Enable Co-Management (external post)
- Part 25 | Cloud Distribution Point (external post)
- Part 26 | Cloud Management Gateway (external post)
- Part 27 | Start your modern management journey (Co-management and Intune) (external post)
Part 1 – Design Recommendation and Installation Prerequisites
SCCM Hardware Requirements
In the first part, we will cover SCCM installation prerequisites most specifically hardware requirements, design recommendations, and server prerequisites.
The hardware requirements for a Primary Site server largely depends on the features that are enabled, and how each of the components is utilized. When the number of clients grows and changes, the server hardware requirements change accordingly. For the initial deployment, hardware requirements can be estimated for each server by determining:
- The overall need for each component (Will you do Operating System Deployment ? How many daily software deployments ? Is Inventory and reporting is important for your organization? Will you manage Internet Client ?)
- The number of clients planned to be installed
- The load on each of the installed SCCM components
In general, medium environments (couple thousand clients) should consider the following recommendations when planning hardware:
- SCCM and SQL Server communicate constantly. We recommend that the main database and SQL Server be installed on the Primary site server. This is fully debatable and we understand that some organization tries to standardize their SQL distribution. Performance is simply better using a local installation when configured properly
- Neither the SCCM site nor the SQL database should share their disks with other applications
- Configure the SQL Server databases and logs to run on a different disk than the disk where the SCCM database is located.
Another issue to consider when determining hardware requirements for a site servers is the total amount of data that will be stored in the database. To estimate the required database size for a single site, an approximate figure of 5Mb to 10Mb per client is typically used.
In our setup, we will install a single Primary Site that has the role of Management Point, Reporting Point, Distribution Point, PXE Service Point, State Migration Point, Fallback Status Point and Software Update Point. SQL Reporting Services will be used to provide consolidated reporting for the hierarchy. This role will also be installed on the SCCM Server. Running reports can have an impact on server CPU and memory utilization, particularly if large poorly structured queries are executed as part of the report generation.
Consider placing client-facing role (Distribution Point, Reporting Point) on a separate server in order to reduce load on your Primary server.
Here’s our recommended reading about hardware requirements:
SCCM Installation Guide
- Design a hierarchy of sites
- Recommended hardware
- Supported configurations
- Plan for the site database
- Plan for site system servers and site system roles
We strongly recommend that you understand SQL Server before installing SCCM. Talk and have a good relation with your DBA if you have one in your organization.
Here’s our recommended reading about SQL :
- Storage Top 10 Best Practice
- SQL Server Best Practices Article
- Disk Partition Alignment Best Practices for SQL Server
Operating System
For this post, our servers run Windows 2019 with latest security patches
Make sure that your OS is supported, see the SCCM Current Branch Technet Documentation
Disks
Disks IOs are the most important aspect of SCCM performance. We recommend configuring the disks following SQL Best practice. Split the load on a different drives. When formatting SQL drives, the cluster size (block size) in NTFS must be 64KB instead of the default 4K. See the previously recommended reading to achieve this.
| Letter | Content | Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C: | Windows | 100GB | ||
| D: | SCCM | 200GB | ||
| E: | SQL Database (64K) | 40GB | ||
| F: | SQL TempDB (64K) | 40GB | ||
| G: | SQL Transaction Logs (64K) SQL TempDB Logs |
40GB |
Primary Site server prerequisites
Once your hardware is carefully planned, we can now prepare our environment and server before SCCM Installation.
Active Directory schema extension
You need to extend the Active Directory Schema only if you didn’t have a previous installation of SCCM in your domain. If you have SCCM 2007 already installed and planing a migration, skip this step.
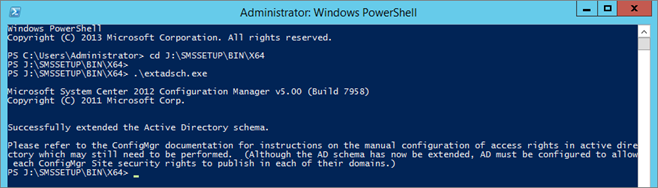
- Logon to a server with an account that is a member of Schema Admins security group
- From SCCM ISO run .SMSSETUPBINX64extadsch.exe
- Check schema extension result, open Extadsch.log located in the root of the system drive
Create the System Management Container
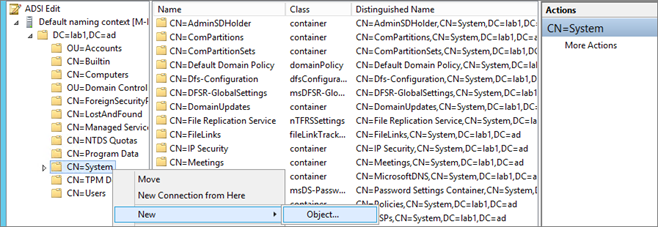
Configuration Manager does not automatically create the System Management container in Active Directory Domain Services when the schema is extended. The container must be created one time for each domain that includes a Configuration Manager primary site server or secondary site server that publishes site information to Active Directory Domain Services
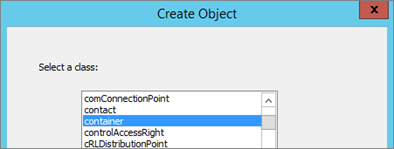
- Start ADSIEdit, go to the System container and create a new Object
- Select Container
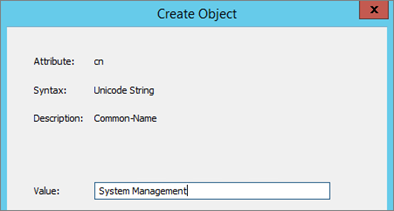
- Enter System Management
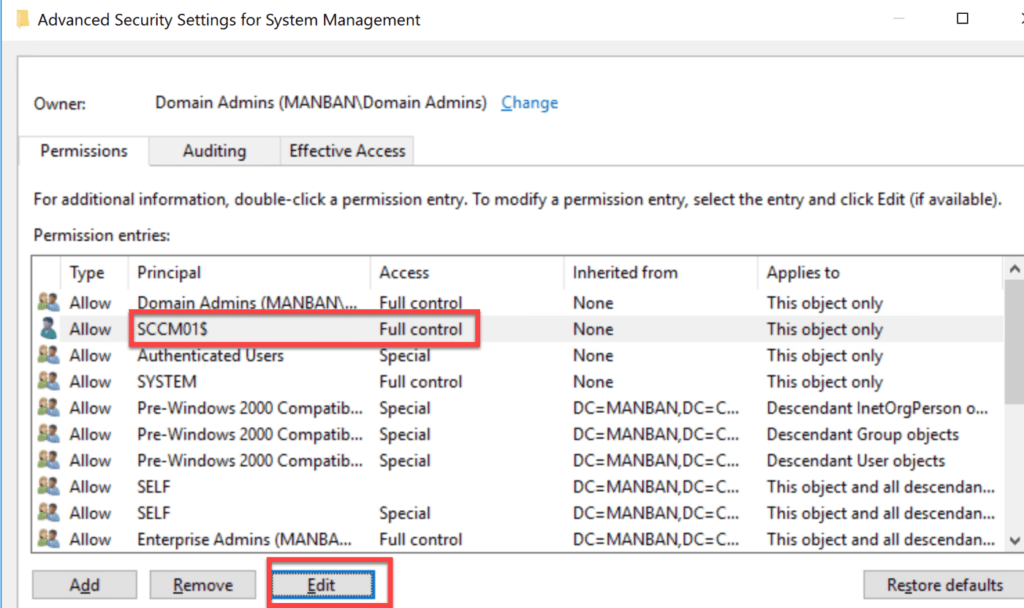
Set security permission
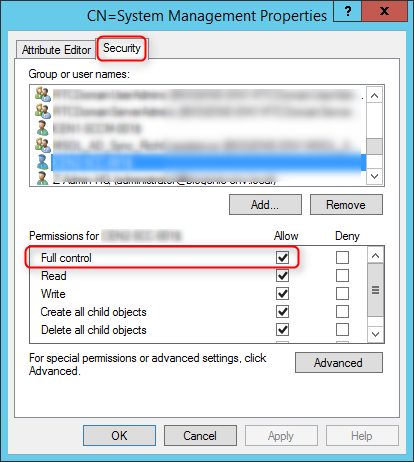
- Open properties of the container System Management created previously
- In the Security tab, add the site server computer account and Grant the Full Control permissions
- Click Advanced, select the site server’s computer account, and then click Edit
- In the Applies to list, select This object and all descendant objects
- Click OK and close the ADSIEdit console
SCCM Accounts
Create the necessary accounts and groups created before installation. You can use a different name but I’ll refer to these names throughout the guide.
- SQL server services account – SCCM-SQLService
- SCCM Network Access Account – SCCM-NAA
- Domain user account for use SCCM client push install – SCCM-ClientPush
- Domain user account for use with reporting services User – SCCM-SQLReporting
- Domain account used to join machine to the domain during OSD – SCCM-DomainJoin
- Domain group containing all SCCM Admins Group – SCCM-Admins
- Domain group containing all SCCM servers in the hierarchy Group – SCCM-SiteServers
Network Configuration
- Make sure that the server has a fixed IP and that internet connection is up
Firewall Configuration
- Make sure the firewall service is ON
Run this script in an elevated command prompt order to open the necessary ports needed for SCCM.
** If you are using custom ports, change the values before running the script. **
@echo ========= SQL Server Ports ===================
@echo Enabling SQLServer default instance port 1433
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Server” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=1433
@echo Enabling Dedicated Admin Connection port 1434
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Admin Connection” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=1434
@echo Enabling conventional SQL Server Service Broker port 4022
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Service Broker” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=4022
@echo Enabling Transact-SQL Debugger/RPC port 135
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Debugger/RPC” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=135
@echo ========= Analysis Services Ports ==============
@echo Enabling SSAS Default Instance port 2383
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”Analysis Services” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=2383
@echo Enabling SQL Server Browser Service port 2382
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Browser” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=2382
@echo ========= Misc Applications ==============
@echo Enabling HTTP port 80
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”HTTP” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=80
@echo Enabling SSL port 443
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SSL” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=443
@echo Enabling port for SQL Server Browser Service’s ‘Browse’ Button
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”SQL Browser” dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=1434
@echo Allowing Ping command
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”ICMP Allow incoming V4 echo request” protocol=icmpv4:8,any dir=in action=allow
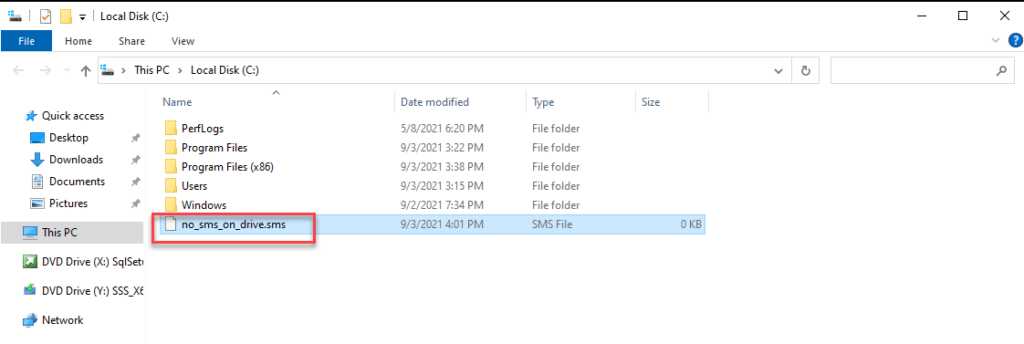
No_sms_on_drive.sms
Place a file name no_sms_on_drive.sms on the root drive of each drive you don’t want SCCM to put content on.
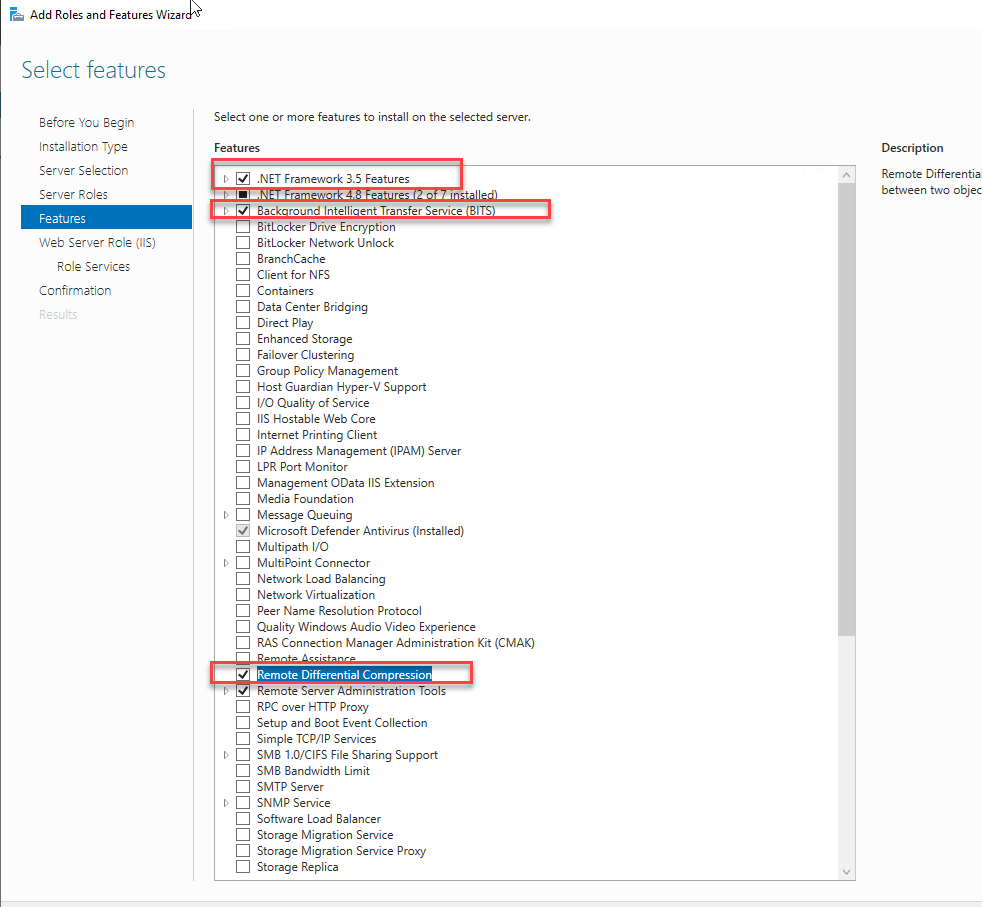
Windows Server Features
On the Primary site server, the following components must be installed before SCCM installation. We’ll install all these components using a PowerShell script.
- .Net Framework 3.51 SP1
- .Net Framework 4
- IIS
- Remote Differential Compression
- BITS Server Extension
- WSUS 3.0 SP2
- Report Viewer
- ADK for Windows 8.1
Roles and features
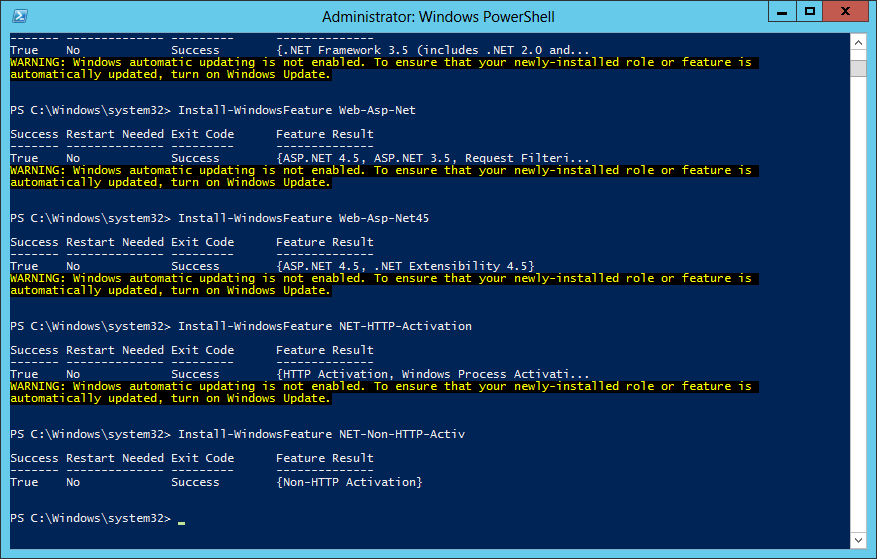
On the Site Sever computer, open a PowerShell command prompt as an administrator and type the following commands. This will install the required features without having to use the Windows 2012 GUI.
Get-Module servermanager
Install-WindowsFeature Web-Windows-Auth
Install-WindowsFeature Web-ISAPI-Ext
Install-WindowsFeature Web-Metabase
Install-WindowsFeature Web-WMI
Install-WindowsFeature BITS
Install-WindowsFeature RDC
Install-WindowsFeature NET-Framework-Features -source yournetworkyoursharesxs
Install-WindowsFeature Web-Asp-Net
Install-WindowsFeature Web-Asp-Net45
Install-WindowsFeature NET-HTTP-Activation
Install-WindowsFeature NET-Non-HTTP-Activ
Ensure that all components are showing as SUCCESS as an EXIT Code. It’s normal to have Windows Update warnings at this point.
Report Viewer
Download and install – here
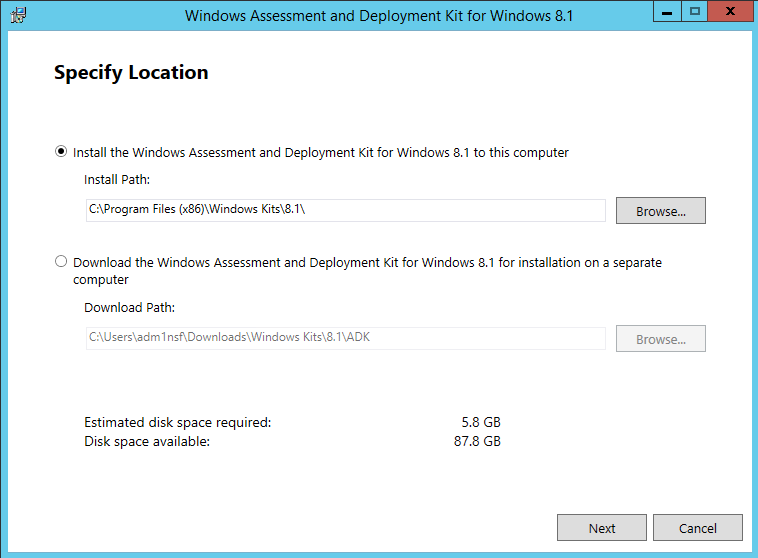
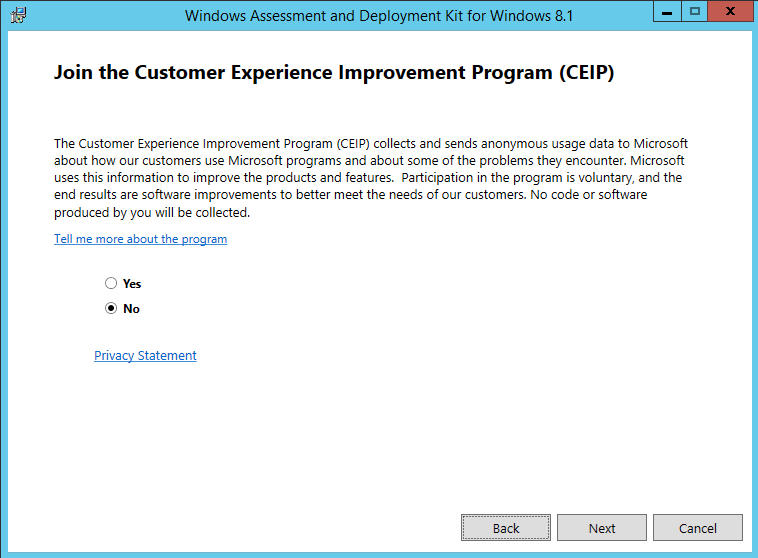
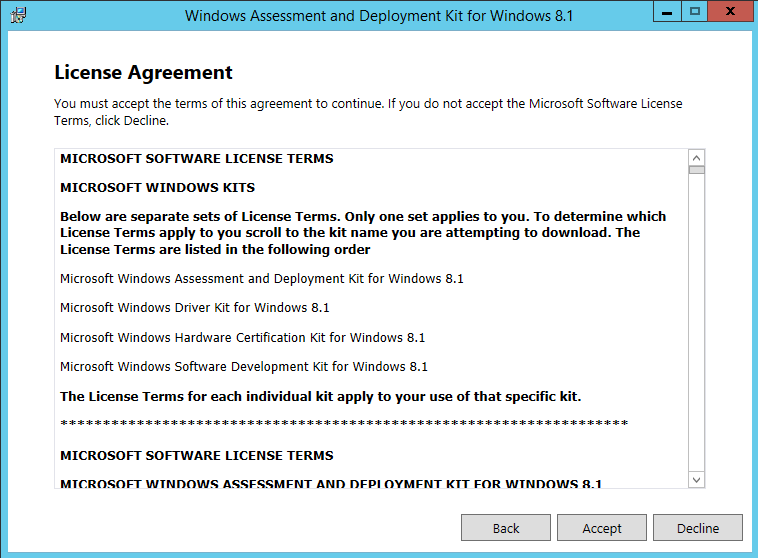
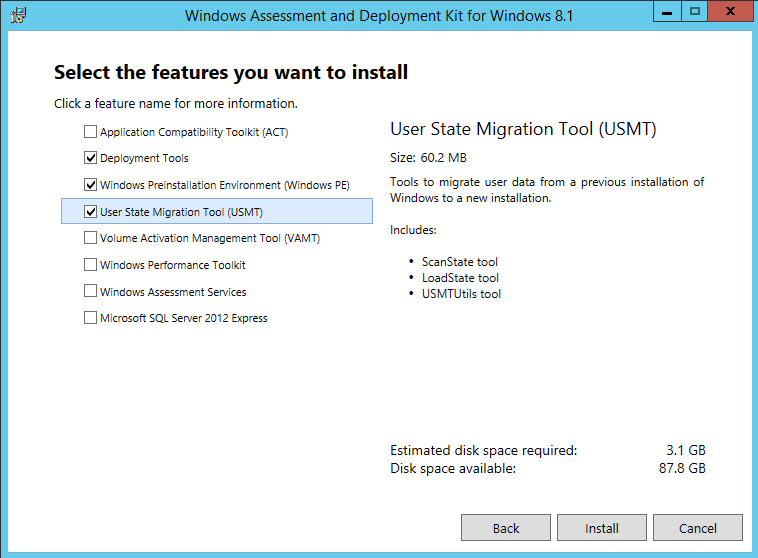
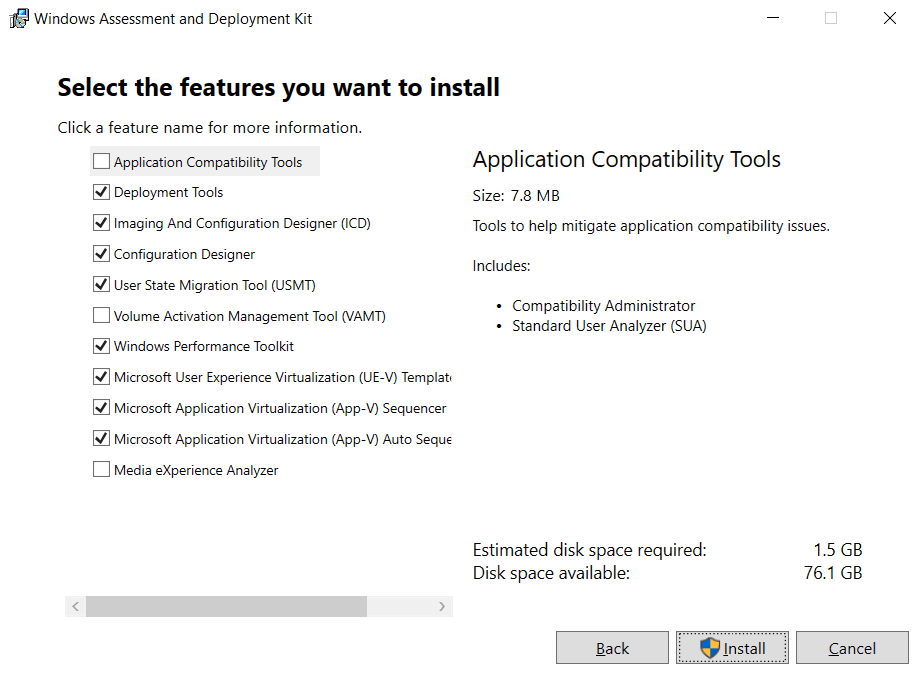
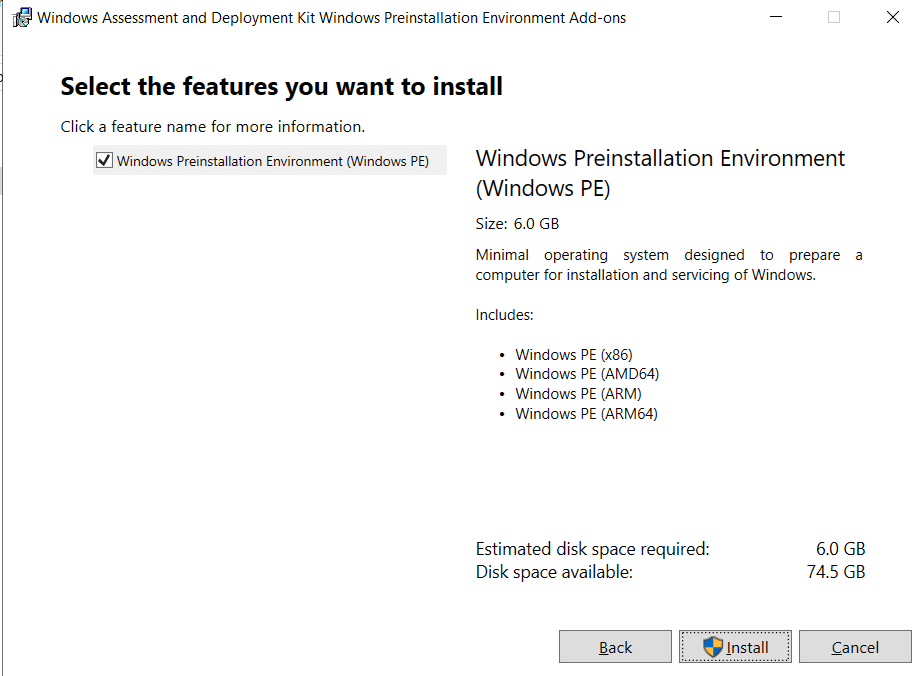
ADK for Windows 10
Download and install – here
- Select the default path
- Do not join CEIP
- Accept the License Agreement
- Install the following components
- Deployment Tools
- Windows Pre-installation Environment
- User state Migration tool
Active Directory
- Add the computer account of all your site servers in the SCCM-SiteServers AD group
- Ensure that the group has Full Control on the SYSTEM Container in Active Directory
Local Admin accounts
Add both SCCM computer account and the SCCM Admin account to the local administrator group on the site server.
- SCCM-Admins
- SCCM-SiteServers
SCCM Client
If applicable, uninstall SCCM 2007 client and FEP if present on the server before the installation. If the client is present, the 2012 SCCM Management Point installation will fail.
Windows Updates
Run windows update and patch your server to the highest level
Your server is now ready for the SQL installation.
Part 2 – SCCM SQL 2017 Installation
We will go through the complete SCCM SQL 2017 Install Guide to install and configure SQL before installing SCCM Current Branch 1806 or higher.
Important Info
This post is our updated version of our SQL install guide for version 2017 and higher. If you are planning on installing an older version of SQL, please follow our previous post here
Click the following link to see all supported SQL versions. For our post, we will install SQL 2017 locally on the same server where the Primary Site will be installed.
- Execute Setup.exe from the SQL installation media, select New SQL server stand-alone installation
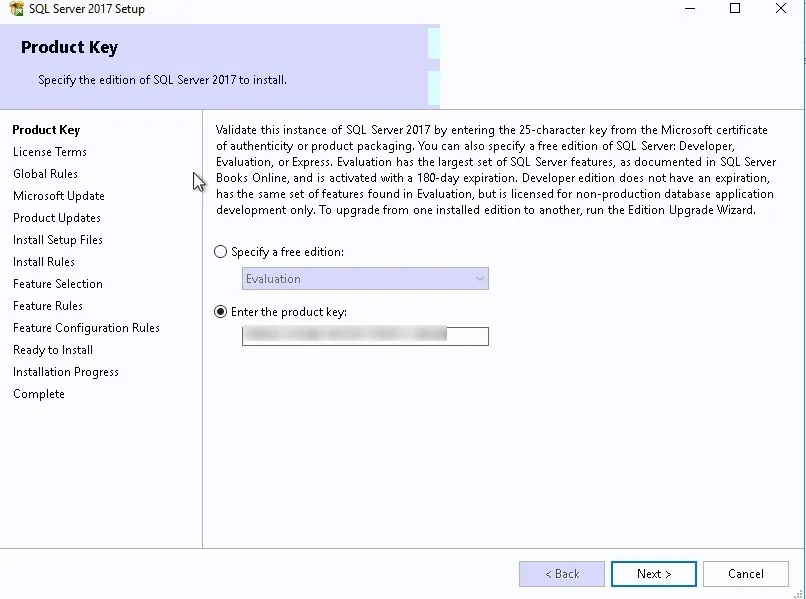
- Provide the product key and click Next
- Review and Click Next
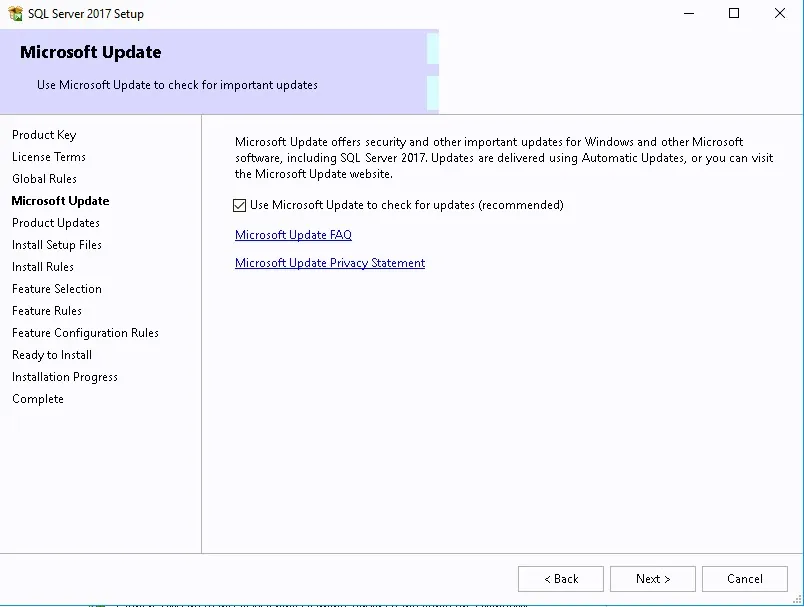
- Check Use Microsoft Update to check for updates and click Next
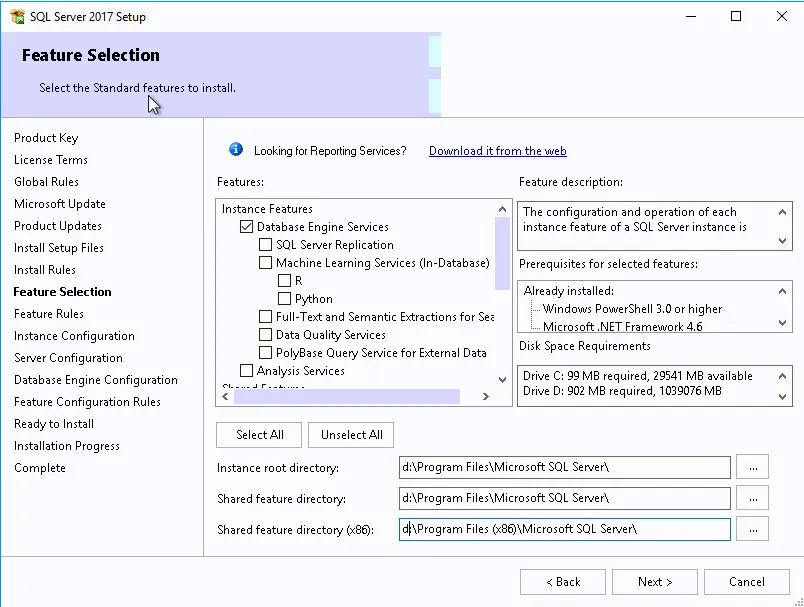
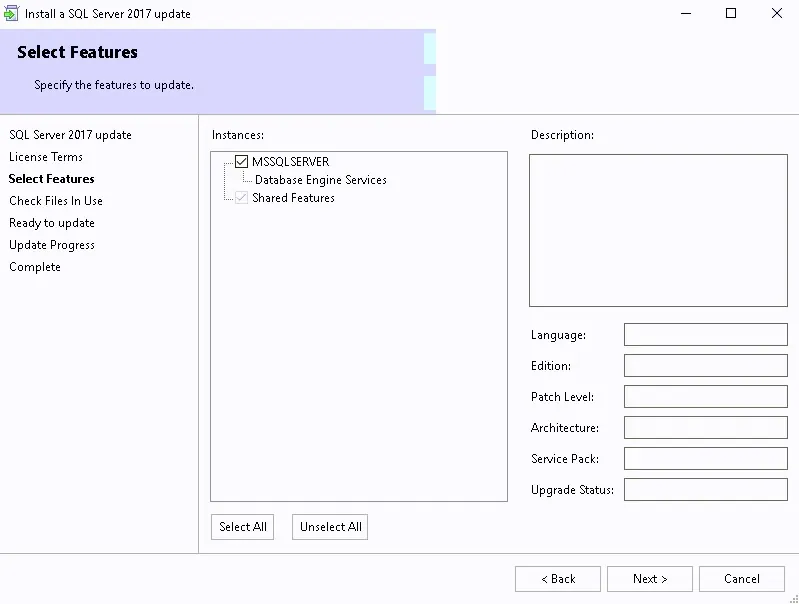
- Select SQL Server Feature Installation
Important Info
Note that some steps in the wizard are automatically skipped when no action is required. For example, Products Updates, Install setup Files and Install Rules might be skipped.
- Select the Database Engine feature and specify the SQL installation directory. This is the directory for the program files and shared features
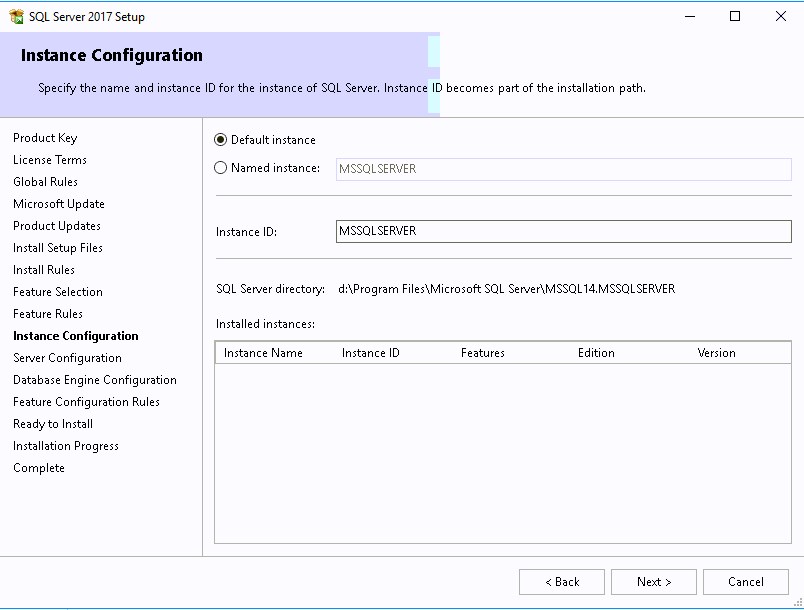
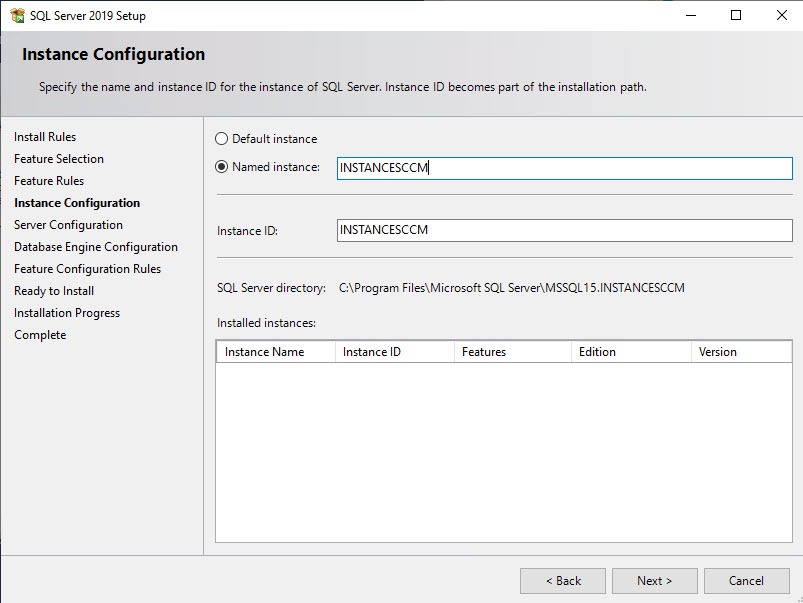
- Select Default instance and ensure that your instance is created on the SQL Volume
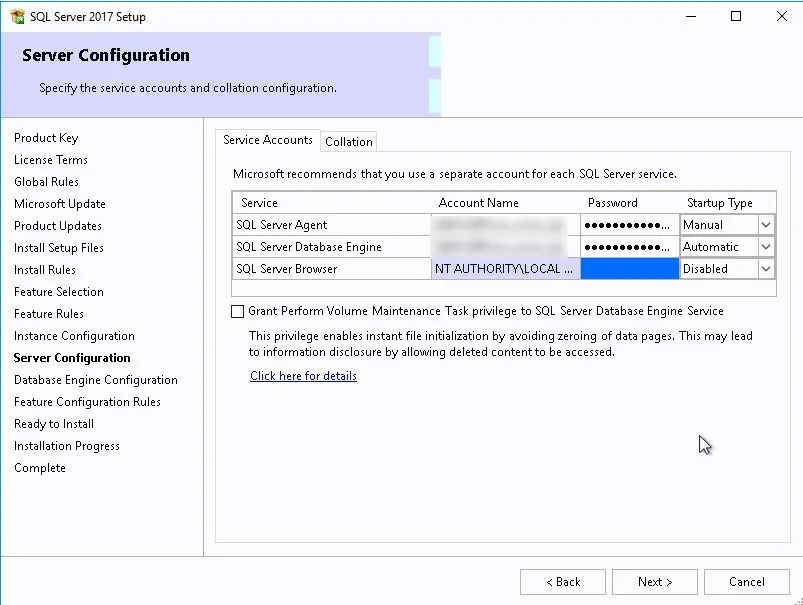
- Set all services to run as the SQL domain account that you created previously and set the services startup type to Automatic
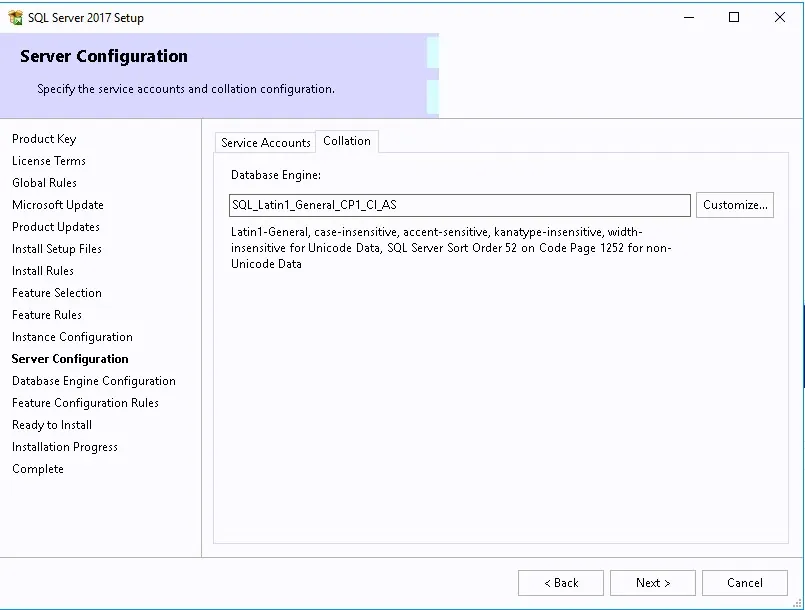
- On the Collation tab, set the Database Engine to use SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
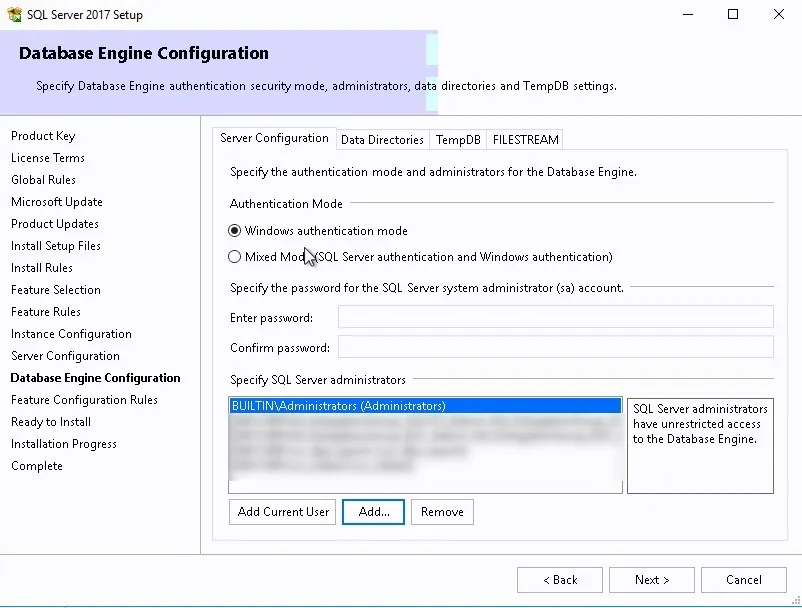
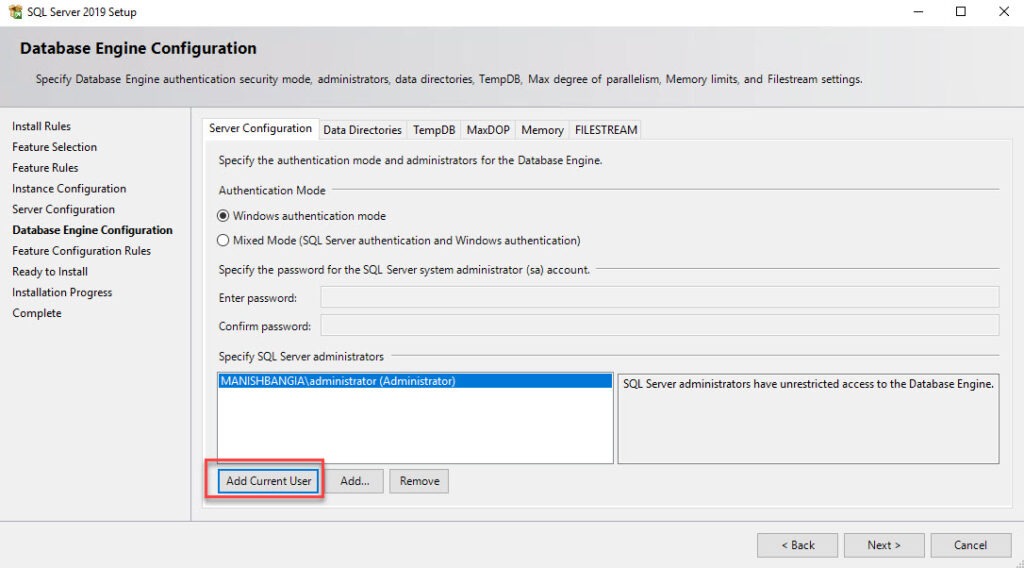
- In the Server Configuration tab, set the authentication mode to Windows Authentication and in the SQL Server Administrators add your SCCM Admins group
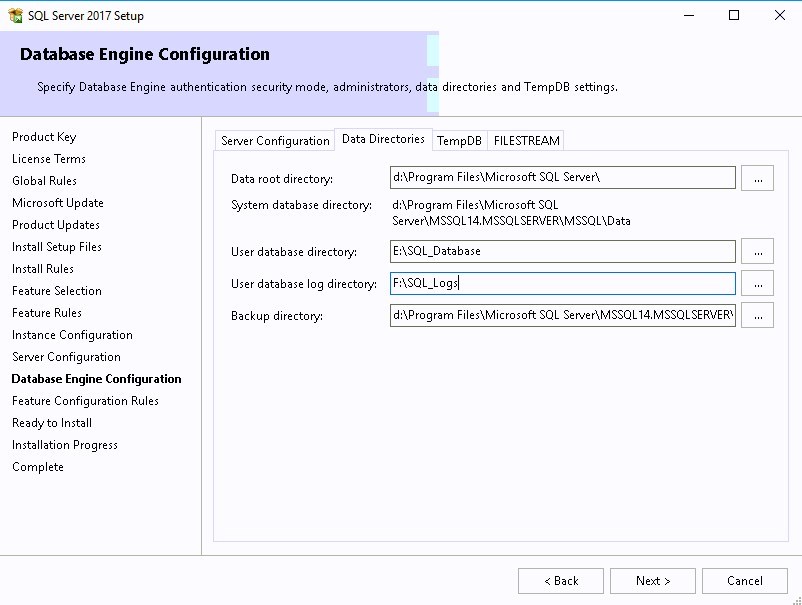
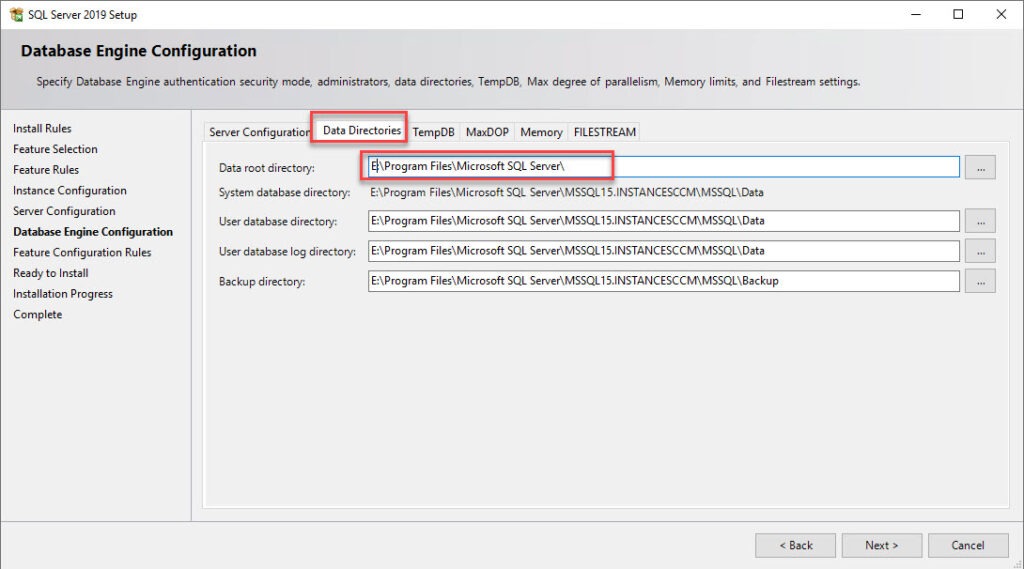
- In the Data Directories tab set your drive letters correctly for your SQL databases, Logs, TempDB, and backup
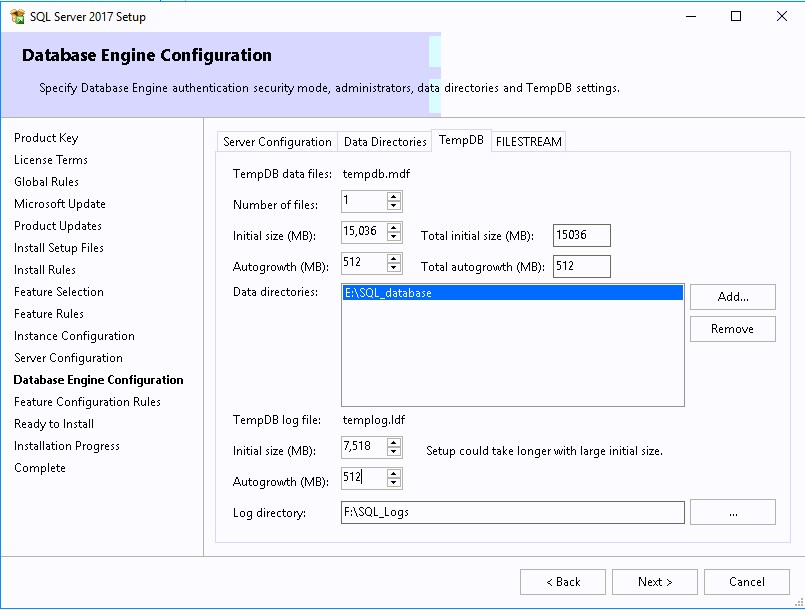
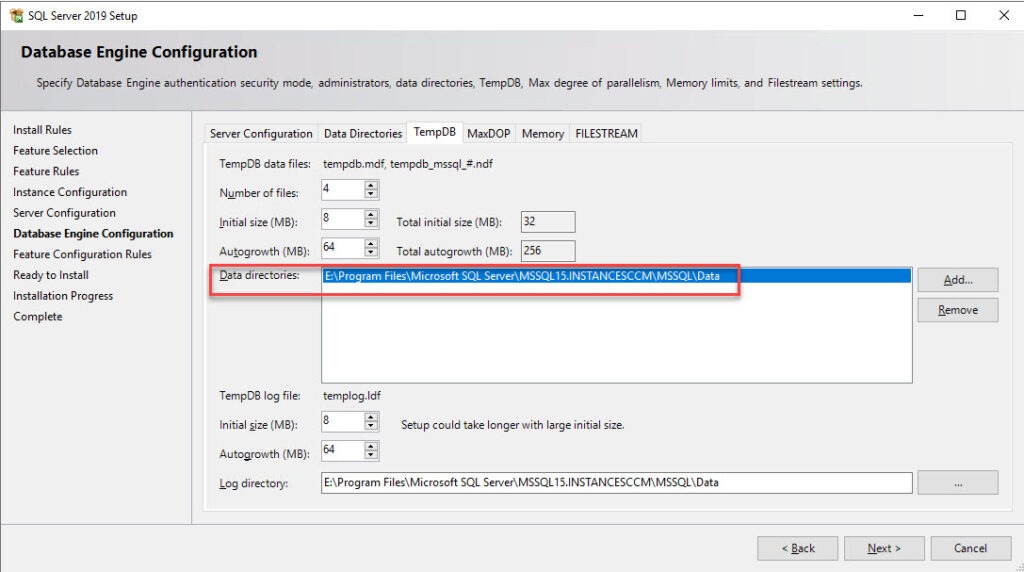
- On the TempDB, complete the various information based on the Database sizing section below.
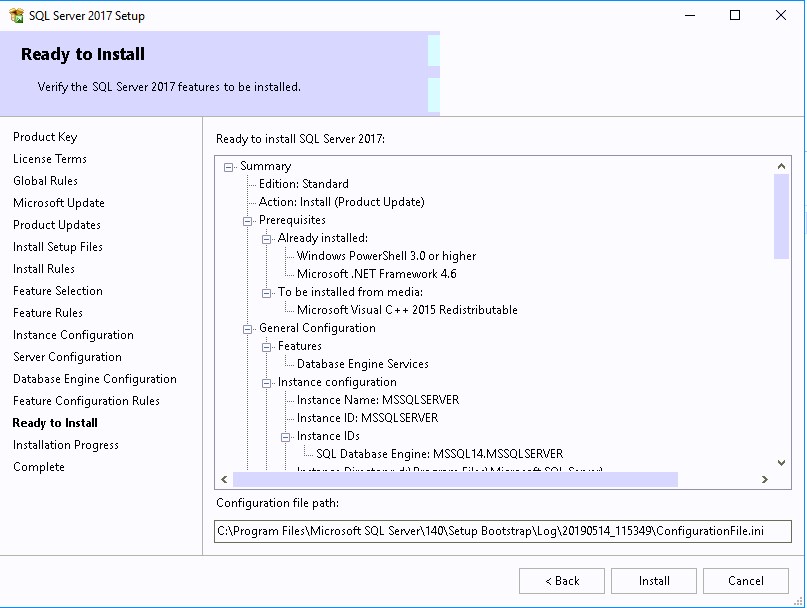
- Click Install
- Complete the installation by clicking Close
Install SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
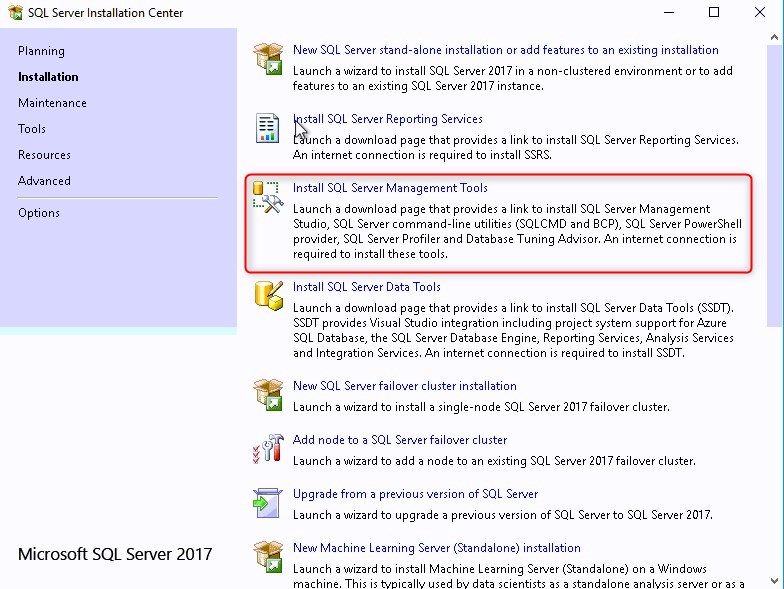
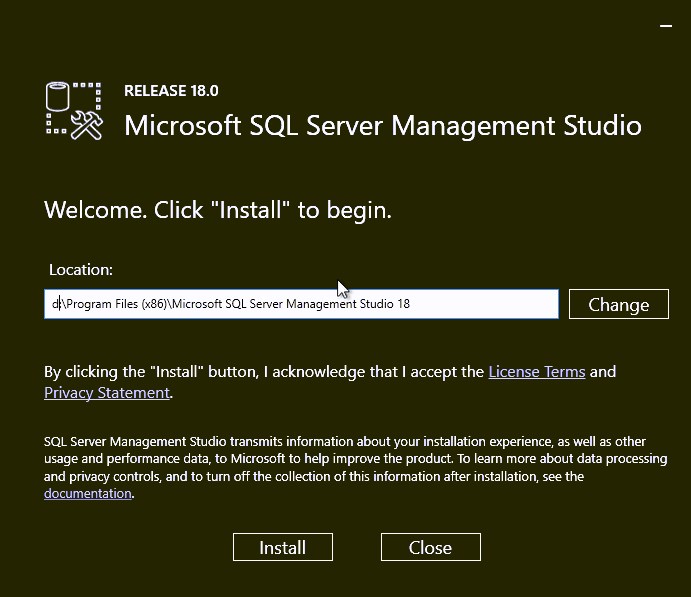
- Back in the SQL Server Installation Center, click on Install SQL Server Management tools.
- This will redirect you to the Download page of SQL Server Management Studio. SSMS is no longer tied to the SQL server installation in terms of version.
- Adjust the installation path if need, then click Install
Install SQL Reporting Services
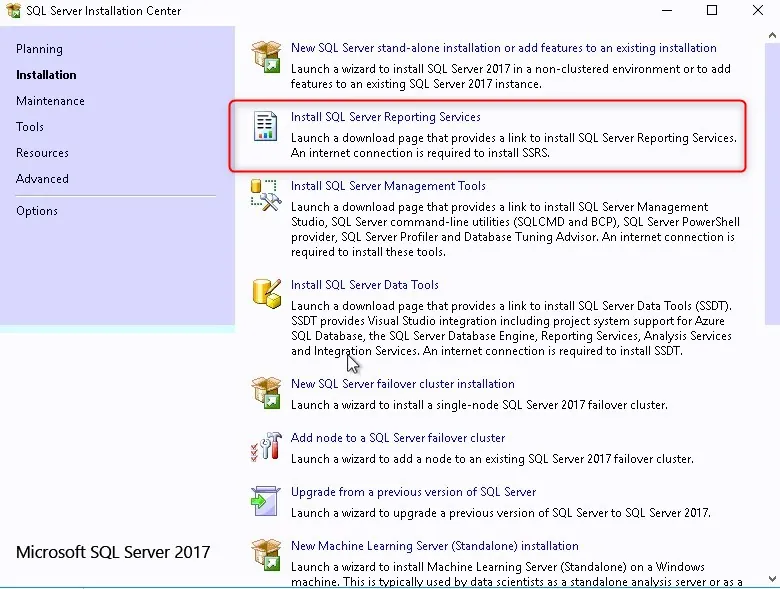
- Back in the SQL Server Installation Center, click on Install SQL Reporting Services.
- The SQL reporting services is just like the Management console, it requires a separate download
- Click on Install Reporting Services
- Provide the Product key
- Accept License terms
- Click Next
- Select the installation path, click Install
- A reboot is required after the installation
Apply SQL 2017 CU2 or higher
At the time of this writing, the latest SQL Cumulative Update is CU17. We will install it in order to have an updated SQL Installation. Note that CU2 is the minimum requirement
- Download and execute SQL 2017 CU17
- Accept the license terms and click Next
- Leave default values, click Next
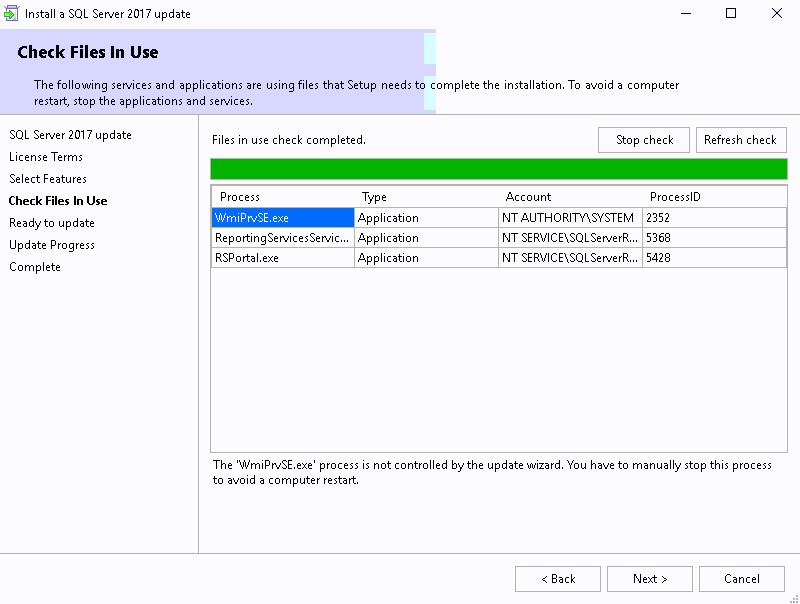
- Wait for Check File in Use and click Next
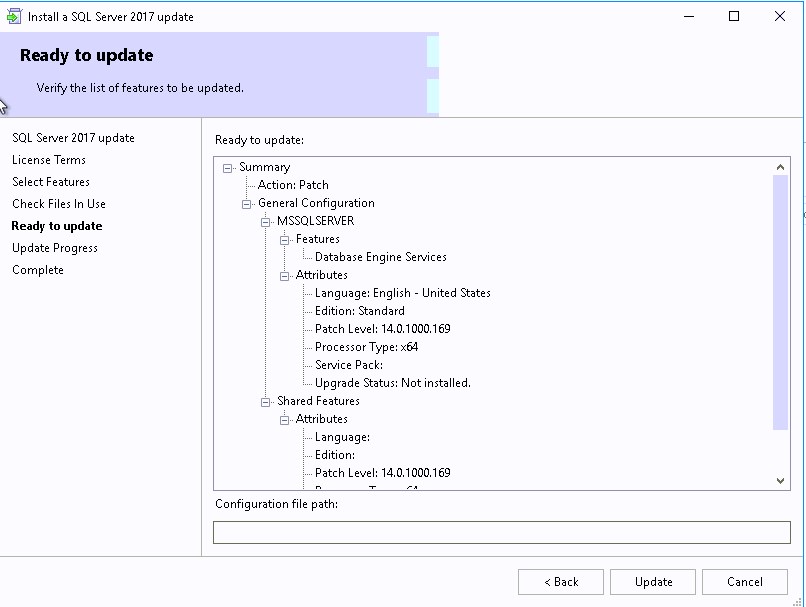
- Click Update
- Update completed, might require a reboot
SPN Creation
When you configure SQL Server to use the local system account, a Service Principal Name (SPN) for the account is automatically created in Active Directory Domain Services. When the local system account is not in use, you must manually register the SPN for the SQL Server service account.
Since we are using a domain account, we must run the Setspn tool on a computer that resides in the domain of the SQL Server. It must use Domain Administrator credentials to run.
Run both commands to create the SPN, Change the server name and account name in each commands.
- setspn -A MSSQLSvc/yourservername:1433 yourdomainSQLSA
- setspn -A MSSQLSvc/yourserver.fullfqdn.com:1433 yourdomainSQLSA
To verify the domain user SPN is correctly registered, use the Setspn -L command
- setspn –L yourdomainSQLSA
SQL Configuration
SCCM setup verifies that SQL Server reserves a minimum of 8 GB of memory for the primary site. To avoid, the warning, we’ll set the SQL Server memory limits to 8GB-12GB (80% of available RAM).
- Open SQL Server Management Studio
- Right click the top SQL Server instance node
- Select Properties
- In the Memory tab define a limit for the minimum and maximum server memory. Configure and limit the memory to 80% of your server available RAM. In my case I have 16GB available.
- Minimum 8192
- Maximum 12288
Database Sizing
We always recommend creating the SCCM database before the setup. This is not mandatory, SCCM will create the database for you during setup but will not create it the optimal way. We strongly recommend watching The Top Ten Lessons Learned in Managing SQL session from MMS2013 which covers it all.
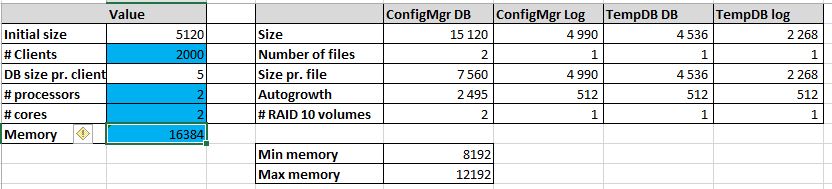
We follow the guide made by MVP, Kent Agerlund to estimate my DB sizing need. Visit his blog post and download the provided Excel file. Input your values in the blue cells and keep it for the next part. We’ll create the DB using those values using a script in the next section.
For this blog post, We’ve created a Database for 2000 clients, 2 processors, 2 cores and 16GB RAM.
Create Database
To create the database, you can use Kent’s script and input your values (as returned previously in the Excel file) OR use the following one which is really simple:
The Name value will become your Site Code during the SCCM installation. Be sure to select a unique Site Code.
- **Replace all XXX value with your 3 character Site Code**
- **Change the values of the Filename, Size, MaxSize and FileGrowth. Change the location of the file to your SQL and Logs drives**
USE master
CREATE DATABASE CM_XXX
ON
( NAME = CM_XXX_1,FILENAME = ‘E:SCCMDBCM_XXX_1.mdf’,SIZE = 7560, MAXSIZE = Unlimited, FILEGROWTH = 2495)
LOG ON
( NAME = XXX_log, FILENAME = ‘G:SCCMLogsCM_XXX.ldf’, SIZE = 4990, MAXSIZE = 4990, FILEGROWTH = 512)
ALTER DATABASE CM_XXX
ADD FILE ( NAME = CM_XXX_2, FILENAME = ‘E:SCCMDBCM_XXX_2.mdf’, SIZE = 7560, MAXSIZE = Unlimited, FILEGROWTH = 2495)
Review the Site Database properties
- Open SQL Management Studio
- Right-click your DB, Select Properties
- In the General tab, verify that the SQL collation name is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
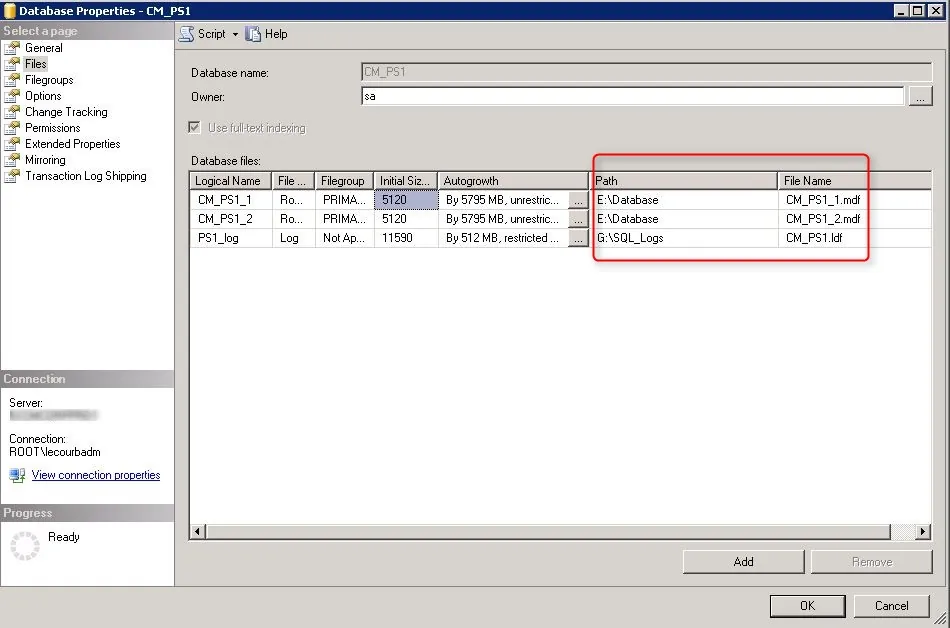
- In the File tab, verify that your database files has been created with the script value
- Verify that the file is located on your SQL Volume
- Change the database owner to SA. By default the owner will be the account that created the database.
If you find out that you made an error, you can safely delete the Database using SQL Management Studio and rerun the script.
- Open SQL Management Studio
- Right-click your DB, Select Delete
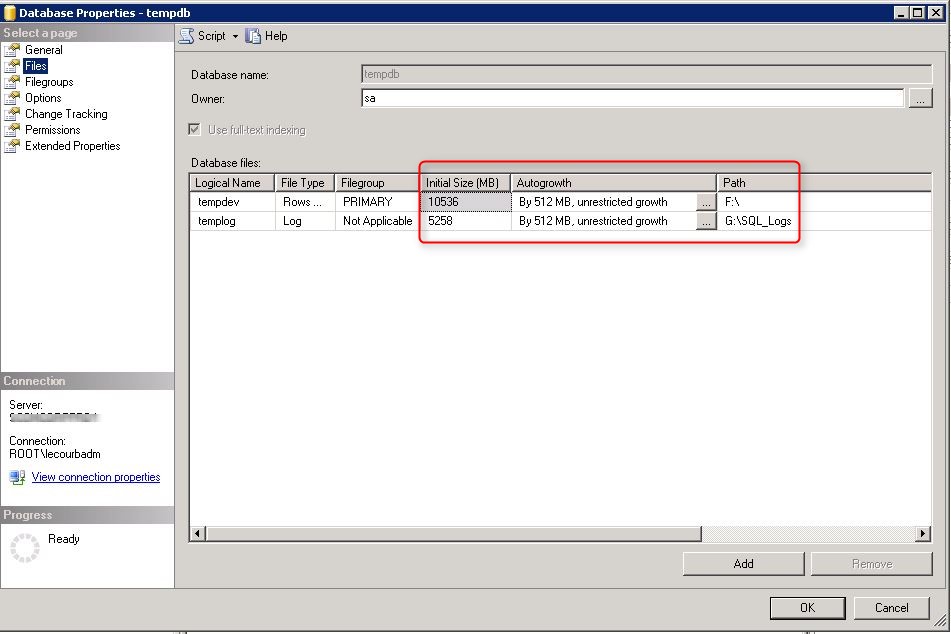
TempDB sizing
Important Info
This section is left here for reference to help configure the TempDB in the installation wizard.
Run the following scripts to size the TempDB. (using the value returned by the Excel file)
**Change the values of Filename, Size, MaxSize and FileGrowth. Change the location of the file to your TempDB drives**
use master
go
alter database tempdb modify file (name=’tempdev’, filename=’F:SCCMTempDBtempDB.MDF’, SIZE= 4536, MAXSIZE = Unlimited, FILEGROWTH = 512)
go
alter database tempdb modify file (name=’templog’, filename=’G:SCCMLogstemplog.LDF’, SIZE= 2268, MAXSIZE = Unlimited, FILEGROWTH = 512)
go
Review the TempDB properties
- Open SQL Management Studio
- In System Database, Right click the TempDB, select Properties
- In the File Tab, verify that your database files has been created with the script value
- Ensure that the TempDB and log are on the TempDB volume
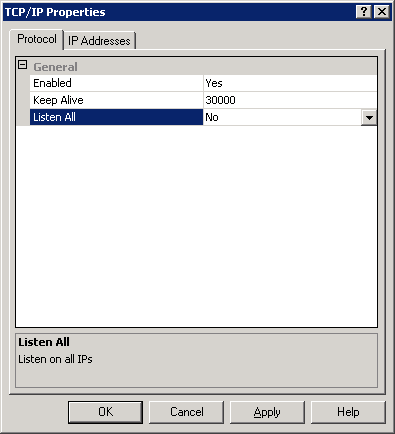
SQL Communications
To ensure proper SQL communication, verify that settings are set accordingly in SQL Network configuration
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager
- Go to SQL Server Network Configuration / Protocols for MSSQLServer
- On the Right Pane, right-click TCP/IP and select Properties
- In the Protocol tab
- Enable: YES
- Listen All : NO
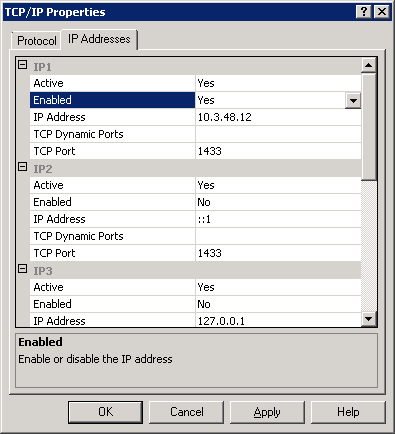
- In the IP Addresses tab
- IP1 (which should have your Server IP)
- Active : YES
- Enabled : YES
- All other IP and IP ALL
- Active : YES
- Enabled : NO
- TCP Dynamic Ports : Blank value
- TCP Port : 1433
Once the modification has been made, restart the SQL Server Service.
The server is now ready for the SCCM installation. We will now run the prerequisite checker and proceed to the complete SCCM Installation. We will install a stand-alone Primary site.
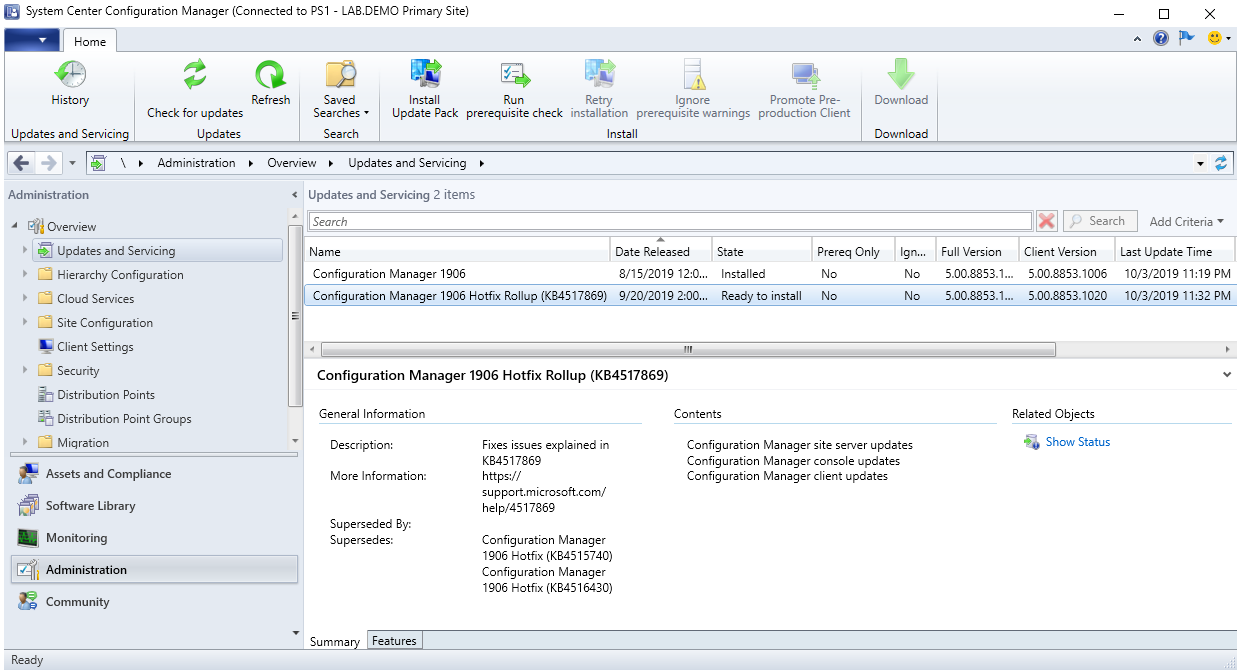
Part 3 – SCCM Current Branch Installation
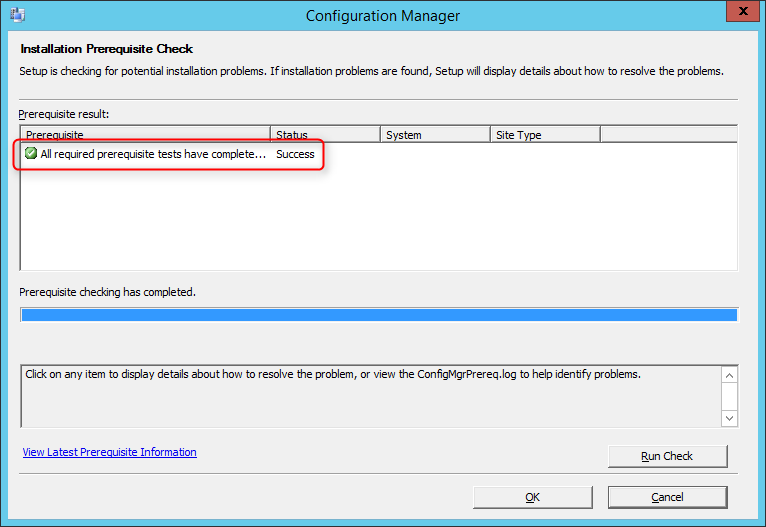
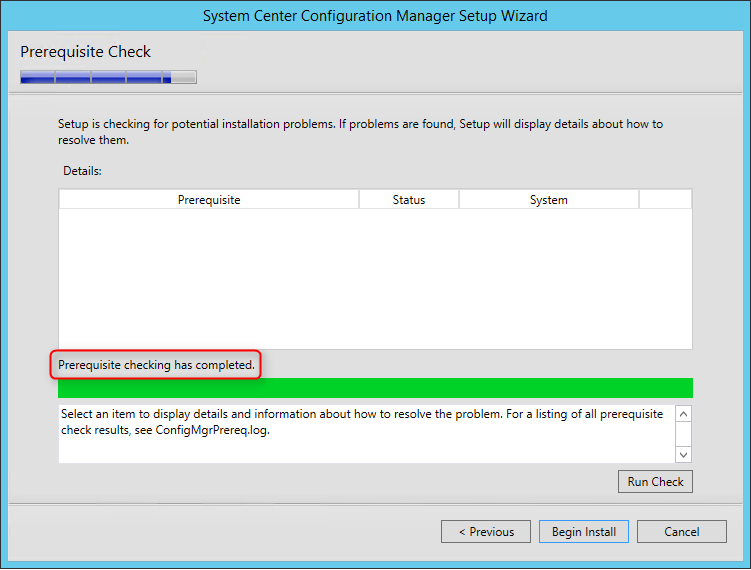
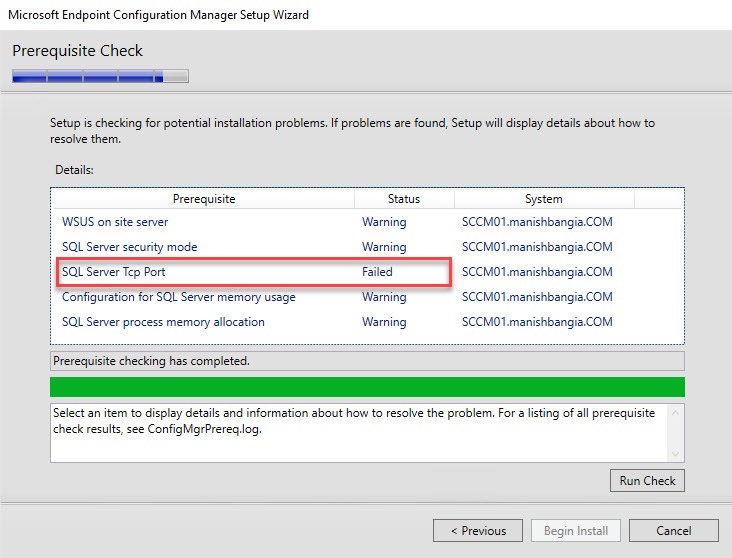
Prerequisite Check
Before launching the SCCM installation, we recommend launching the Prereqchk tool in order to verify if all components are configured correctly. The SCCM installation wizard will also run this check but if you’re missing a requirement, you’ll have to go through the whole installation wizard again after fixing it. We prefer to use the standalone tool before running the setup.
To start the prerequisite check tool :
- Open an Administrator command prompt
- Browse to .SMSSETUPBINX64
- Run the following command: Prereqchk.exe /AdminUI
If you follow the prerequisite guide correctly you’ll have this result :
Refer to this Technet article to see the list of all checks done by the tool.
If you have any warning or error refer to this Technet article in order to resolve it, or go thought part 1 and part 2 of this guide.
New SCCM Installation
We are finally ready to launch the setup. First, reboot the server. This will make sure that the machine is not in a Reboot pending state.
- Mount and open the SCCM ISO that was previously downloaded from the Microsoft Volume Licensing Site
- Run Splash.hta
- Select Install
- On the first screen, Click Next
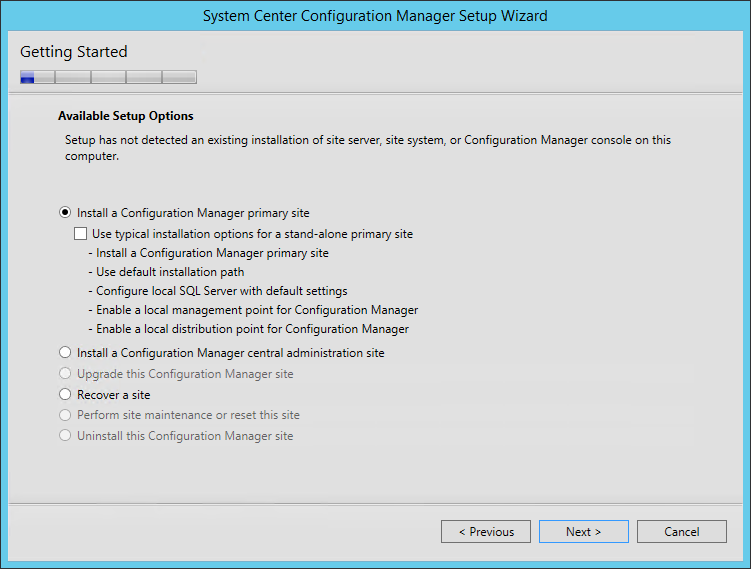
- On the Getting Started screen, Select Install a Configuration Manager Primary Site and click Next
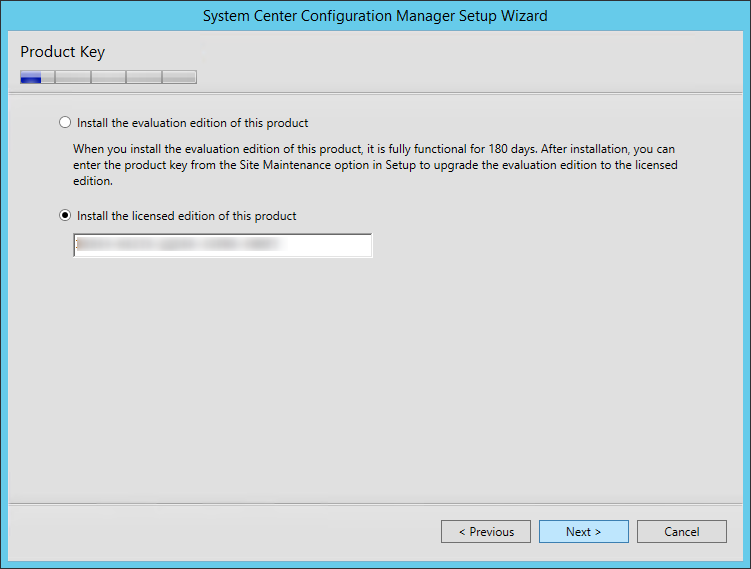
- On the Product Key screen, enter it and click Next
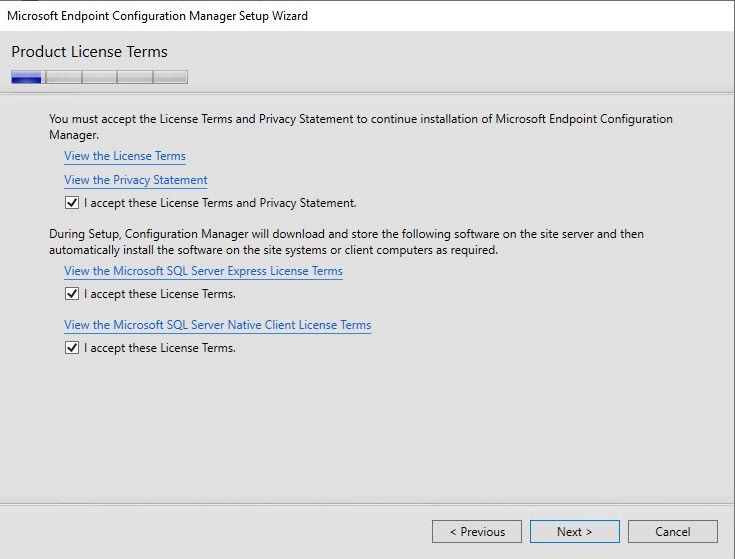
- On the Microsoft Software License Terms screen, accept the terms and click Next
- On the Product License Terms screen, accept the License Terms and click Next
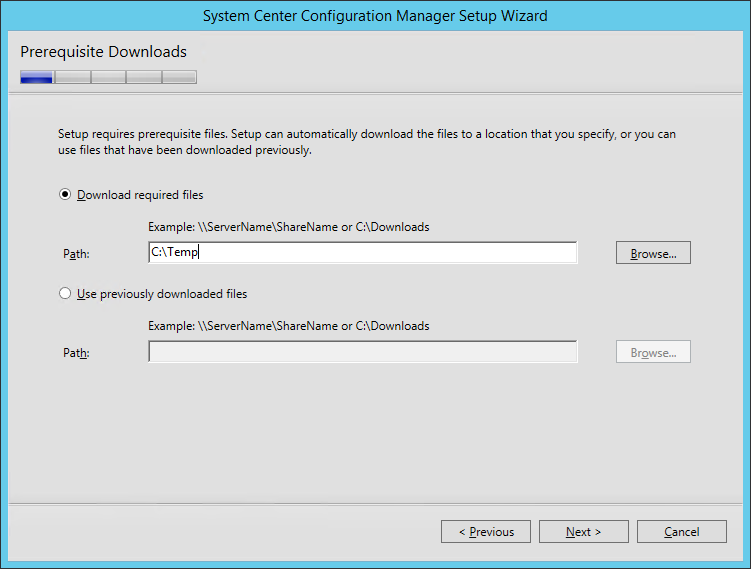
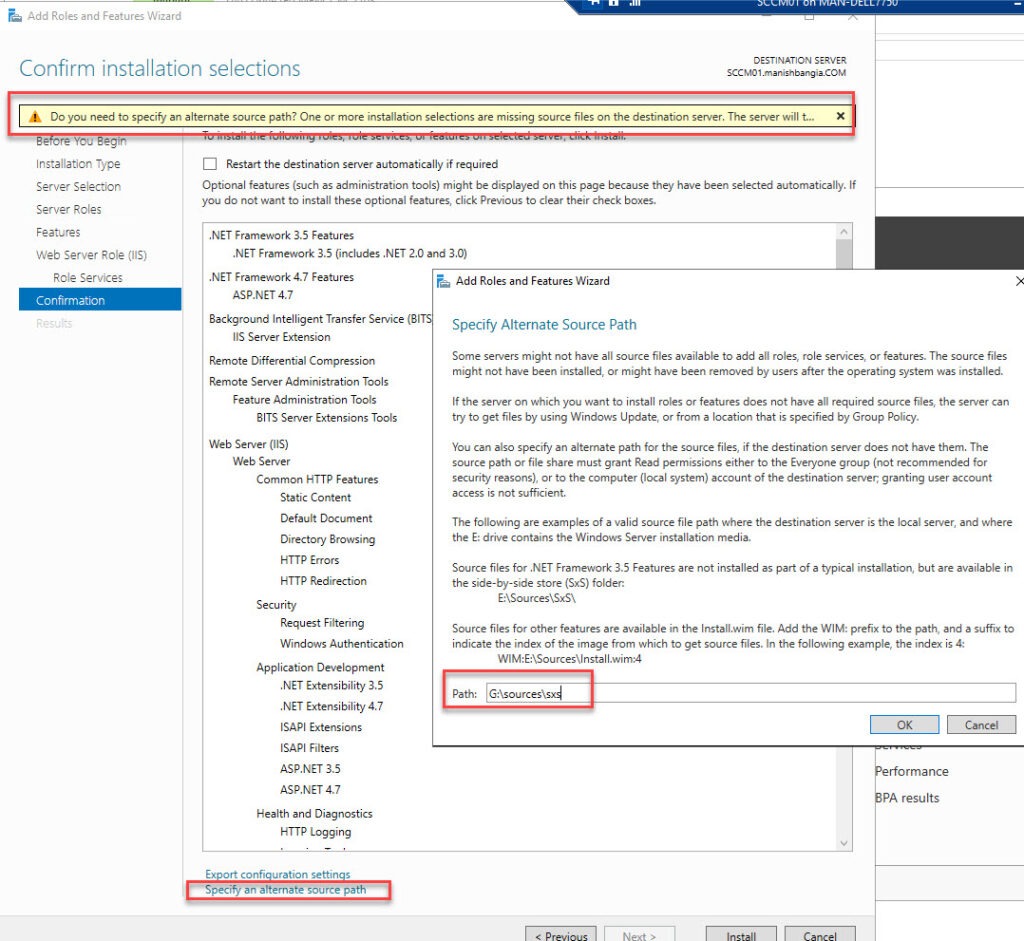
- On the Prerequisite Downloads screen, specify a location to download the prerequisite file. This folder can be deleted after setup
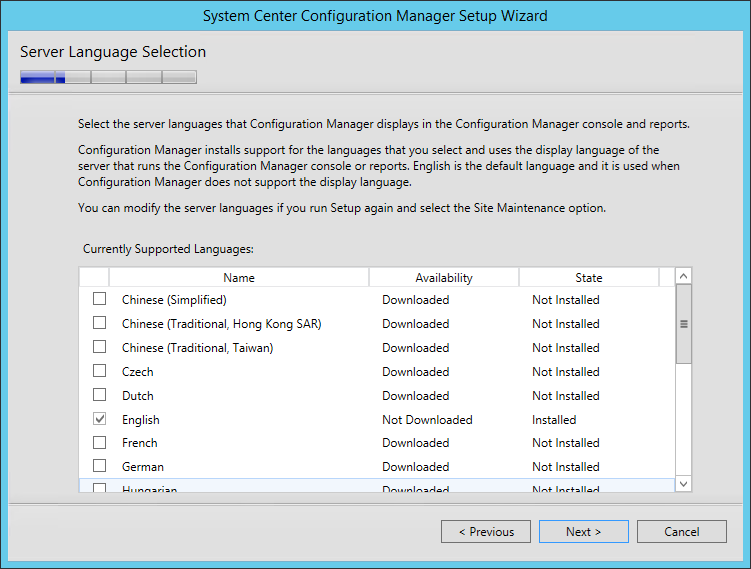
- On the Server Language Selection screen, select the language you want to display in the SCCM Console and Reports. You can modify language later by running setup again and select the Site Maintenance option
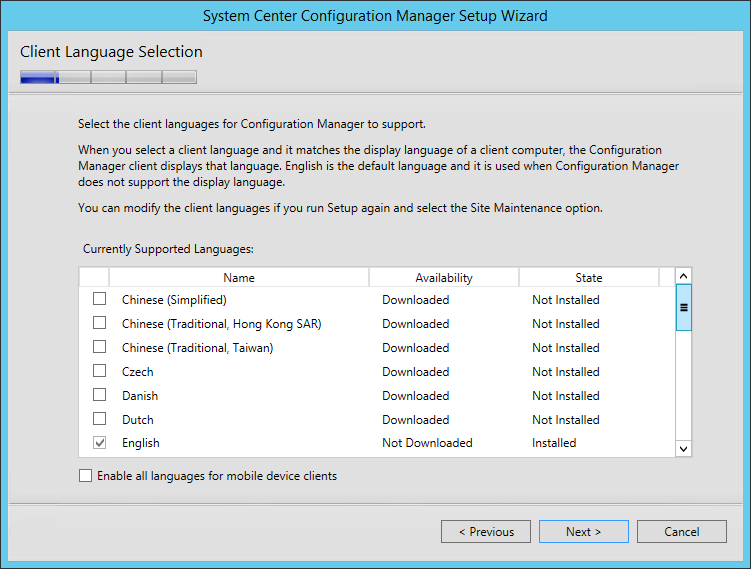
- On the Client Language Selection screen, select the Client language to support. You can modify languages later by running setup again and select the Site Maintenance option
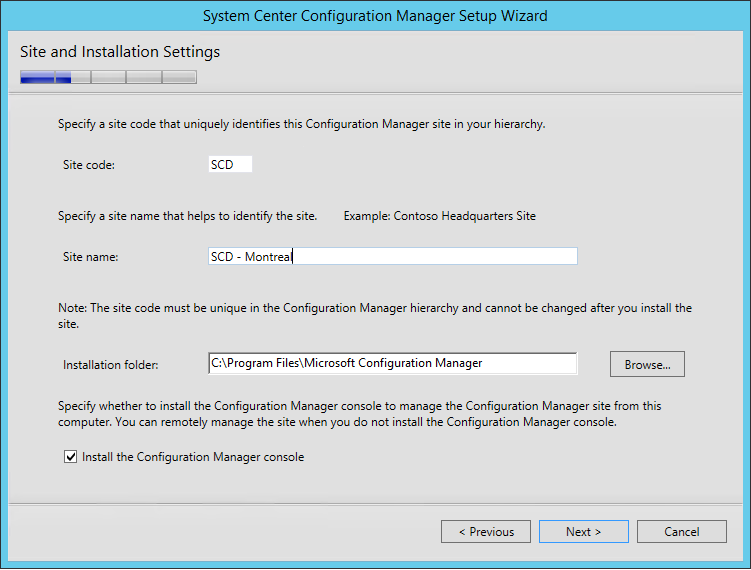
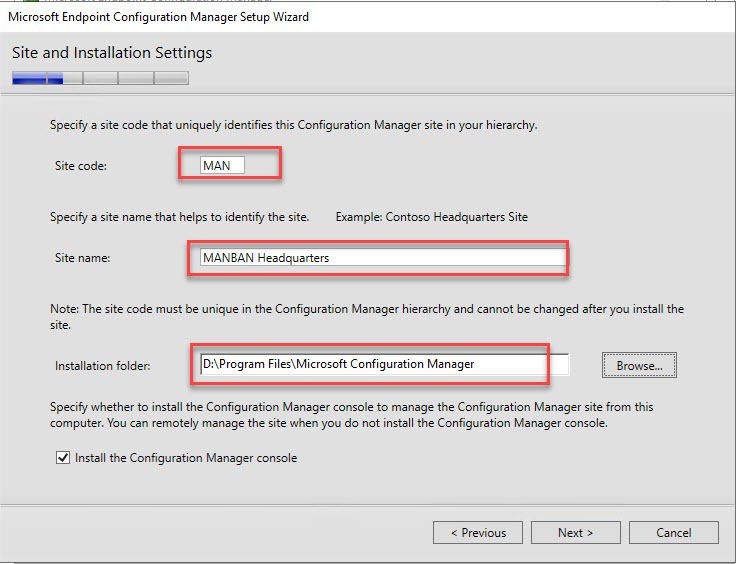
- On the Site and Installation Settings screen, enter your Site Code. Use the same Site Code as you specified when creating your Database
- Note : Site codes cannot be used more than one time in a Configuration Manager hierarchy for a central administration site or primary sites. If you reuse a site code, you run the risk of having object ID conflicts in your Configuration Manager hierarchy. This applies also if you’re doing a migration from an earlier version.
- Enter your Site Name. This name will appear in the console so choose accordingly
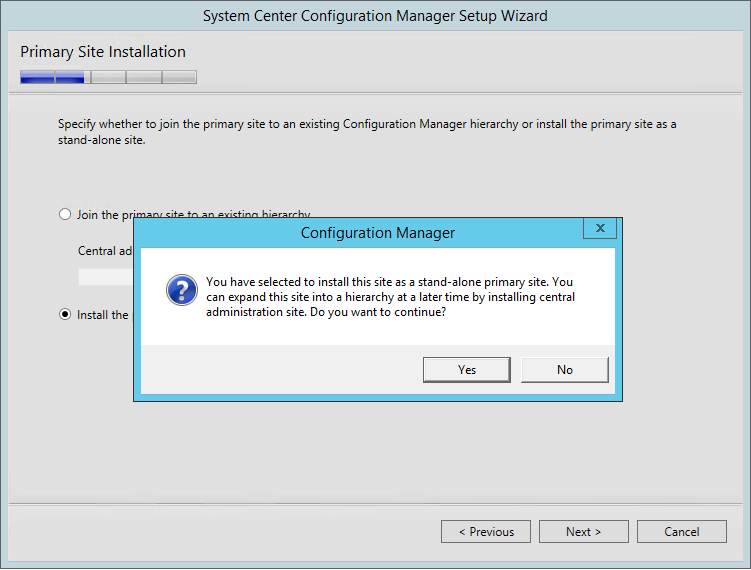
- On the Primary Site Installation screen, select Install the primary site as a stand-alone site. If you have a Central Administration site, this is where you would join the Primary Site to the existing hierarchy
- On the warning, click Yes
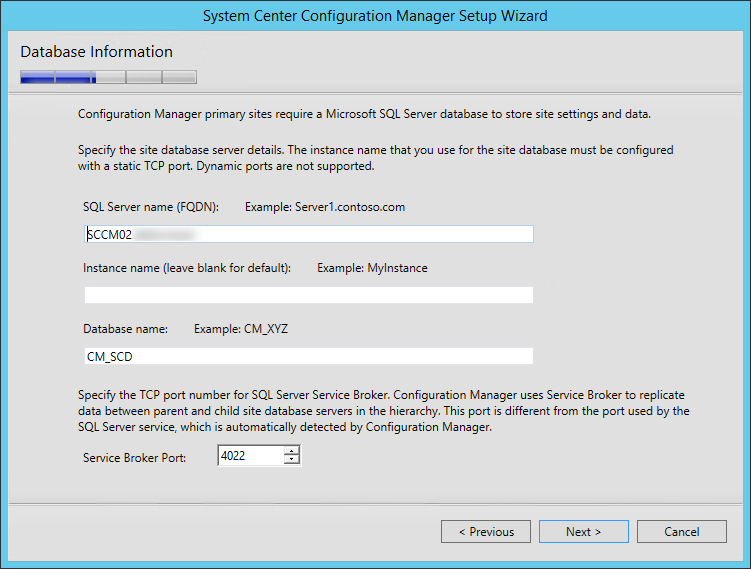
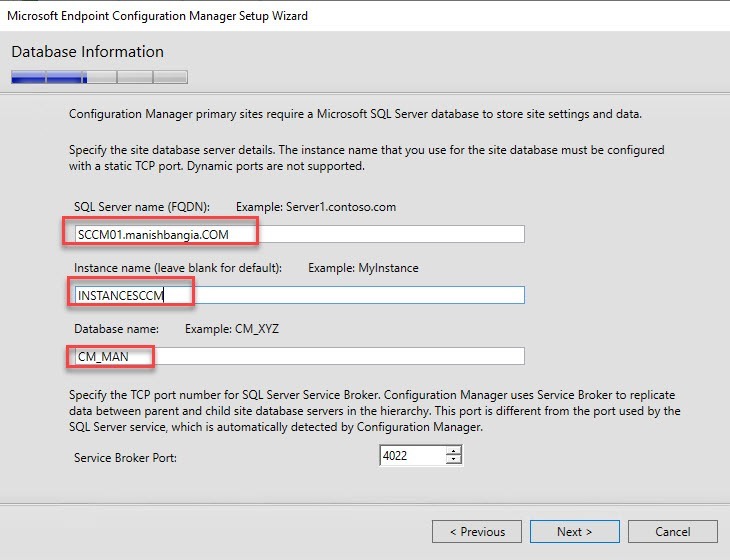
- On the Database Information screen
- Enter your SQL Server Name. In our case the SQL server is the same box as SCCM
- Leave the Instance Blank
- Enter your Database name. Once again, this must match the previously created Database in part 2
- Leave the Service Broker Port to 4022
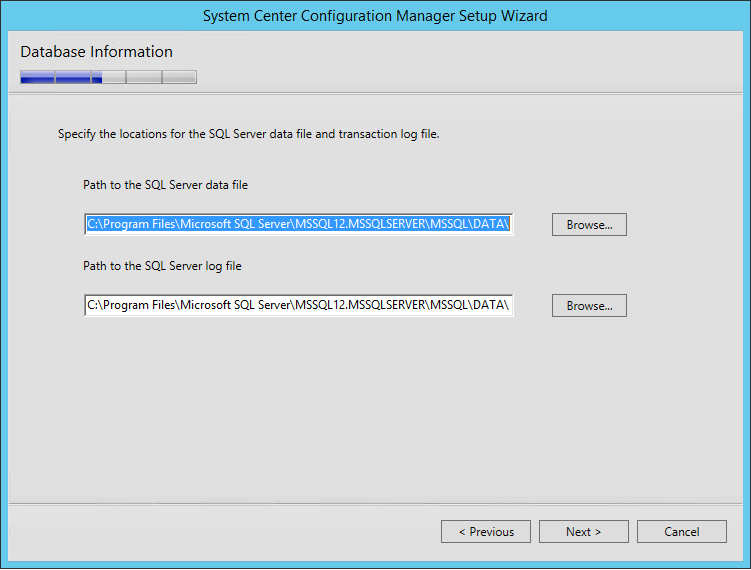
- On the Database Information screen :
- Enter the path to the SQL Server data file. Locate this on the SQL Volume
- Enter the path to the SQL Server log file. Locate this on the SQL Logs Volume.
- I like to use the same directory where I created my database and logs (E:SCCMDB, G:SCCMLogs)
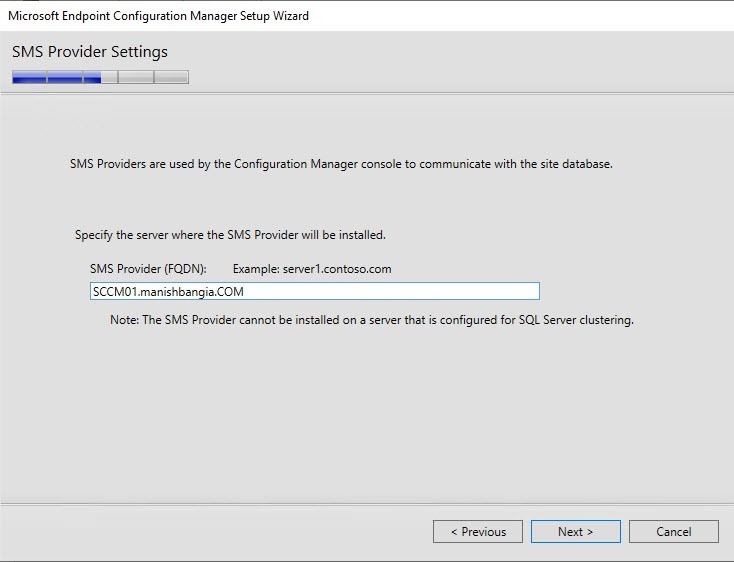
- On the SMS Provider Settings screen, leave the SMS Provider to the default value which is the local server. Refer to the following Technet article to read about the SMS Provider.
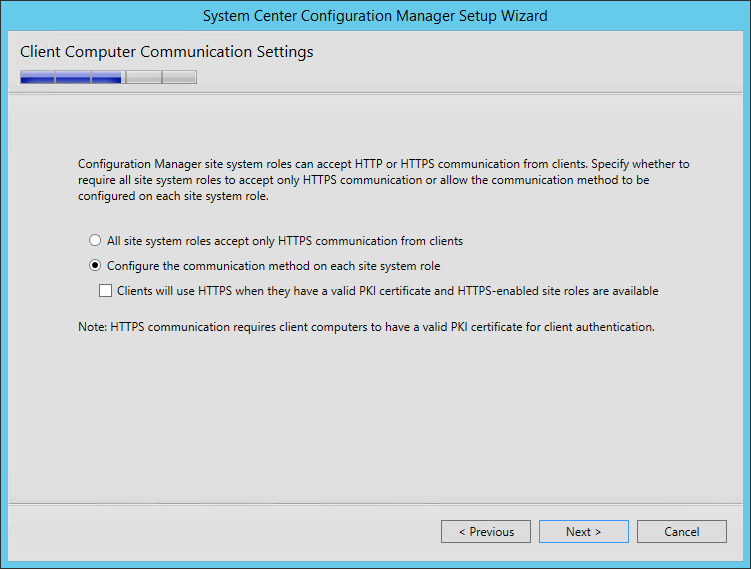
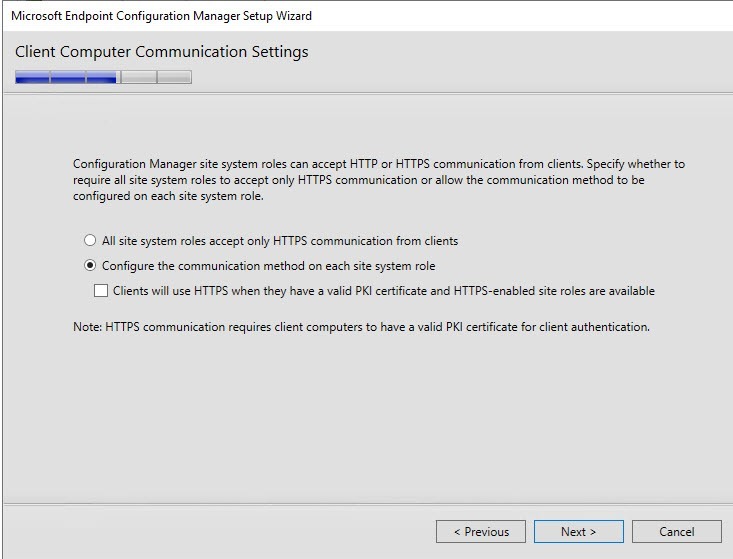
- On the Client Computer Communication Settings screen, select Configure the communication method on each site system role. This is where you select to have HTTPS or not on your initial Management Point and Distribution Point. This setting can be changed later
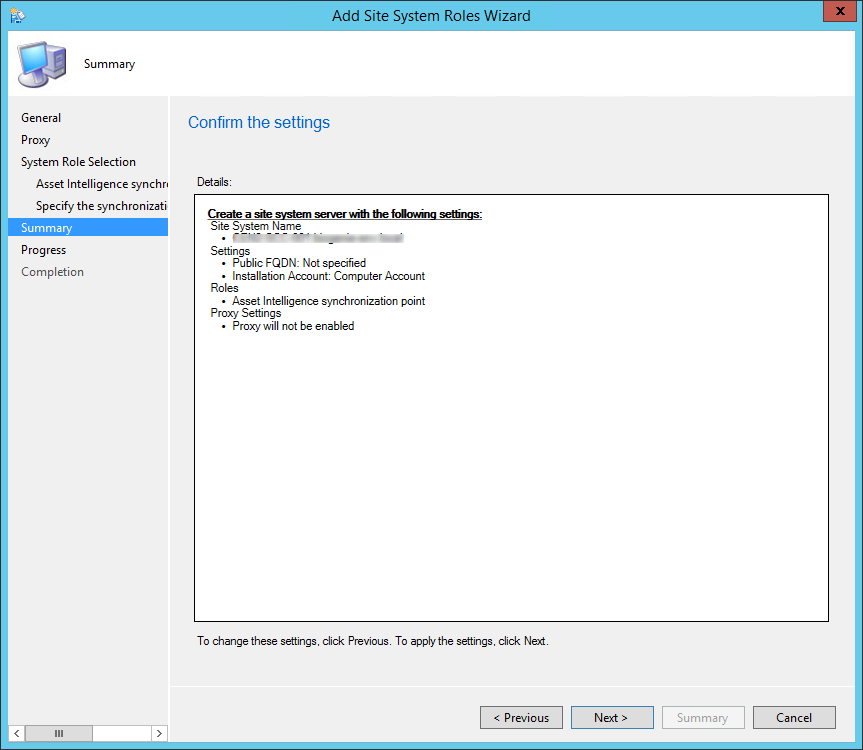
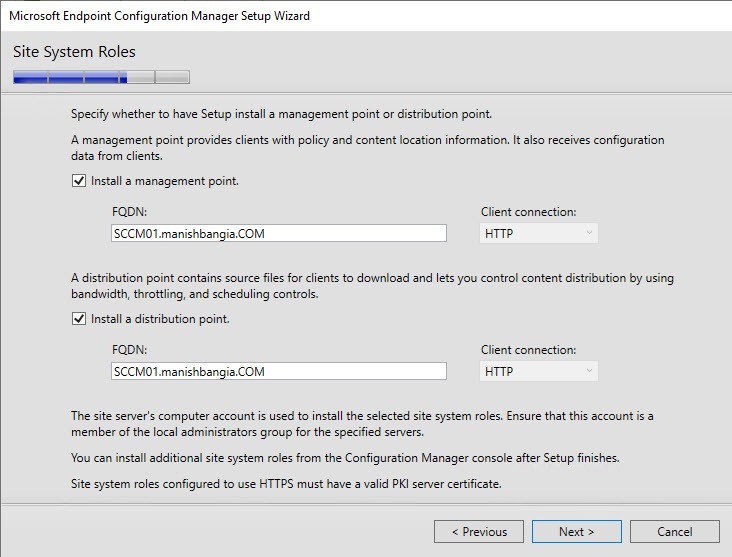
- On the Site System Roles screen :
- Check Install a Management Point
- Check Install a Distribution Point
- We will install both MP and DP on the same box so leave the FQDN as is
- The Client connection drop-down is unavailable due to our previous selection
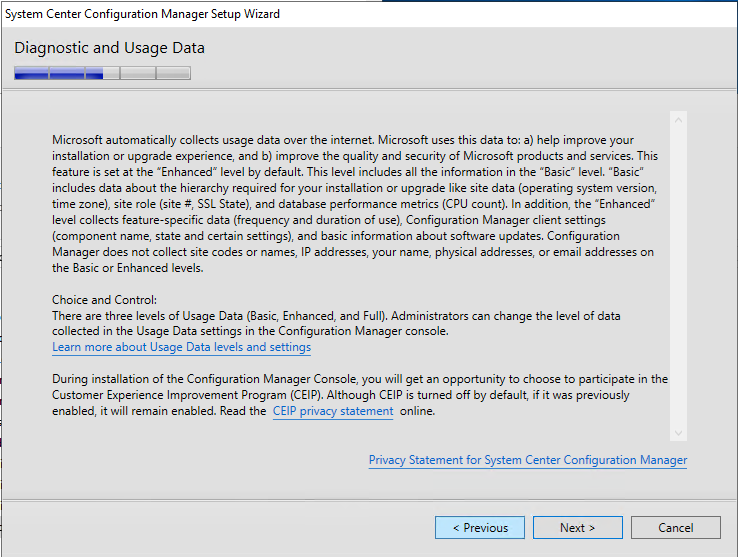
- On the Usage Data screen, click Next. This new screen basically tells that you accept that you will send some telemetry data to Microsoft
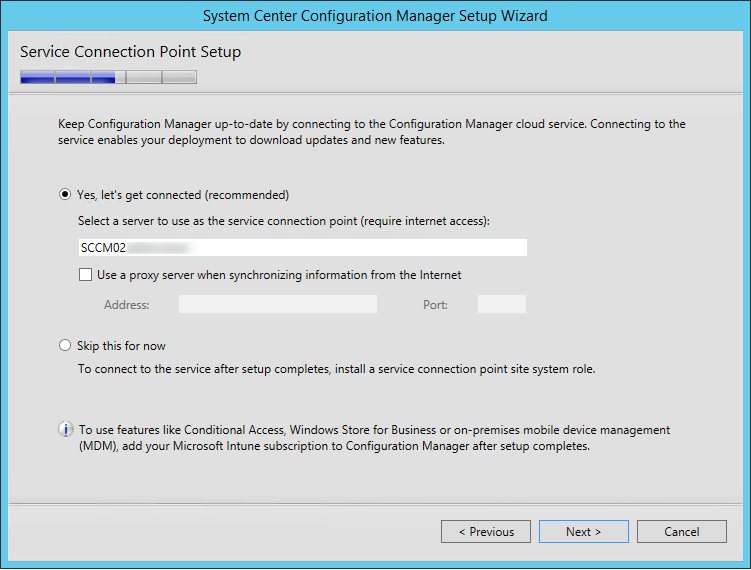
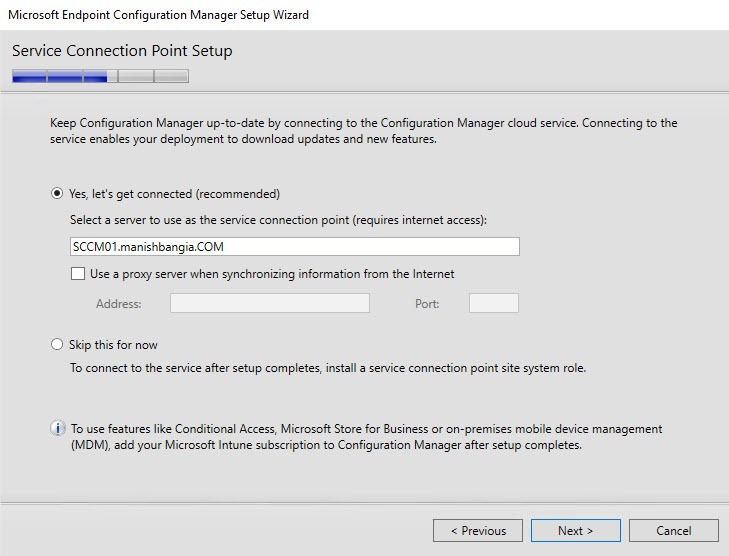
- On the Service Connection Point screen, click Next. This new role enables your deployment to download updates and new features
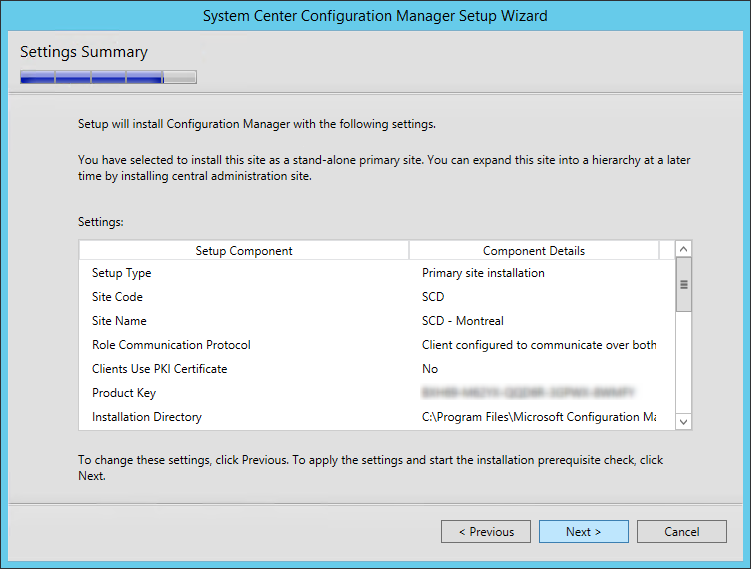
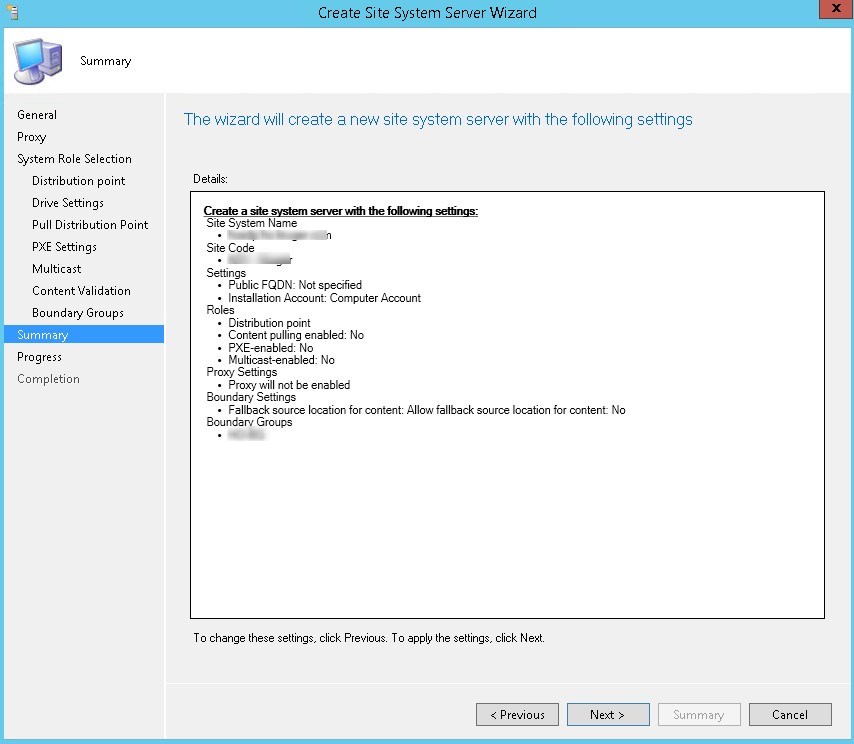
- On the Settings Summary Screen, review your options and click Next
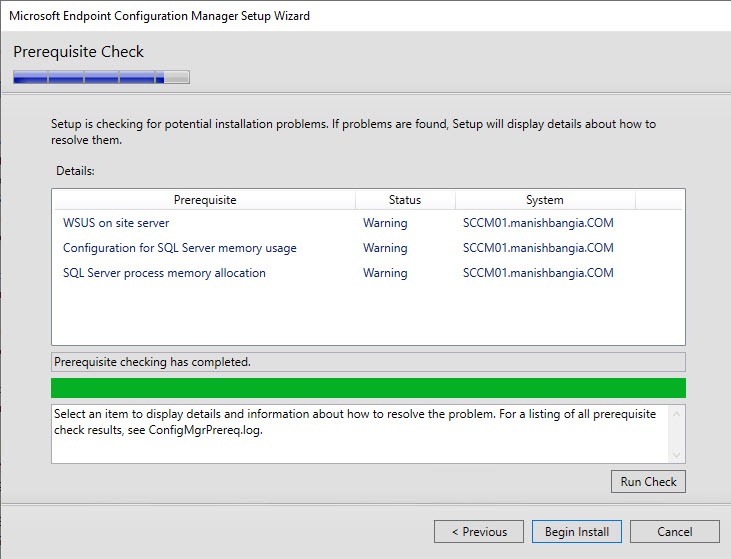
- On the Prerequisite Check screen, you should have no error since you’ve run it before setup, click Next
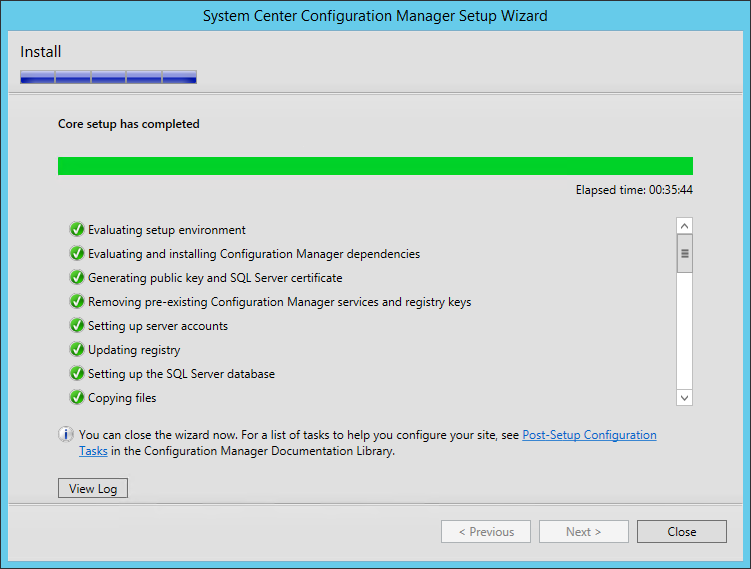
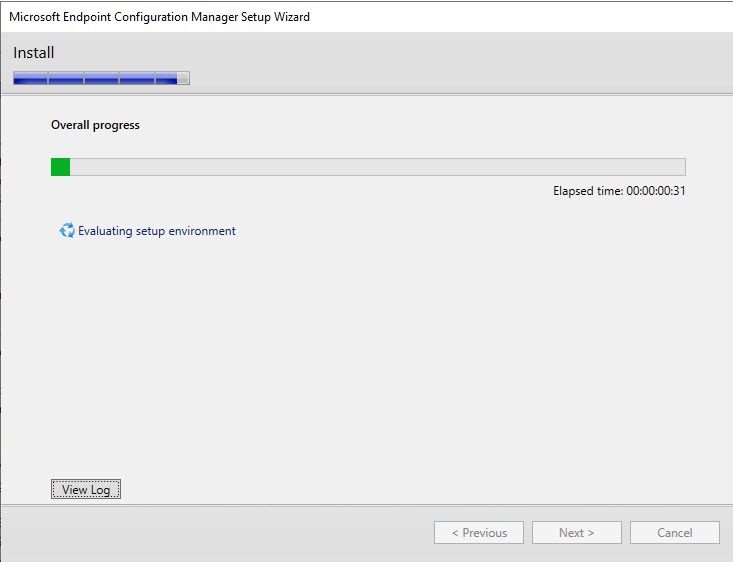
- The installation is in progress. You can count between 15 and 30 minutes depending of your server specifications
- You can follow the progress by clicking the View Log button or open the ConfigMgrSetup.log file on the C: drive
- Wait for Core setup has completed and close the wizard
We’re still not done yet ! Before opening the SCCM console, we suggest to install the following tools :
CMTrace
CMTrace will become your best friend when reading log files.
- Open the SCCM ISO
- Browse to .SMSSETUPTOOLS
- Click on CMTrace.exe
- Click on YES to set is as your default log viewer
Additionally, you can read our blog post :
- How to use CMTrace like a Pro Part 1
- How to use CMTrace like a Pro Part 2
System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager Toolkit
The SCCM 2012 R2 toolkit is compatible with SCCM Current Branch and contains fifteen downloadable tools to help you manage and troubleshoot SCCM.
Download and install it here
SCCM Current Branch Installation Extra Information
You can also refer to our blog post about Useful Resources to help you begin with SCCM. If you need further help to understand and configure various SCCM site components, consult our Step-by-Step SCCM 1511 Installation Guide blog series. It covers all you need to know.
SCCM Current Branch Upgrade
The first task we like to do after a new SCCM installation is to upgrade it to the latest version. If you’re not familiar with this, Microsoft releases a Baseline version that you can install from scratch and then, you must upgrade to the latest version. We have a bunch of guides for each version. For reference, at the time of this blog post, the baseline is 1902 and the latest version is SCCM 1910. Just follow our latest upgrade guide and you’ll be at the latest available version.
SCCM Current Branch Configuration
The next sections will be for configuring the various site server roles in your newly installed SCCM server. Role installation order is not important, you can install roles independently of others.
Part 4 – Application Catalog web service point
This part will describe how to install the SCCM Application Catalog web service point and the Application Catalog website point. Both of these roles are now unsupported. We do not recommend adding this role to your hierarchy.
The application catalogue’s Silverlight user experience isn’t supported as of current branch version 1806. Starting in version 1906, updated clients automatically use the management point for user-available application deployments. You also can’t install new application catalogue roles. Support ends for the application catalogue roles with version 1910.
Role Description
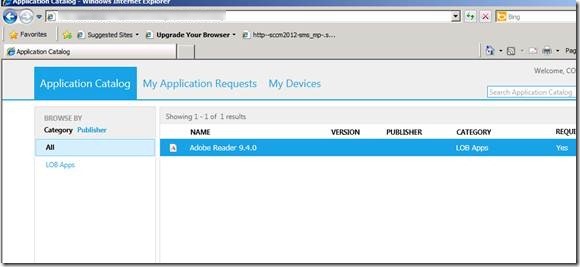
The Application Catalog web service point provides software information to the Application Catalog website from the Software Library.
The Application Catalog website point provides users with a list of available software.
This is not a mandatory site system but you need both the Application Catalog website point and the Application Catalog web service point if you want to provide your user with a Self-Service application catalog (web portal).
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
The Application Catalog web service point and the Application Catalog website point are hierarchy-wide options. It’s supported to install those roles on a stand-alone Primary site or child Primary site. It’s not supported to install it on a Central Administration site or Seconday site. The Application Catalog web service point must reside in the same forest as the site database.
If you’re having less than 10,000 users in your company, co-locating the Application Catalog web service and Application Catalog website roles on the same server should be ok. The web service role connects directly to the SCCM SQL database so ensure that the network connectivity between the SQL server and the Application Catalog web service servers is robust.
If you have more geographically distributed users, consider deploying additional application catalogs to keep responsiveness high and user satisfaction up. Use client settings to configure collections of computers to use different Application Catalog servers.
Read more on how to provide a great application catalog experience to your user in this Technet blog article.
If your client needs HTTPS connections, you must first deploy a web server certificate to the site system. If you need to allow Internet clients to access the application catalog, you also need to deploy a web server certificate to the Management Point configured to support Internet clients. When supporting Internet clients, Microsoft recommends that you install the Application Catalog website point in a perimeter network, and the Application Catalog web service point on the intranet. For more information about certificates see the following Technet article.
Prerequisites
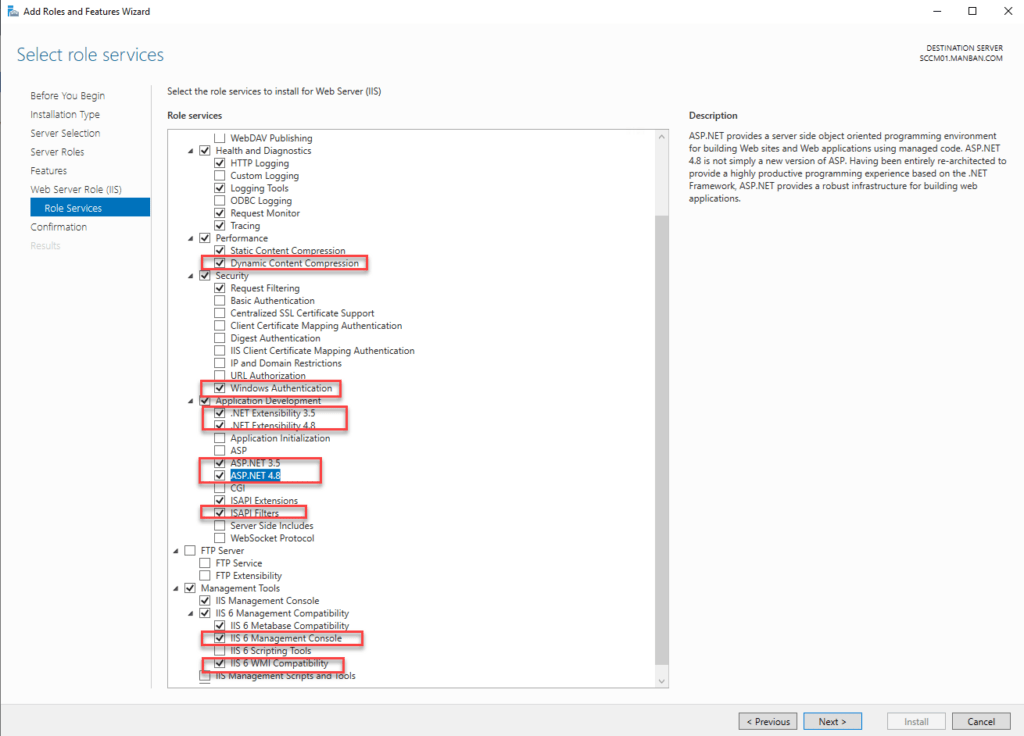
Using Windows Server 2012, the following features must be installed before the role installation:
Application Catalog web service point
Features:
- .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 and 4.0
WCF activation:
- HTTP Activation
- Non-HTTP Activation
IIS Configuration:
- ASP.NET (and automatically selected options)
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility
- IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility
Application Catalog website point
Features:
- .NET Framework 4.0
IIS Configuration:
- Common HTTP Features
- Static Content
- Default Document
- Application Development
- ASP.NET (and automatically selected options)
- Security
- Windows Authentication
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility
- IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility
SCCM Application Catalog Installation
For this post, we will be installing both roles on our stand-alone Primary site using HTTP connections. If you split the roles between different machines, do the installation section twice, once for the first site system (selecting Application Catalog web service point during role selection)and a second time on the other site system (selecting Application Catalog website point during role selection).
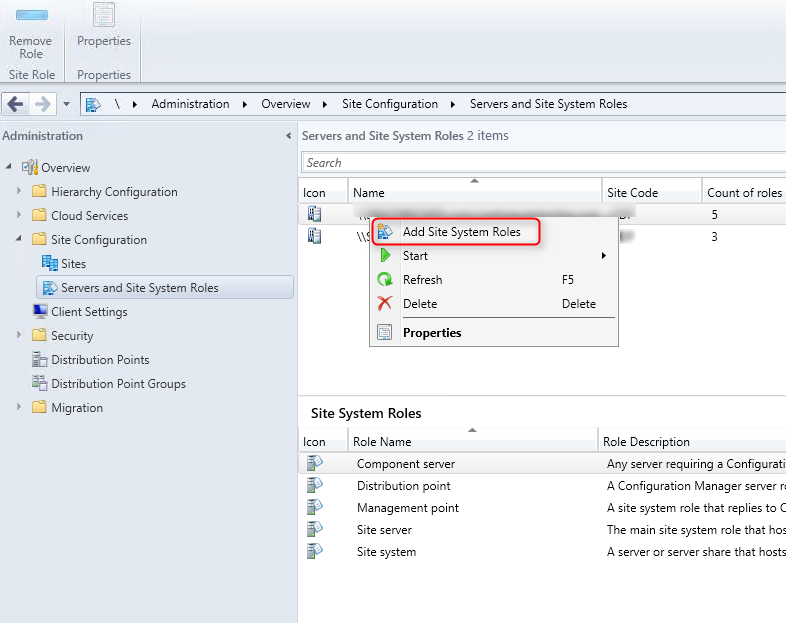
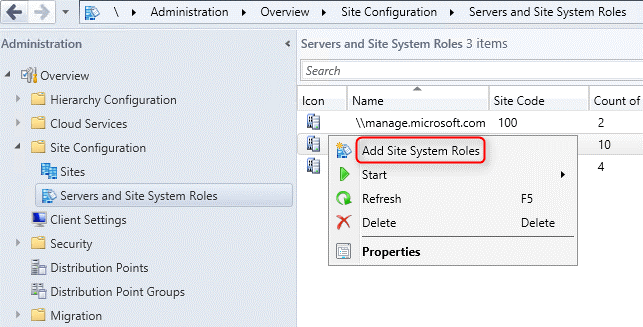
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
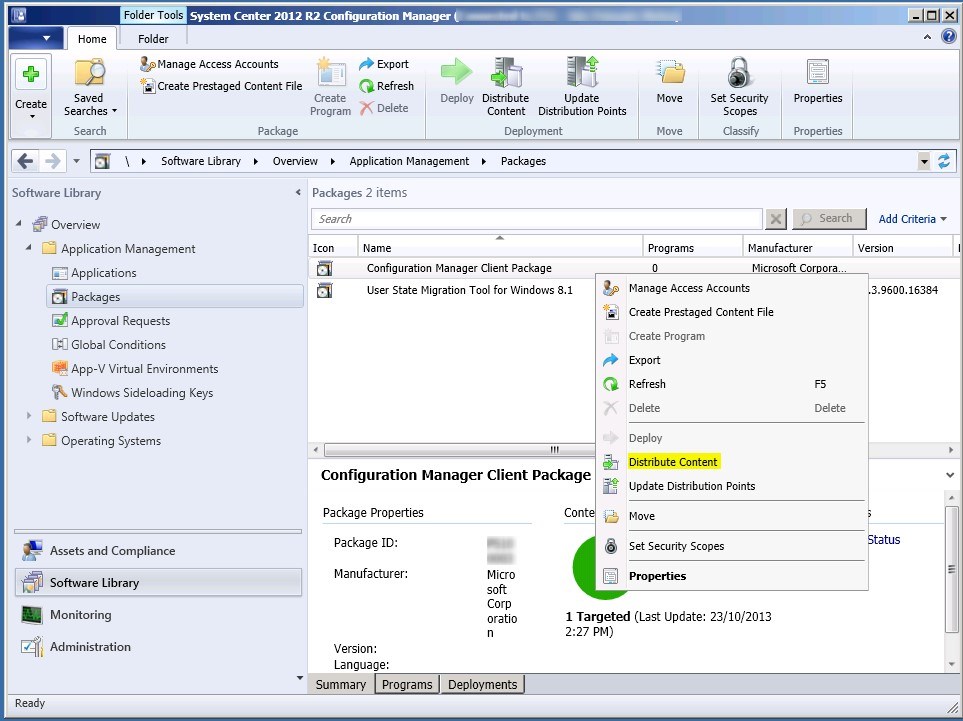
- Right-click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
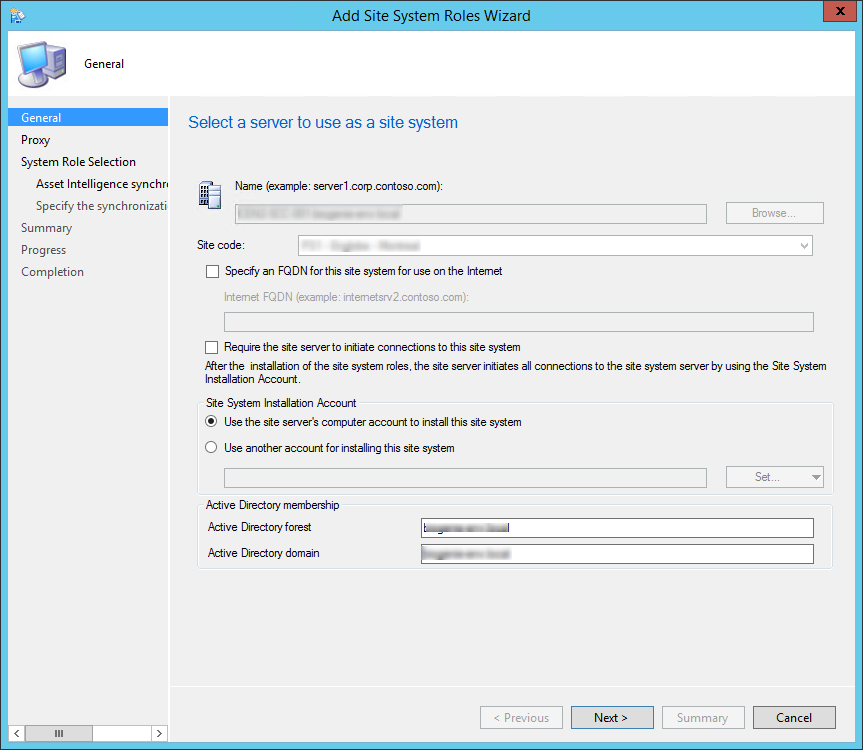
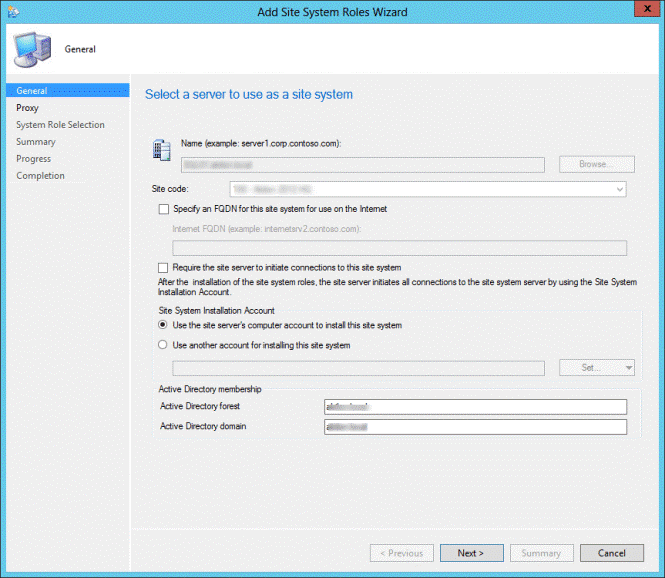
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
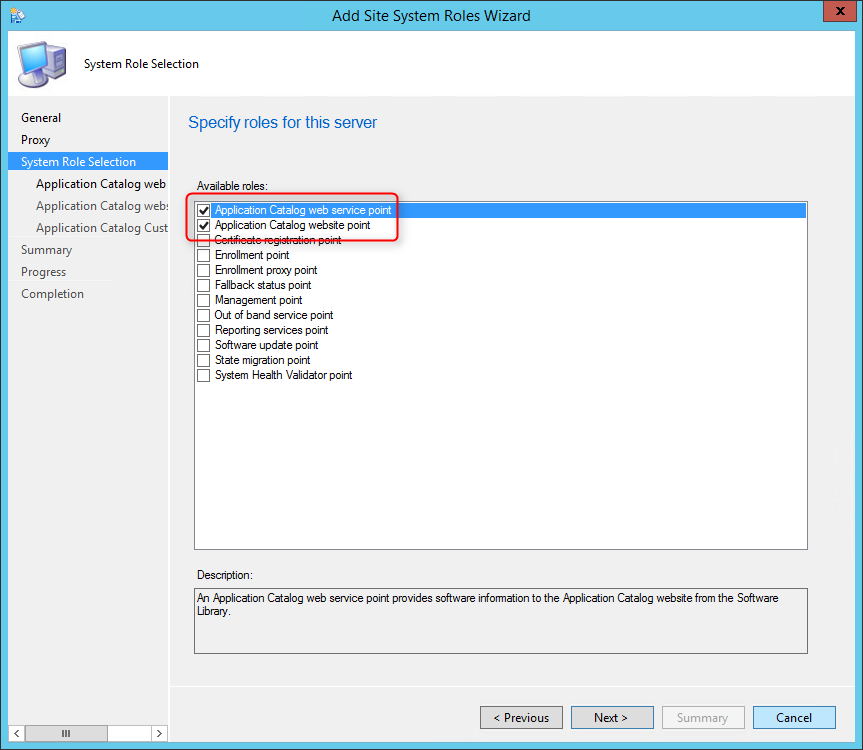
- On the Site System Role tab, select Application Catalog web service point and Application Catalog website point, click Next
- On the Application Catalog Web Service Point
- In the IIS Website and Web application name fields,leave both to the default values
- This is just the name that you’ll see in IIS after the installation (see next screenshot). It has nothing to do with your user facing portal
- Enter the port and protocol that you want to use
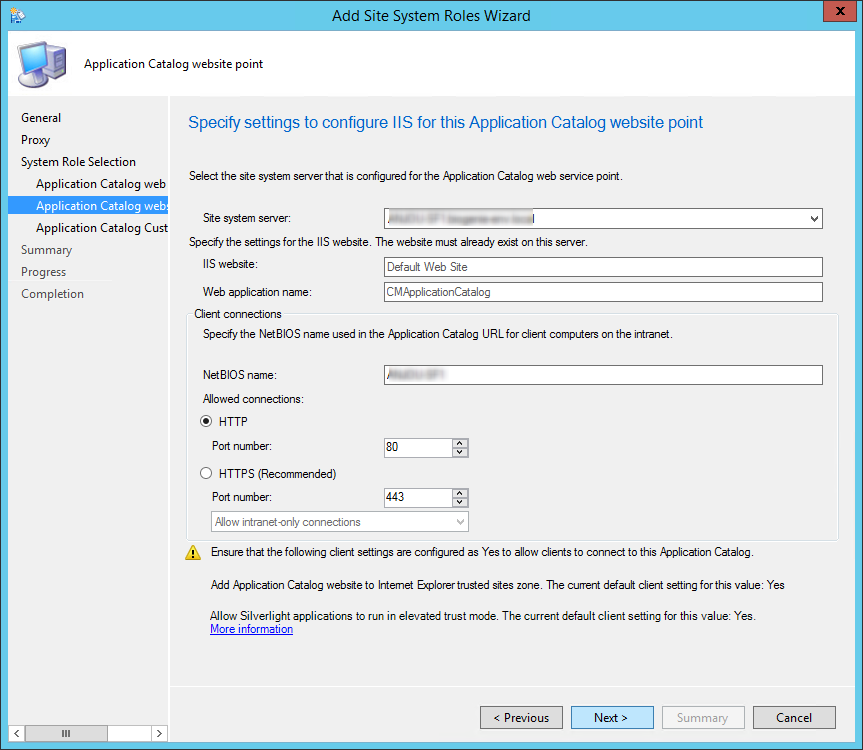
- On the Application Catalog WebSite Point
- In the IIS Website keep the default value
- In Web application name, enter the name that you want for your Application Catalog. This is the URL that will be published to your users
- Enter the port and protocol that you want to use
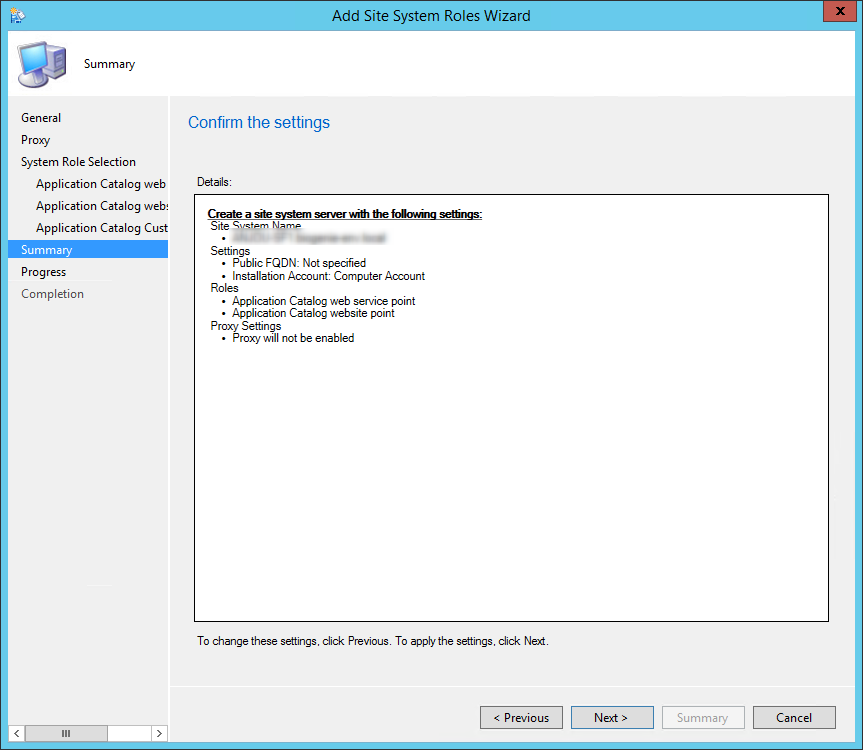
- On the Application Catalog Customizations tab, enter your organization name and the desired colour for your website
- On the Summary tab, review your settings, click Next and complete the wizard
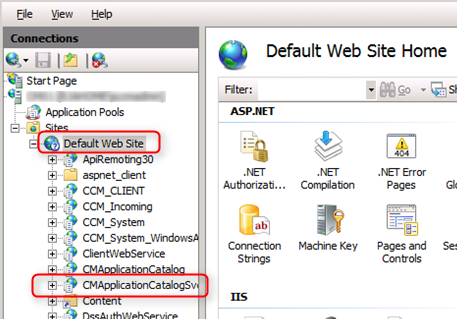
Verification and Logs files
You can verify the role installation in the following logs:
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsSMSAWEBSVCSetup.log and awebsvcMSI.log – Records details of about the Application Catalog Web Service Point installation
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsSMSPORTALWEBSetup.log and portlwebMSI.log – Records details of about the Application Catalog Website Point installation
In the console :
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Monitoring / System Status / Component Status
- See status of the components SMS_PORTALWEB_CONTROL_MANAGER and SMS_AWEBSVC_CONTROL_MANAGER
Web browser
Verify that the Application Catalog is accessible :
- Open a web browser
- Browse to http://YourServerName/CMApplicationCatalog
- Replace YourServerName with the server name on which you installed the Application Catalog Website Point
- Replace CMApplicationCatalog with the name that you give your Application Catalog. (Default is CMApplicationCatalog)
If everything is set up correctly, you’ll see a web page like this :
URL Redirection
The default URL to access the Application Catalog is not really intuitive for your users.
It’s possible to create a DNS entry to redirect it to something easier (ex: http://ApplicationCatalog)
The following Coretech article describe how to achieve that.
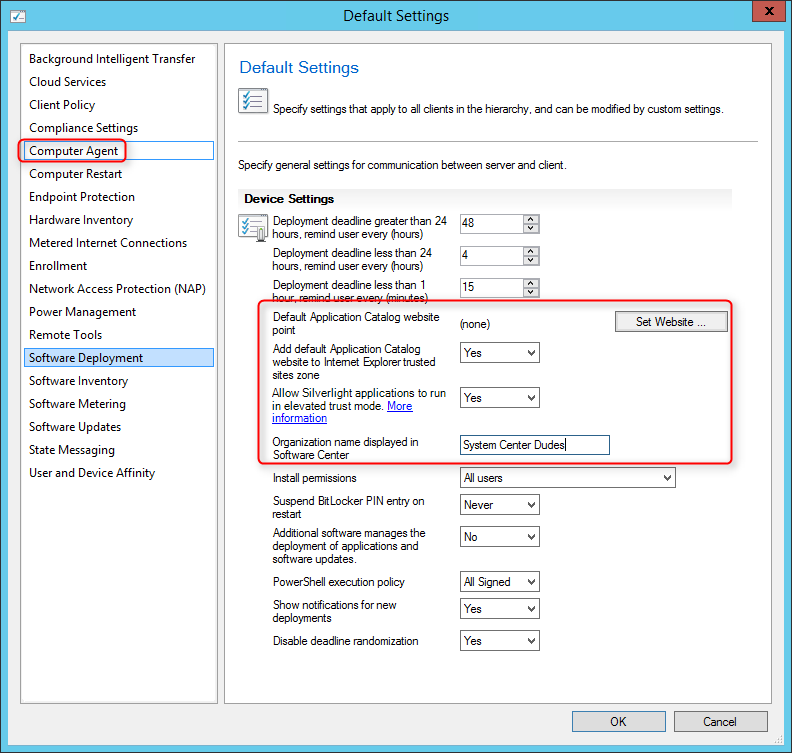
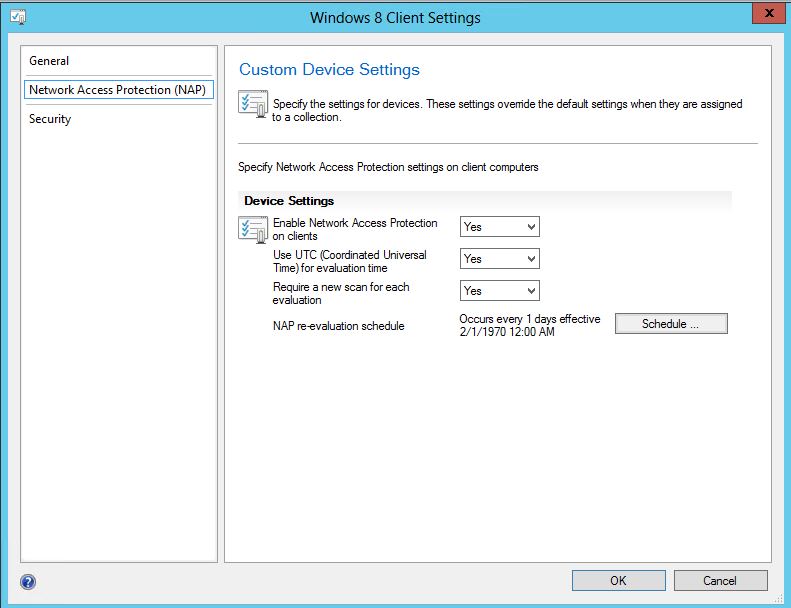
Client Settings
Ensure that the client settings for your clients are set correctly to access the Application Catalog
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Administration / Client Settings
- Right-click your client settings and select Properties
- On the left pane, select Computer Agent
- Click the Set Website button and select your Application Catalog (the name will be automatically populated if your Application Catalog is installed)
- Select Yes on both Add Default Application Catalog website to Internet Explorer trusted site zone and Allow Silverlight application to run in elevated trust mode
- Enter your organisation name in Organisation name displayed in Software Center
That’s it, you’ve installed your SCCM Application Catalog, publish the link to your user and start publishing your applications.
Part 6 – Asset Intelligence Synchronization Point
This part will describe the Asset Intelligence Synchronization Point (AISP).
Role description
The AISP is used to connects to Microsoft in order to download Asset Intelligence catalog information and upload uncategorized titles. For more information about planning for Asset Intelligence, see Prerequisites for Asset Intelligence in Configuration Manager.
This is not a mandatory Site System but we recommend to install the AISP if you are planning to use Asset Intelligence. Read our blog post on Why should you use Asset Intelligence in SCCM.
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
The AISP is a hierarchy-wide option. SCCM supports a single instance of this site system role in a hierarchy and only at the top-level site. Install it on your Central Administration Site or stand-alone Primary Site depending of your design.
AISP Installation
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and site System Roles
- Right-click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
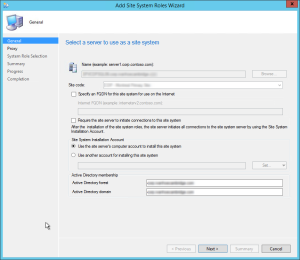
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, enter your Proxy server information if needed and click Next
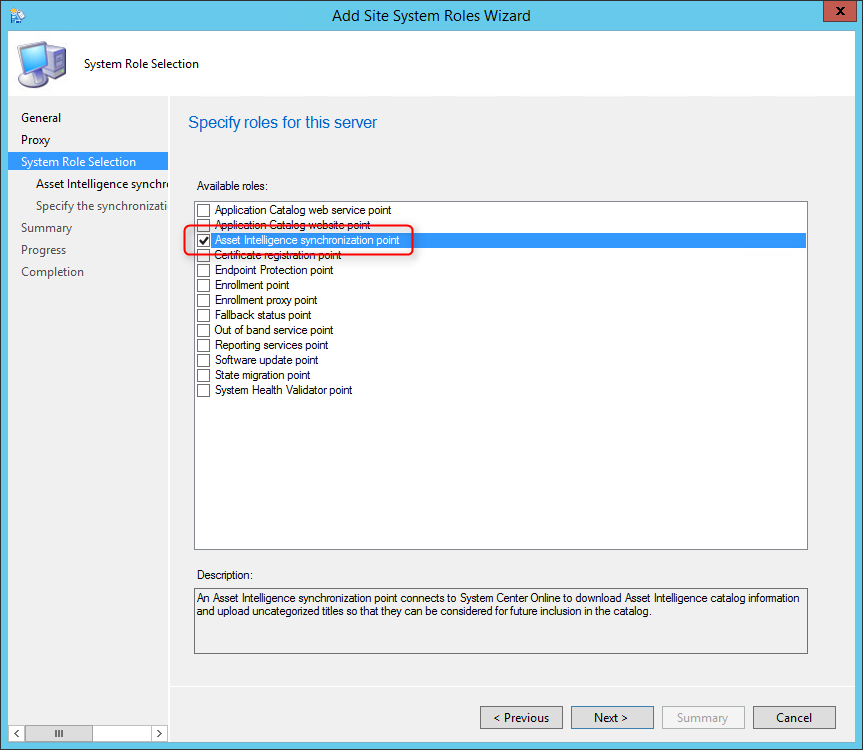
- On the Site System Role Selection tab, select Asset Intelligence Synchronization Point, click Next
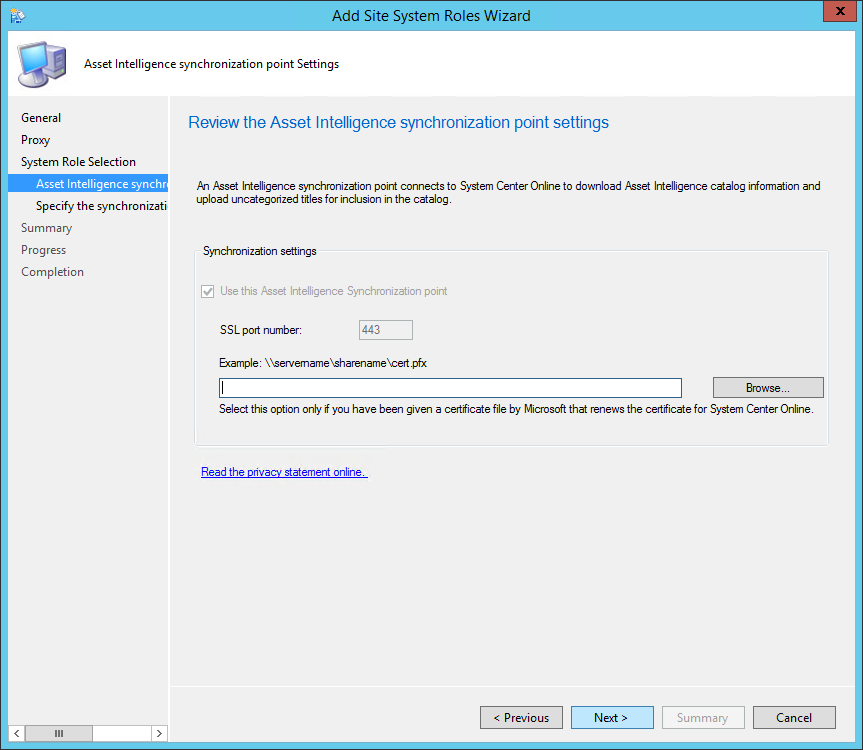
- On the Certificate page, click Next
- By default, the Use this Asset Intelligence Synchronization Point setting is selected and cannot be configured on this page. System Center Online accepts network traffic only over TCP port 443, therefore the SSL port number setting cannot be configured on this page of the wizard
- You can specify a path to the System Center Online authentication certificate (.pfx) file. Typically, you do not specify a path for the certificate because the connection certificate is automatically provisioned during site role installation
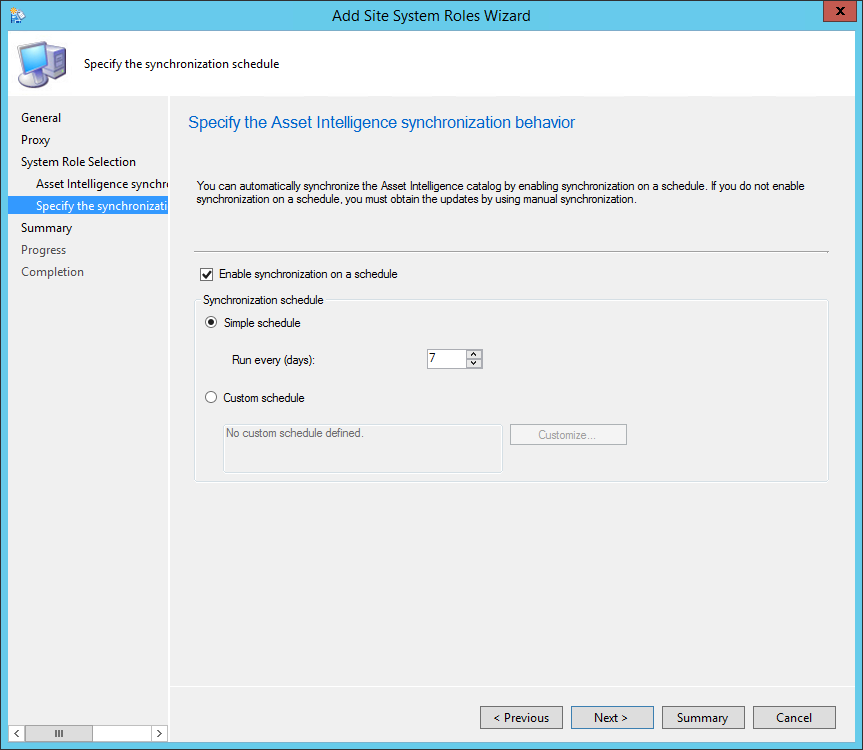
- Specify the desired catalog Synchronization Schedule, click Next
- On the Summary tab, review your setting and click Next
- Wait for the setup to complete and close the wizard
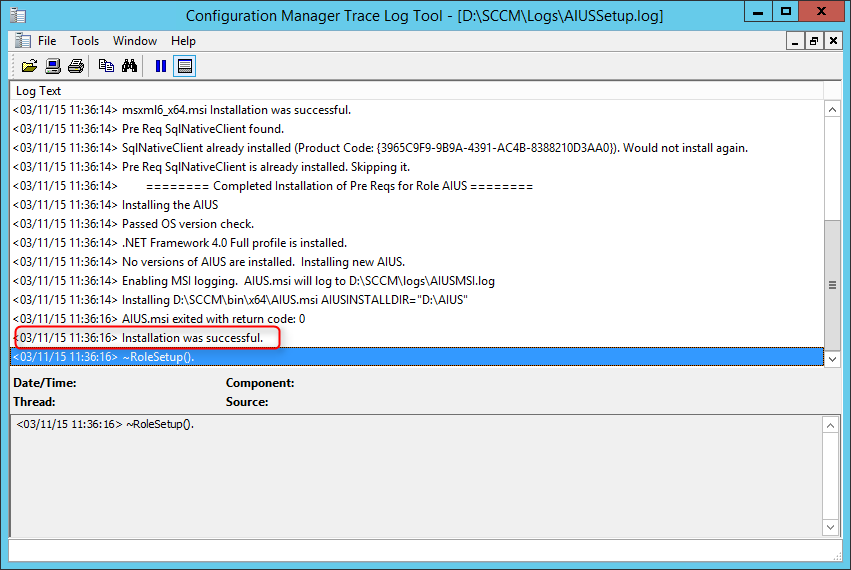
AISP Logs
- AIUSSetup.log – Information about the installation of the Asset Intelligence catalog synchronization point site system role
- AIUpdateSvc.log – Information about the Asset Intelligence catalog synchronization service
- Aikbmgr.log – Information about the Asset Intelligence catalog manager service
Verification
- Verify that the role installation is completed in AIUSSetup.log
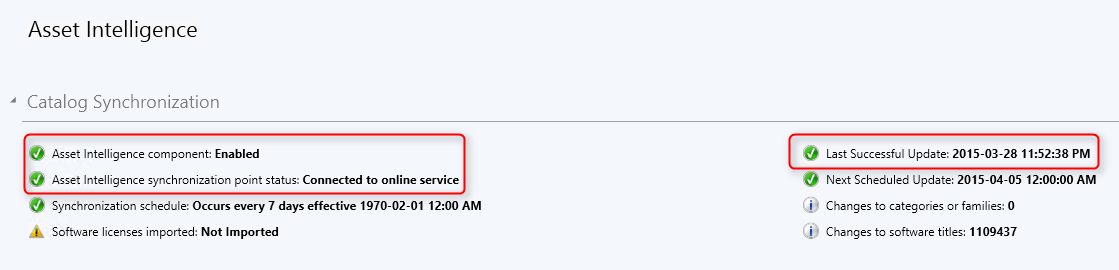
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Assets and Compliance / Overview / Asset Intelligence
- Verify that the Sync is Enabled and Successful
Enable Inventory Reporting Classes
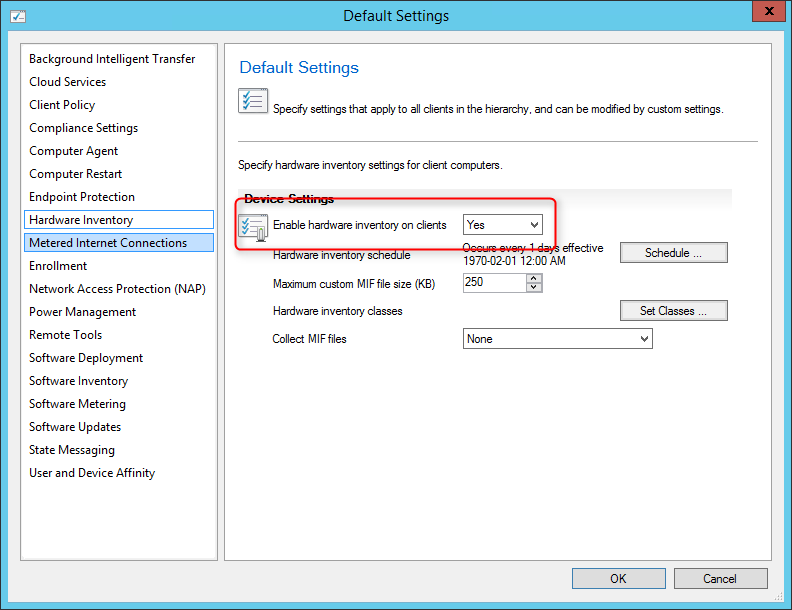
In order to have inventory data, first ensure that Hardware Inventory is enabled in your Client Settings.
- Navigate to Administration / Client Settings
- Right-click your Client Settings and choose Properties
- On the Hardware Inventory Tab
- Ensure that your hardware inventory is Enabled
Once confirmed, enable inventory reporting classes :
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Assets and Compliance / Asset Intelligence
- Right-click Asset Intelligence and select Edit Inventory Classes
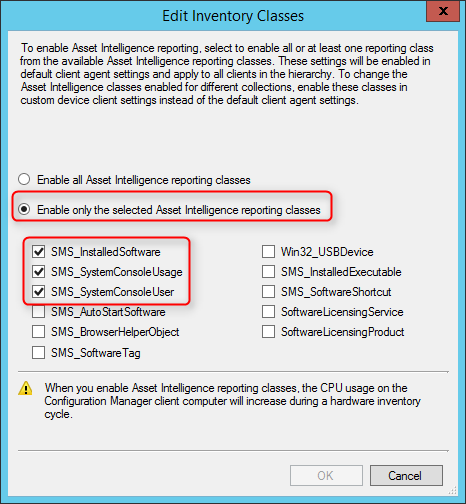
- Select Enable only the selected Asset Intelligence reporting classes
- Select SMS_InstalledSoftware, SMS_ConsoleUsage and SMS_SystemConsoleUser
- See the following Technet article to see dependencies between hardware and reporting class
- On the warning, click Yes
Maintenance Tasks
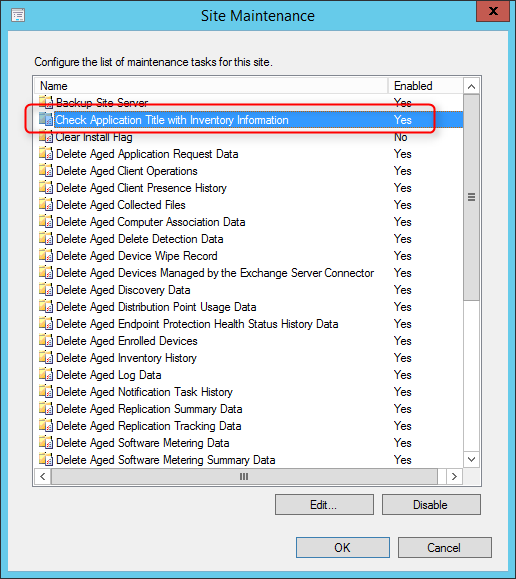
2 maintenance tasks are available for Asset Intelligence :
- Check Application Title with Inventory Information
- This maintenance task checks that the software title that is reported in software inventory is reconciled with the software title in the Asset Intelligence catalog.
- Summarize Installed Software Data
- This maintenance task provides the information that is displayed in the Assets and Compliance workspace. When the task runs, Configuration Manager gathers a count for all inventoried software titles at the primary site.
To set the maintenance tasks :
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Sites
- Select Site Maintenance on the top ribbon
- Select the desired schedule for both tasks
You’re now done installing the AISP.
Part 7 – Certificate Registration Point
We will describe how to install SCCM Certificate Registration Point (CRP).
Role Description
Using SCCM and Intune, the CRP communicates with a server that runs the Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES) to provision device certificate requests.
This is not a mandatory Site System but we recommend to install a CRP if you need to provision client certificates to your devices (like VPN or WIFI).
Prerequisites
Before the CRP can be installed, dependencies outside SCCM is required. I won’t cover the prerequisite configuration in details as they are well documented on this Technet article and it goes beyond SCCM. Here’s an overview of what needs to be done :
- Install the NDES role on a Windows 2012 R2 Server
- Modify the security permissions for the certificate templates that the NDES is using
- Deploy a PKI certificate that supports client authentication
- Locate and export the Root CA certificate that the client authentication certificate chains to
- Increase the IIS default URL size limit
- Modify the request-filtering settings in IIS
On the machine that will receive the CRP role, install the following using Windows server role and features:
- IIS
- ASP .NET 3.5
- ASP .NET 4.5
- WCF HTTP Activation
If you are installing CRP on a remote machine from the site server, you will need to add the machine account of the site server to the local administrator’s group on the CRP machine.
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
The Certificate Registration Point must not be installed on the same server that runs the Network Device Enrollment Service. It’s supported to install this role on a Central Administration Site, child Primary Site or stand-alone Primary Site but it’s not supported on a Secondary Site.
CRP Installation
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
- Right click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
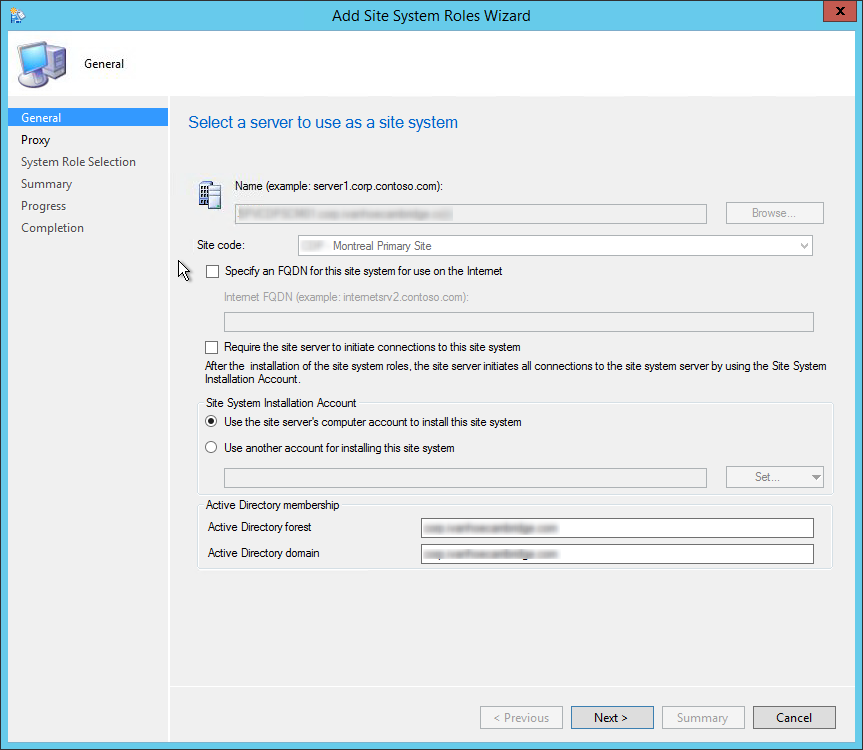
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
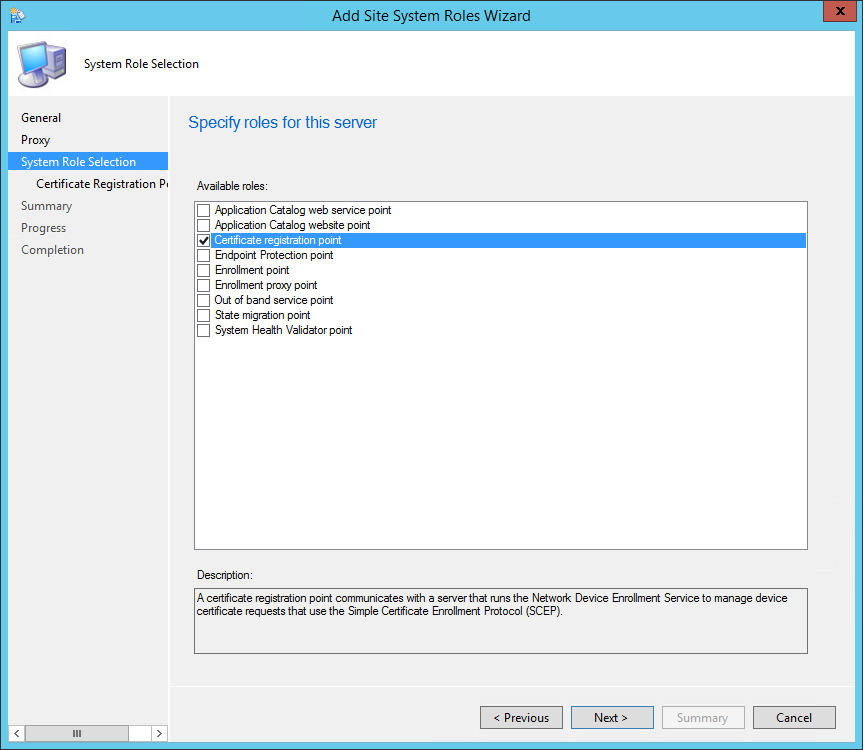
- On the Site System Role tab, select Certificate Registration Point, click Next
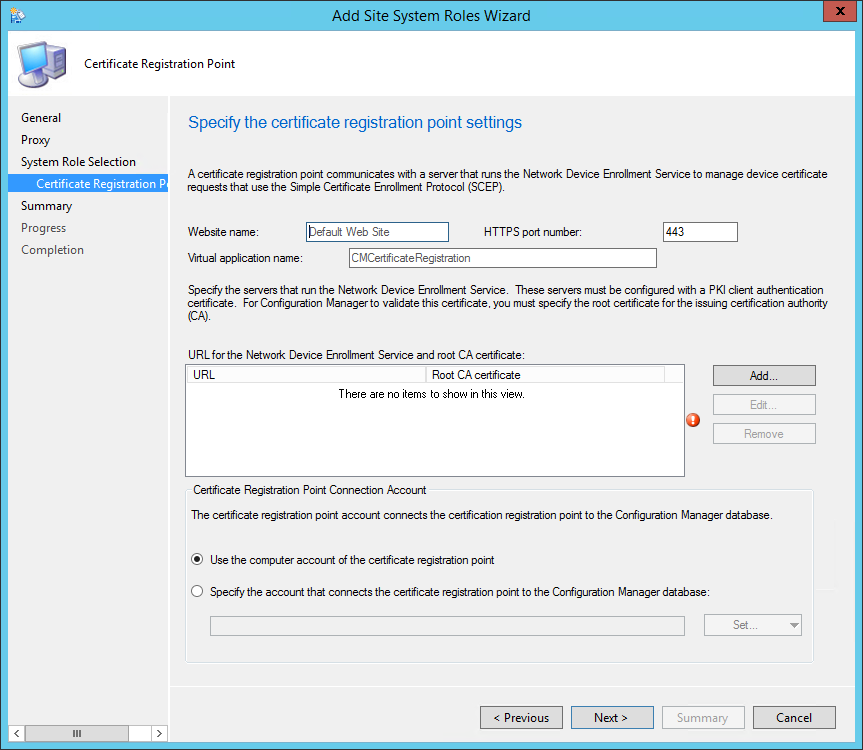
- On the Certificate Registration Point Properties, leave the default website name and virtual application name. Take note of your Virtual Application Name, you will need it later.
- Click on Add
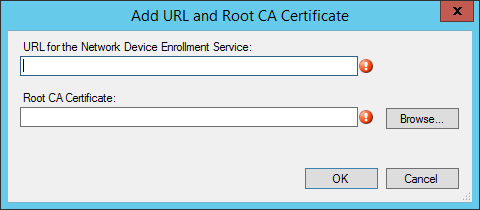
- Enter the URL of your NDES server
- This URL will be part of the profile send to the devices. The device will needs to access this URL from the internet
- Example : https://ndes.systemcenterdudes.com/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll
- Enter the path to your exported Root CA Certificate (.cer file)
- Once completed, click on Next, review the Summary and close the wizard
Verification and Logs files
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogscrpmsi.log – Detailed CRP Installation status
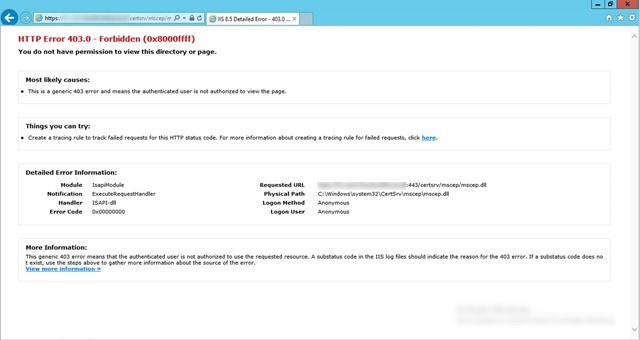
- Using a browser, verify that you can connect to the URL of the certificate registration point—for example, https://crp.systemcenterdudes.com/CMCertificateRegistration
- HTTP Error 403 is ok. If you have a 404 error or 500 error, look at the logs file before continuing
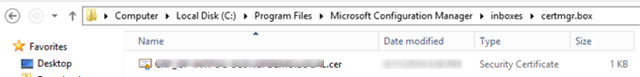
- After the CRP is installed, the system will export the certificate that will be used for NDES plugin to the certmgr.box folder. It may take up to 1 hour to appear.
- Save this .cer file on the NDES server as we will need it in the next section.
Configuration Manager Policy Module
Now that the Certificate Registration Point has been installed, we must install a plug-in on the NDES server to establish the connection with SCCM.
On the server that runs the Network Device Enrollment Service :
- Copy the SMSSETUPPOLICYMODULEX64 folder from the the Configuration Manager installation media to a temporary folder
- From the temporary folder, run PolicyModuleSetup.exe
- Click Next, accept the license terms and click Next
- On the Installation Folder page, accept the default installation folder click Next
- On the Certificate Registration Point page, specify the URL of the Certificate Registration Point. This is the Virtual Application Name created during the SCCM role installation (Example : https://crp.systemcenterdudes.com/CMCertificateRegistration)
- Accept the default port of 443, click Next
- On the Client Certificate for the Policy Module page, browse to and specify the client authentication certificate. This is the same certificate you used in the CRP Installation wizard in SCCM
- On the Certificate Registration Point Certificate page, click Browse to select the exported certificate file (the one exported from inboxescertmgr.box)
- Click Next and complete the wizard
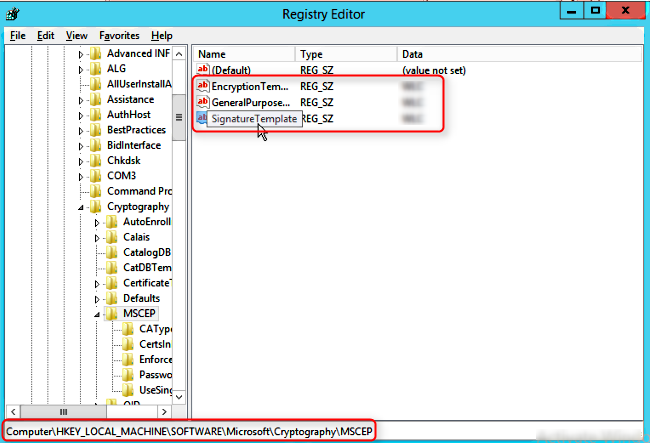
- Open the registry editor and browse to HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftCryptographyMSCEP
- Make sure that the values of EncryptionTemplate, GeneralPurposeTemplate and SignatureTemplate match the names of the template on your CA
- Open Internet Explorer on the NDES server and browse to https://ndes.systemcenterdudes.com/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll, you will no longer see the web page but instead you should see an error 403, this is expected
Once all the above has been configured and verified, you are ready to create your certificate profile in SCCM.
References
Here are my favourites articles covering the subject :
- Technet Article
- Configuration Team Blog article
- Pieter Wigleven’s installation (Technical Solution Professional at Microsoft)
- Peter van der Woude’s key configuration steps
Part 8 – Distribution Point Installation
In this part, we will describe how to perform an SCCM distribution point installation.
I saw a lot of posts recently on the Technet forum which leads me to think that there’s a lack of documentation explaining this.
Introduction
Several distribution points can provide better access to available software, updates, and operation systems. A local Distribution Point also prevents the installation thought the WAN.
Pre-Requisites
- Functional SCCM hierarchy
- SCCM Admin console access
- RDP access on the Distribution Point server
- The required level of security in the SCCM console
Distribution point server configuration
Prevent package from replication on the wrong drive
- Logon locally on the target machine with remote desktop
- Create an empty file called NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS on the root of each drive where SCCM should NOT write. (If any)
Local Administrator group
On the DP, add a group that contains your site system computer account in the Administrators group.
I like to create a SCCM system groups that contain all my distribution points.
- Open Server Manager
- Expand Local Users and Groups
- Click on Groups
- Double-click on “Administrators”
- Add the security groups that contain the SCCM computer account
Windows Server configuration – Roles and Features
Configuration Manager requires some roles and features to be installed on the server prior to the DP installation
Remote Differential Compression
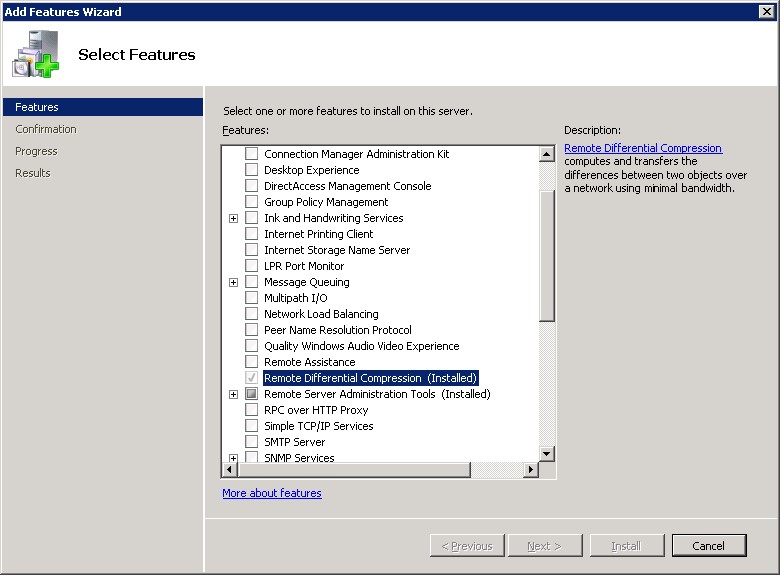
- Open Server Manager, on the Features node, starts the Add Features Wizard.
- On the Select Features page, select Remote Differential Compression
IIS
IIS needs to be installed on the server but it will automatically be installed using the site installation wizard.
Make sure that these roles are installed on your server prior to the installation :
- IIS WMI Compatibility tool
- IIS Scripting Tool
Windows Deployment Service
For Windows Server 2012+, WDS is installed and configured automatically when you configure a distribution point to support PXE or Multicast.
For Windows Server 2003, you must install and configure WDS manually.
BITS
The distribution point site system role does not require Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS). When BITS is configured on the distribution point computer, BITS on the distribution point computer is not used to facilitate the download of content by clients that use BITS
Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributable
You can run the Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributable Setup from the Configuration Manager installation at: <ConfigMgrInstallationFolder>Clientx64vcredist_x64.exe
For Configuration Manager SP1, vcredist_x64.exe is installed automatically when you configure a distribution point to support PXE.
Powershell 3.0
For Windows 2012 only, you need to enable Powershell 3.0 (or further) before installing the distribution point.
Firewall
Ensure that your firewall is set correctly. 2 ports need to be opened.
Distribution Point site server installation
Reboot your server to avoid the case where your server is in “Reboot pending State” which will result in unexpected reboot during distribution point installation.
Now that the Distribution point server is ready to receive a new role, we need to add the server to the site server list
Add new distribution point server to the SCCM console – Site System
- In the Configuration Manager console, click Administration
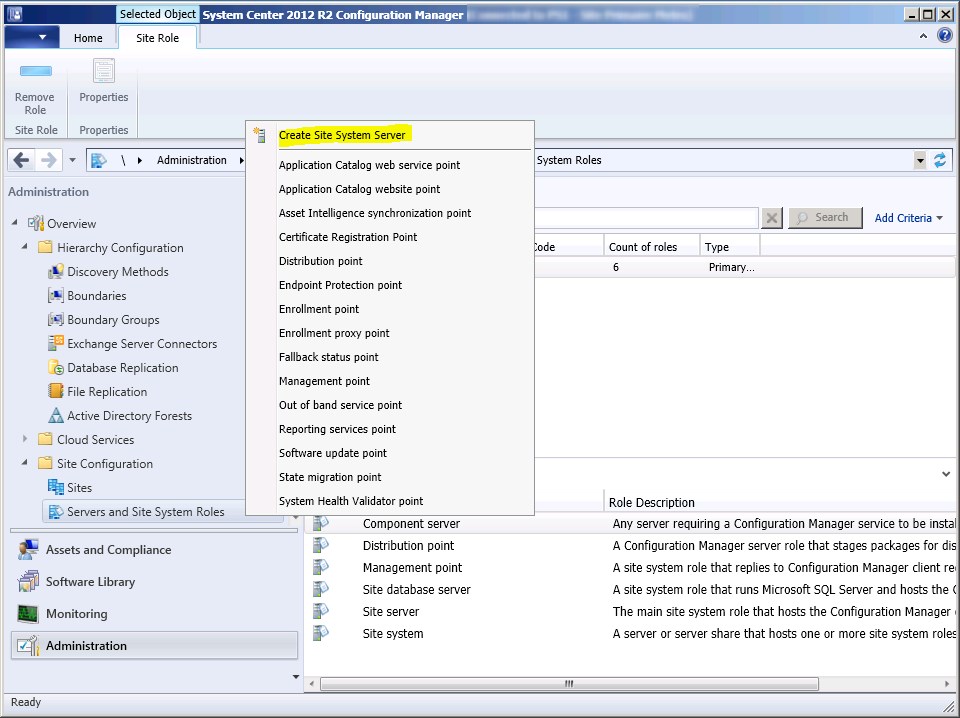
- In the Administration workspace, expand Site Configuration, and then right click Servers and Site System Roles.
- Select Create Site System Server. The Create Site System Server Wizard opens.
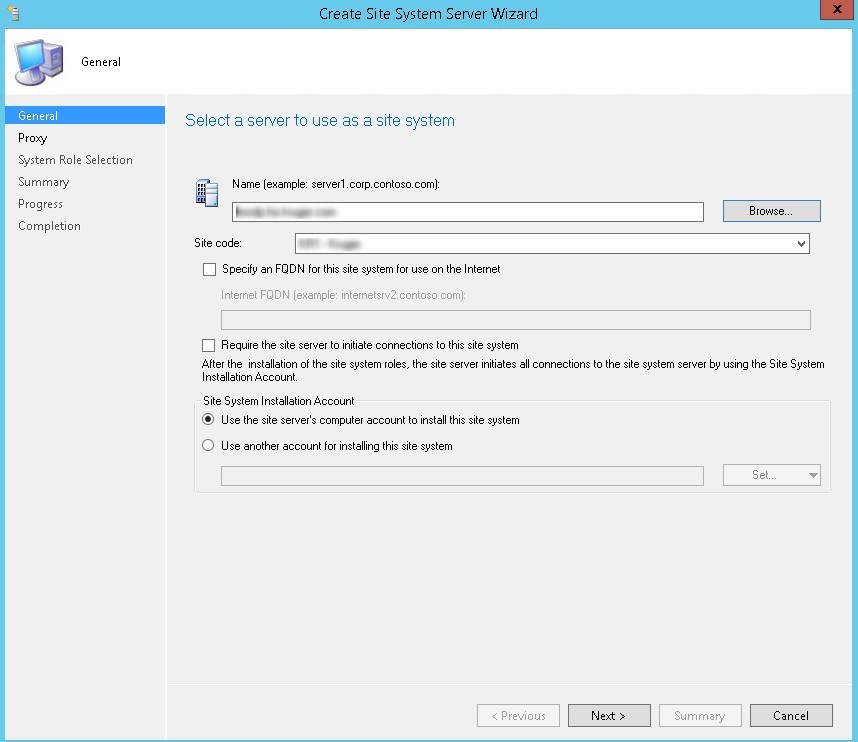
- On the General page, specify the Name for the site system server
- Select the Site Code and Click Next
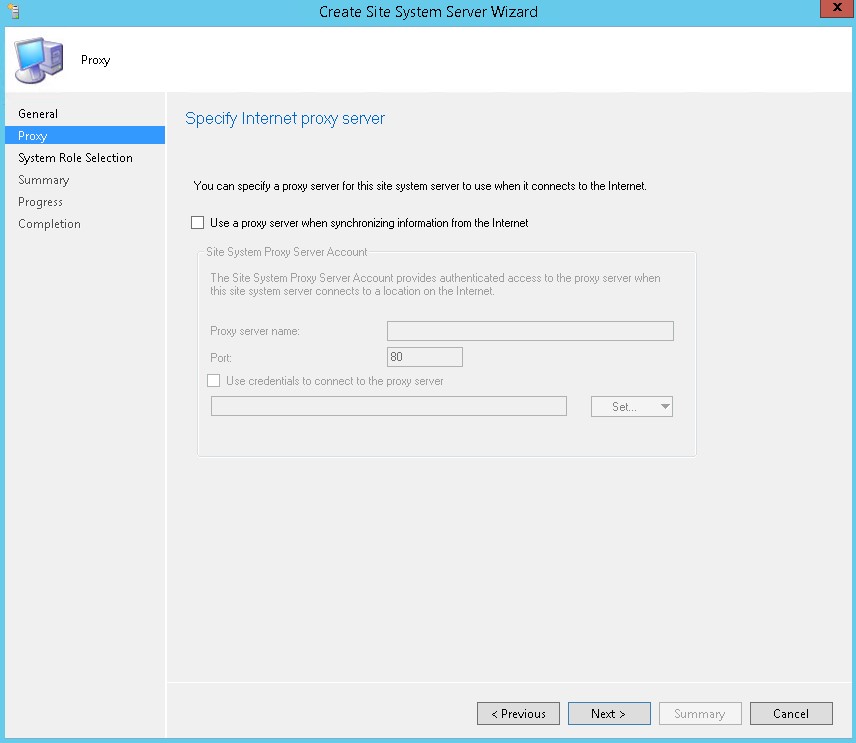
- Do not specify a proxy server, click Next
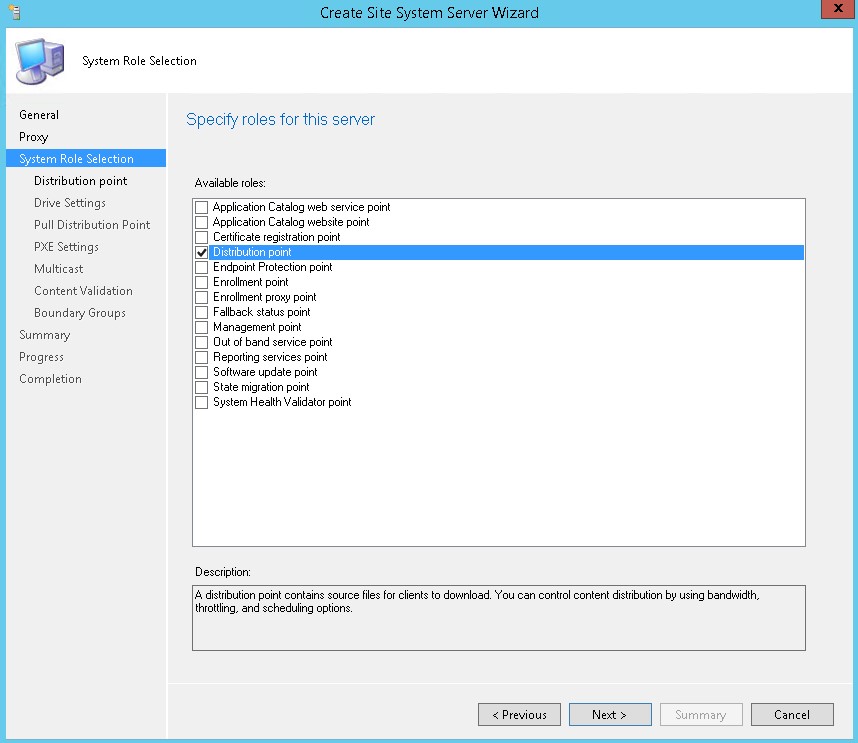
- Select Distribution point in the role selection screen, click Next
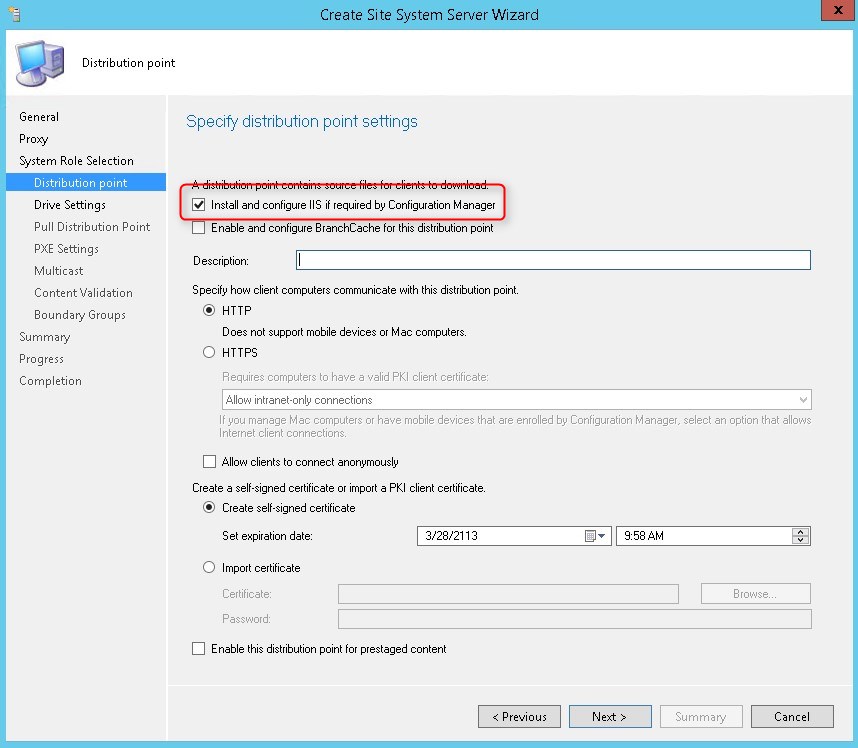
- Check Install and configure IIS if required by CM
- Add a description if needed
- Select HTTP
- Select Create self-signed certificate, click Next
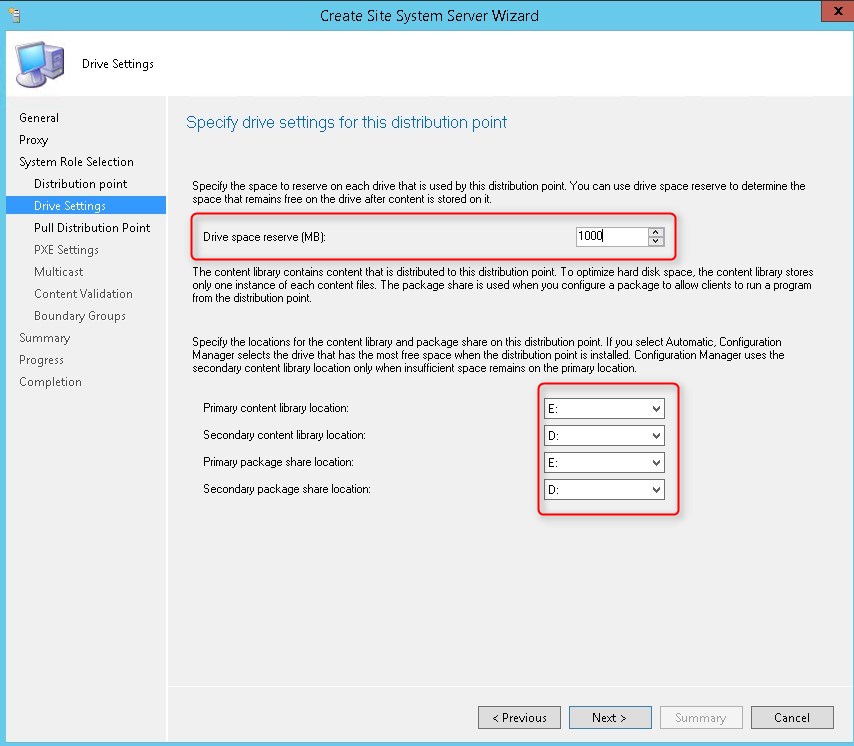
- Set drive configuration to your needs. This is where the SCCMContentLib will be created so select a drive with enough storage space, click Next
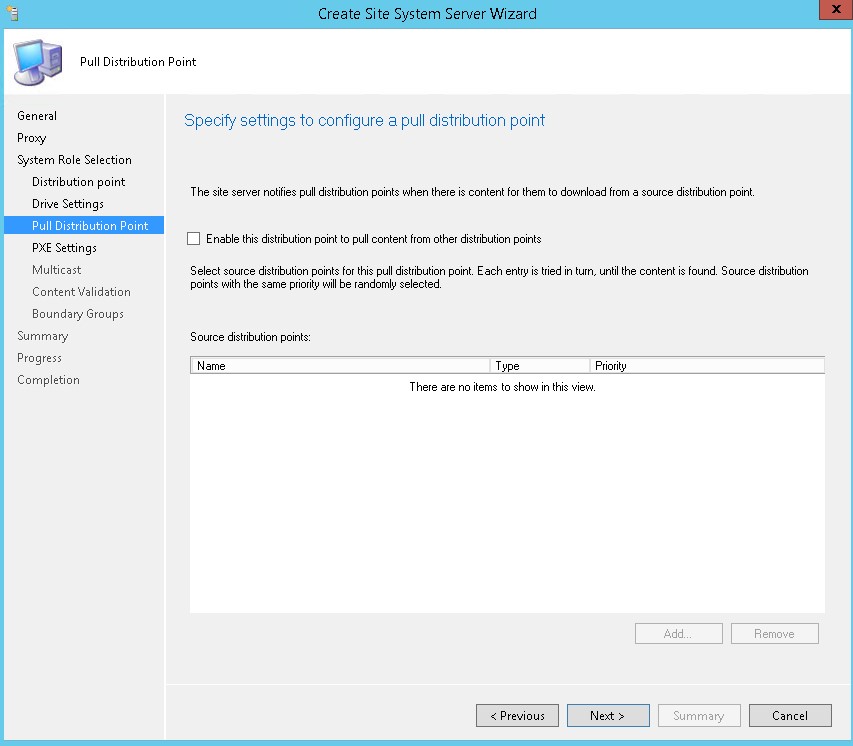
- Do not configure a pull distribution point, click Next
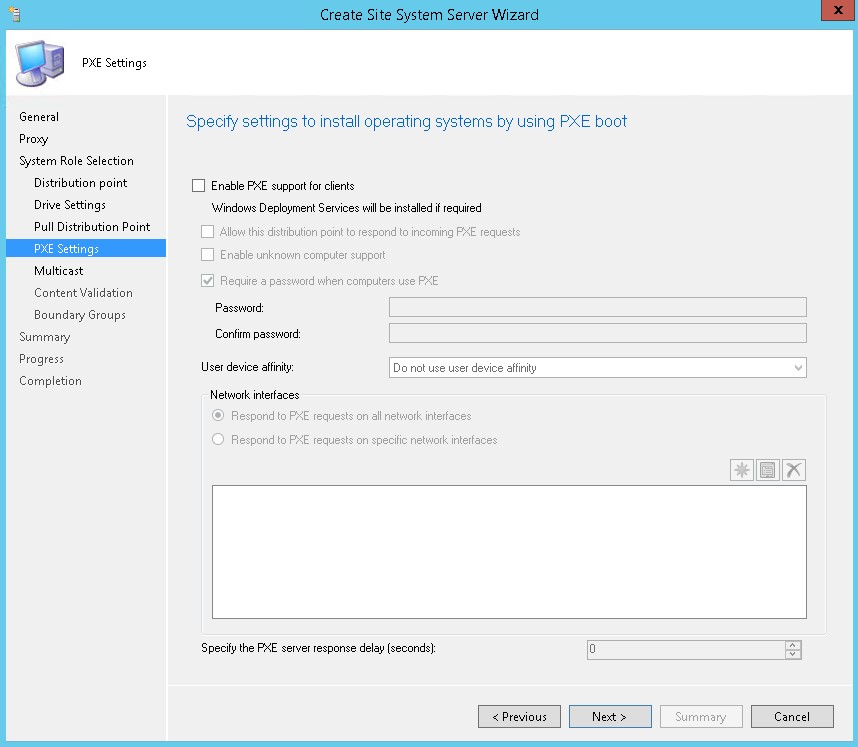
- Do not configure PXE for now, click Next
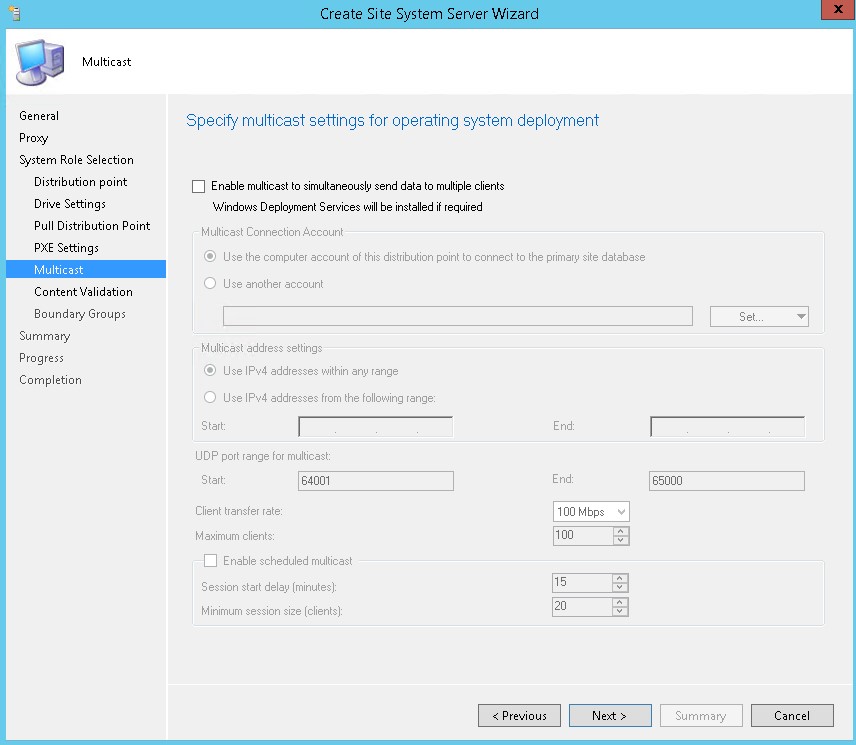
- Do not enable multicast for now, click Next
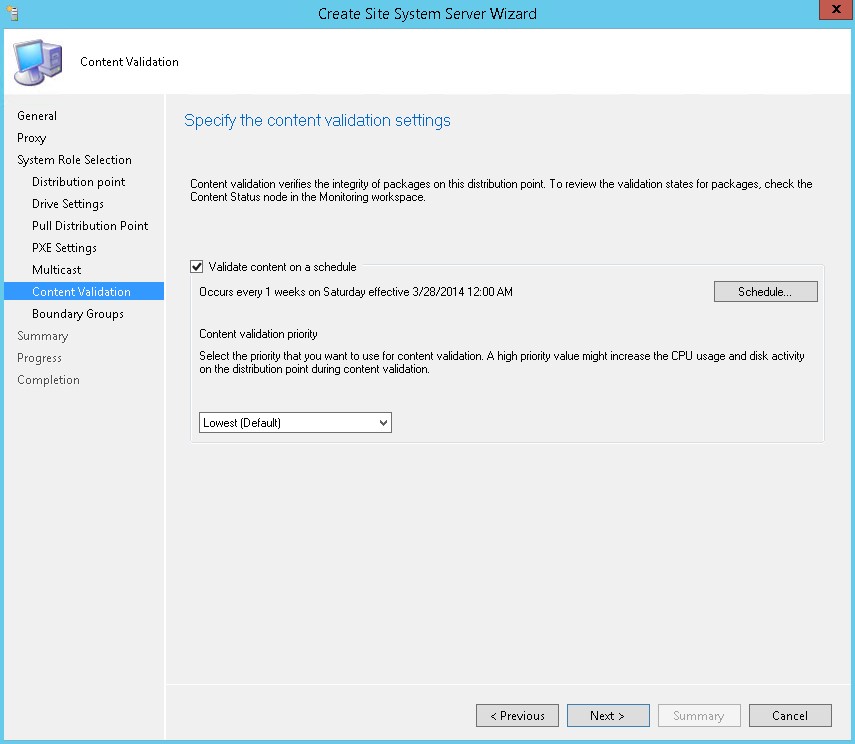
- Enable content validation to occur where it fits your environment, click Next
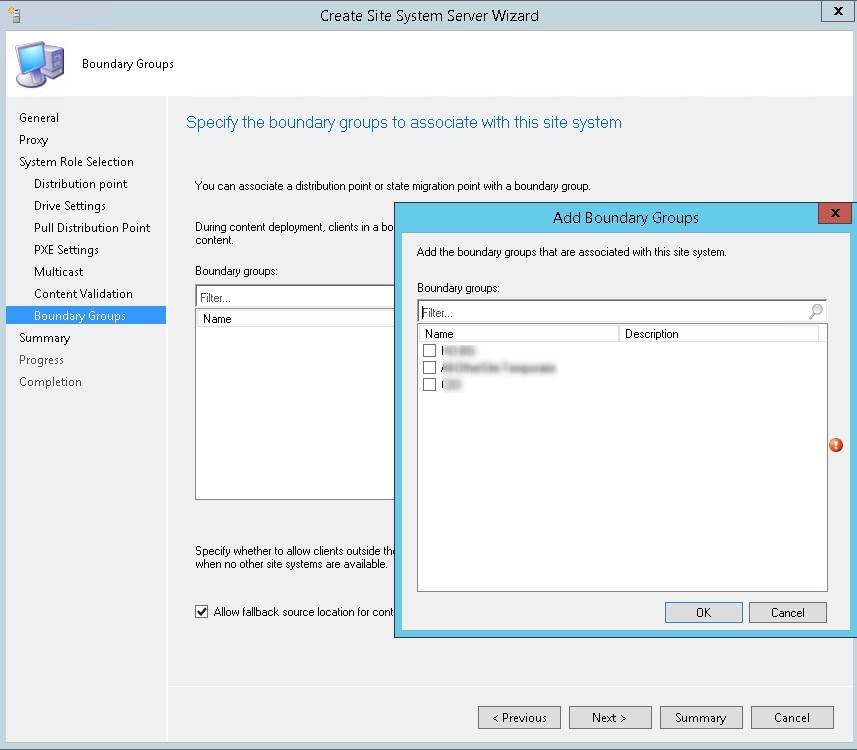
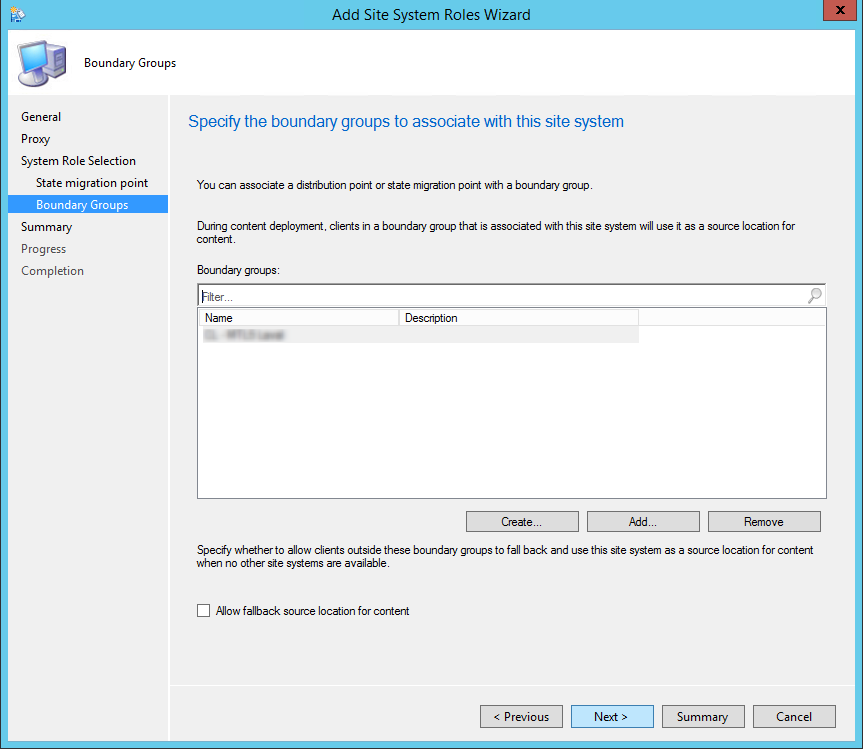
- Add the boundary group that needs to be associated with this DP and Uncheck the Allow fallback source location for content, click Next
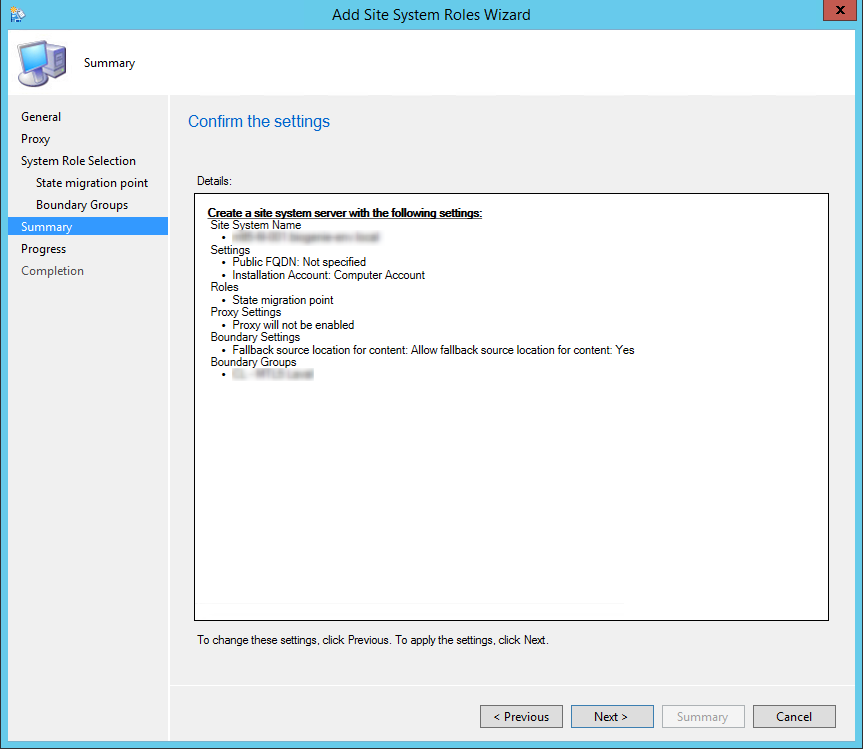
- Review the summary page and complete the installation, click Next
WARNING Your remote server may reboot if there’s a missing requirement
At this point, the major part of installation a distribution point server is completed.
Verification
Logs
You can track the installation progress in 2 logs:
- Distmgr.log on the site server
- Smsdpprov.log on the distribution point. (InstallationDriveSMS_DP$SMSLogs)
Windows Explorer
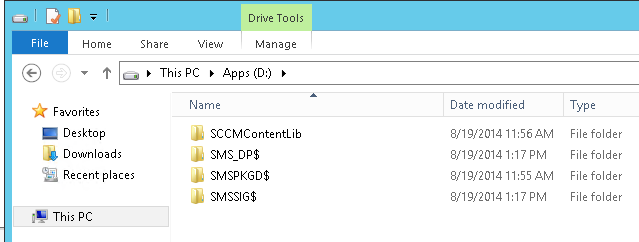
At this point, you will the SCCM file structure created on the site server.
Console
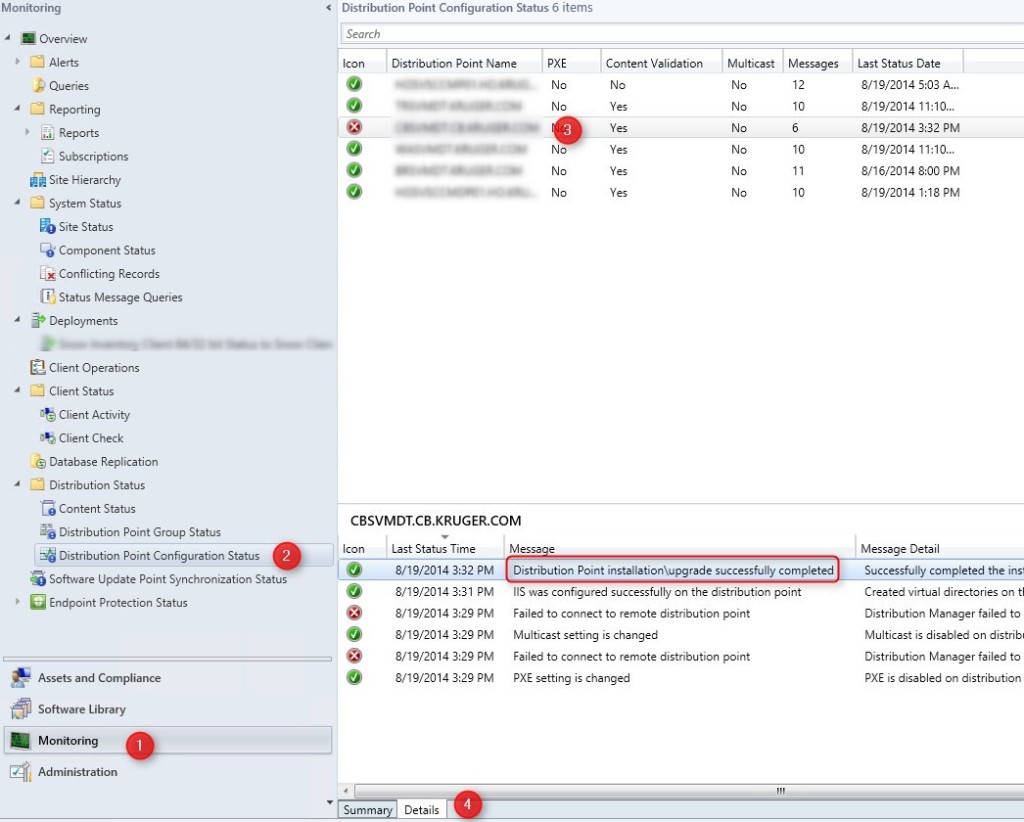
You can also track the installation progress in the SCCM console under Monitoring / Distribution Status / Distribution Point Configuration Status
- Click on your DP
- Click the detail tab on the bottom
- Check for green check mark on all components
Note: Error on the IIS Virtual directory is normal at the start of the process. SCCM is making a check as if IIS is installed at the start of the process even if you tell SCCM to enable you IIS for you. That results in errors but be patient and the installation should succeed anyway
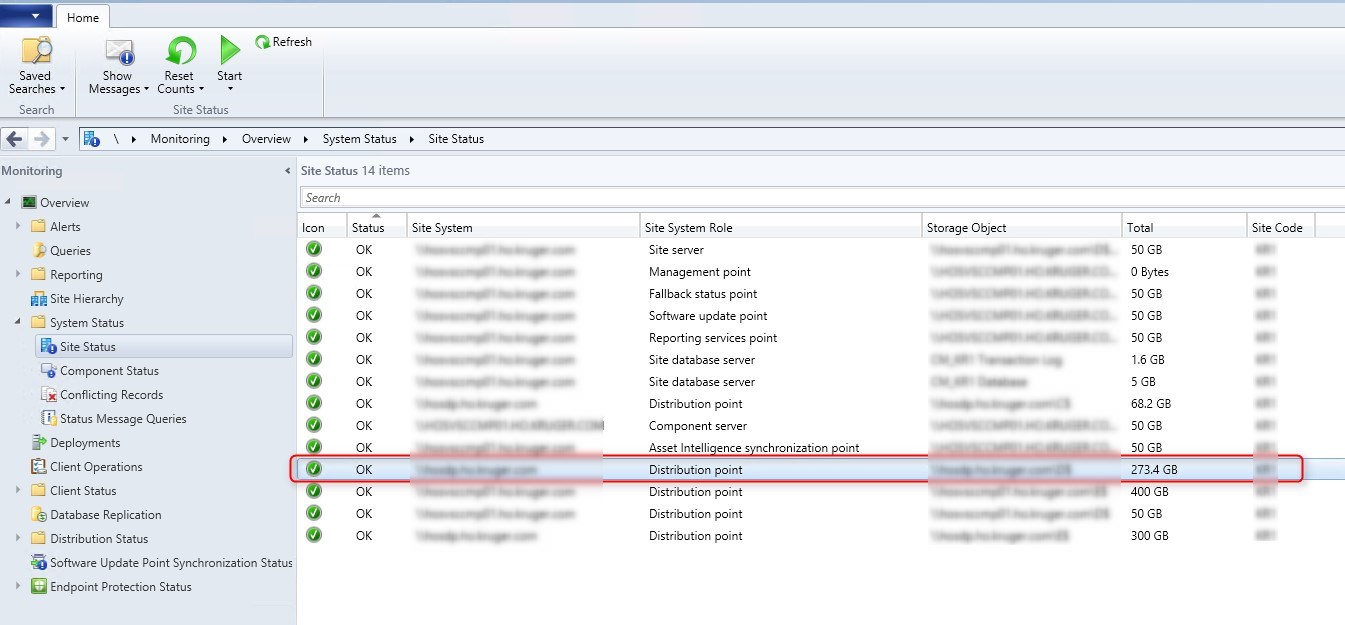
- Verify the status of your new DP in Administration / System Status / Site Status
Replicate content
You can now replicate your content to your newly created DP. Replicate manually all your content or add your DP in an existing DP group.
Replicate a package or Application to your newly created site system
Verify that the content is well replicated in the SCCM Console. (or check distmgr.log)
That’s it ! You’re done creating your DP.
Distribution Point Monitoring
If you have multiple Distribution Points, I suggest you read our post on 8 ways to monitor your distribution points. This post explains in detail the various options to make sure that your DP is healthy.
You can also check our custom report about Distribution Point Monitoring to display all your DP status using a single click.
Part 9 – Endpoint protection point
In this part, we will describe how to install SCCM Endpoint Protection Point (EPP).
Role Description
The Endpoint Protection Point provides the default settings for all antimalware policies and installs the Endpoint Protection client on the Site System server to provide a data source from which the SCCM database resolves malware IDs to names. When you install this Site System Role, you must accept the license terms for System Center 2012 R2 Endpoint Protection.
This is not a mandatory Site System but you need to install a EPP if you’re planning to use SCCM as your anti-virus management solution (using Endpoint Protection).
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
This Site System is a hierarchy-wide option. SCCM supports a single instance of this site system role in a hierarchy and only at the top-level site in the hierarchy. It’s supported to install this role on a Central Administration Site or stand-alone Primary Site.
Requirements
Before installing the EP role, you must have a Software Update Point installed and configured.
EPP Installation
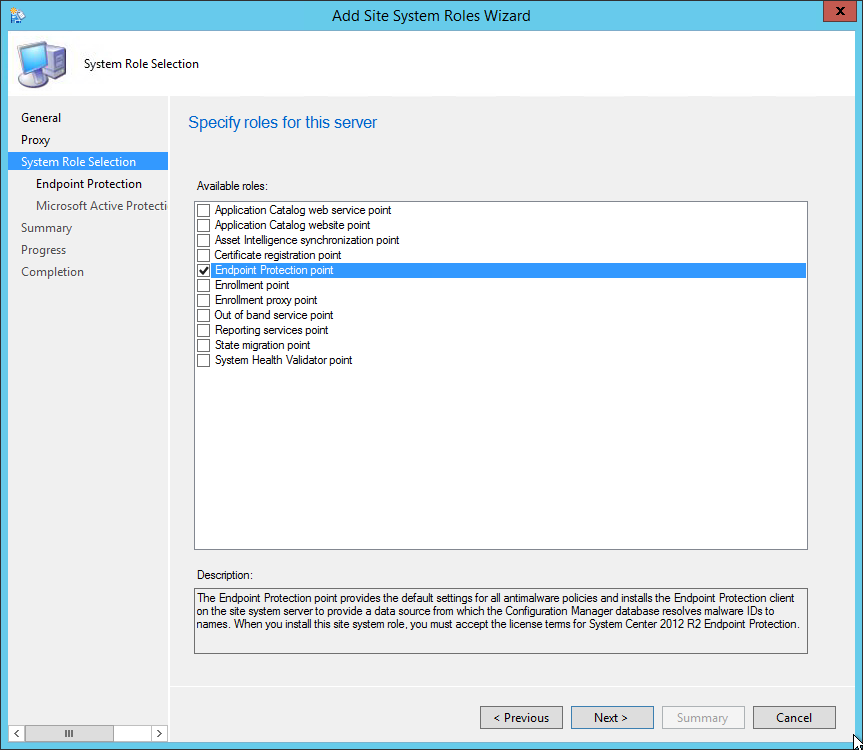
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
- Right-click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
- On the Site System Role tab, select Endpoint Protection Point, click Next
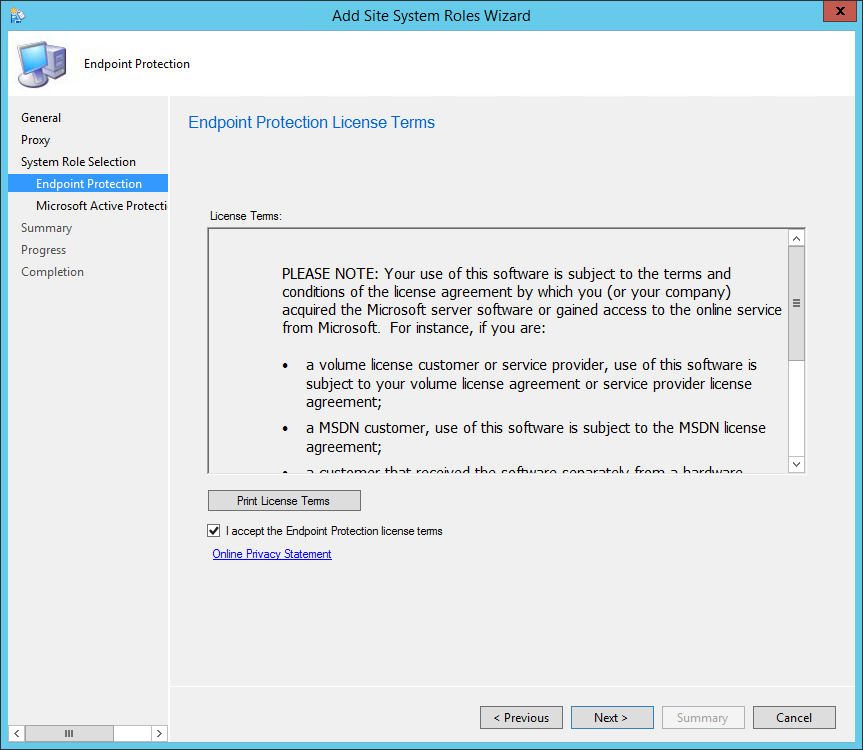
- Accept the License Terms and click Next
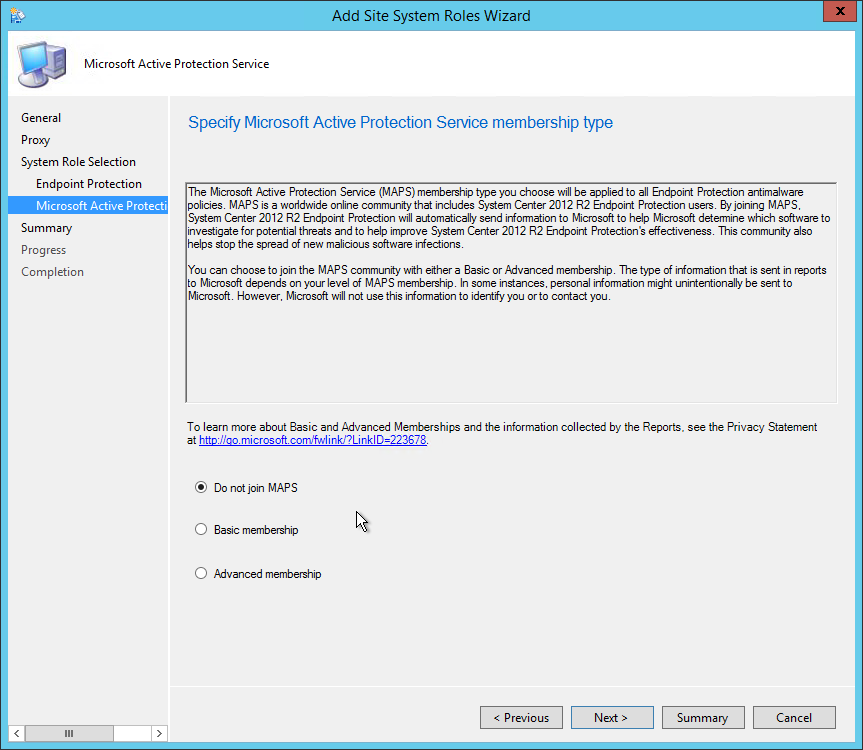
- Select Do not join MAPS, click NEXT
• On the Summary tab, review your settings and click Next
- Wait for the setup to complete and click Close
SUP Configuration
After the installation, you must add Endpoint Protection definition files in your Software Update Point.
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
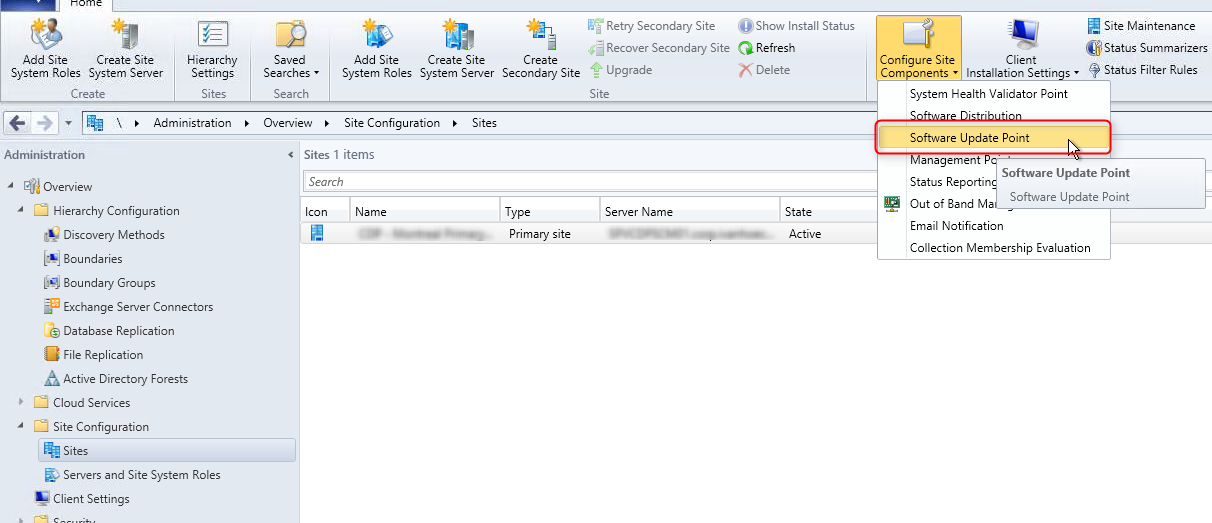
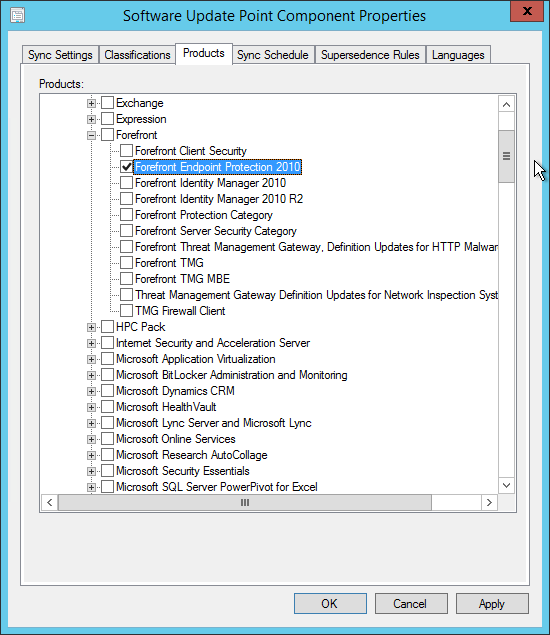
- Click the Configure Site Components button and select Software Update Point
- On the Product tabs, check Forefront Endpoint Protection 2010 and click Ok
Verification
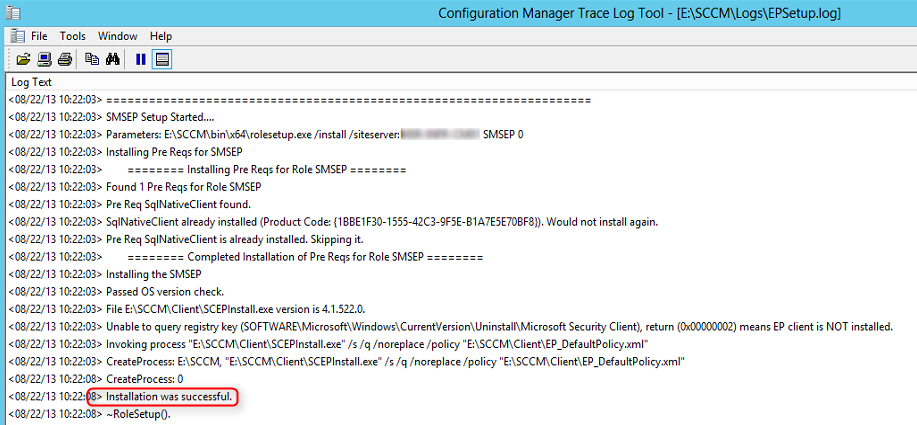
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsEPSetup.log – Detailed EP Installation status
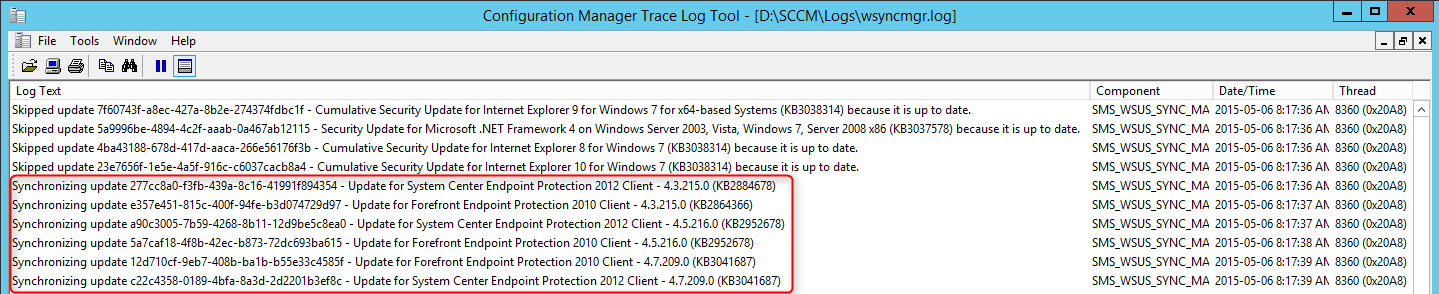
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsWsyncmgr.log – SUP Synchronization status
You are now ready to manage EndPoint Protection using SCCM. We have a complete guide to managing endpoint protection. You can download it from our product page.
Part 10 – Enrollment Point Installation
We will describe how to install SCCM Current Branch Enrollment Point and Enrollment Proxy Point site system roles.
Role Description
The Enrollment Point uses PKI certificates for Configuration Manager to enroll mobile devices, Mac computers and to provision Intel AMT-based computers.
The Enrollment Proxy Point manages Configuration Manager enrollment requests from mobile devices and Mac computers.
This is not a mandatory site system but you need both Enrollment Point and Enrollment Proxy Point if you want to enroll legacy mobile devices, Mac computers and to provision Intel AMT-based computers. Since modern mobile devices are mostly managed using Windows Intune, this post will focus mainly on Mac computer enrollment.
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
The SCCM Enrollment Point and Enrollment Proxy Point are site-wide options. It’s supported to install those roles on a stand-alone or child Primary site. It’s not supported to install it on a Central Administration site or Secondary site.
You must install an SCCM Enrollment Point in the user’s forest so that the user can be authenticated if a user enrolls mobile devices by using SCCM and their Active Directory account is in a forest that is untrusted by the site server’s forest.
When you support mobile devices on the Internet, as a security best practice, install the Enrollment Proxy Point in a perimeter network and the Enrollment Point on the intranet.
Prerequisites
Beginning with System Center 2012 Configuration Manager SP2, the computer that hosts the SCCM Enrollment Point or Enrollment Proxy Point site system role must have a minimum of 5% of the computers available memory free to enable the site system role to process requests. When those site system role are co-located with another site system role that has this same requirement, this memory requirement for the computer does not increase, but remains at a minimum of 5%.
Using Windows Server 2012, the following features must be installed before the role installation:
Enrollment Point
Features:
- .NET Framework 3.5
- .NET Framework 4.5
- HTTP Activation (and automatically selected options)
- ASP.NET 4.5
- Common HTTP Features
- Default Document
- Application Development
- ASP.NET 3.5 (and automatically selected options)
- .NET Extensibility 3.5
- ASP.NET 4.5 (and automatically selected options)
- .NET Extensibility 4.5
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility
- IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility
Enrollment Proxy Point
Features:
- .NET Framework 3.5
- .NET Framework 4.5
- HTTP Activation (and automatically selected options)
- ASP.NET 4.5
IIS Configuration:
- Common HTTP Features
- Default Document
- Static Content
- Application Development
- ASP.NET 3.5 (and automatically selected options)
- ASP.NET 4.5 (and automatically selected options)
- .NET Extensibility 3.5
- .NET Extensibility 4.5
- Security
- Windows Authentication
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility
- IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility
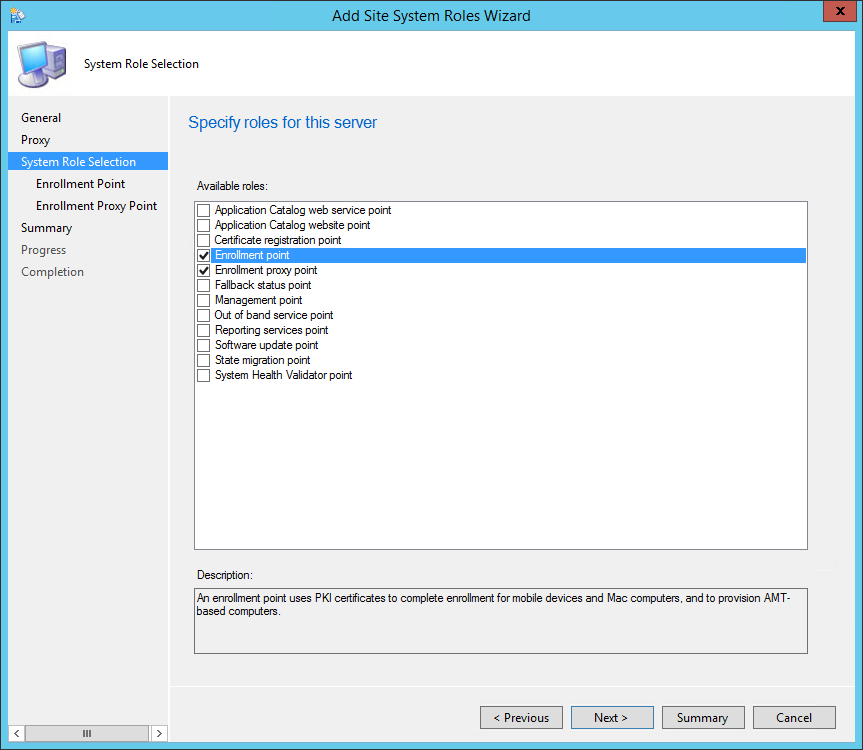
SCCM Enrollment Point Installation
For this post we will be installing both roles on a stand-alone Primary site using HTTPS connections. If you split the roles between different machine, do the installation section twice, once for the first site system (selecting Enrollment Point during role selection)and a second time on the other site system (selecting Enrollment Proxy Point during role selection).
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
- Right click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
- On the Site System Role tab, select Enrollment Point and Enrollment Proxy Point, click Next
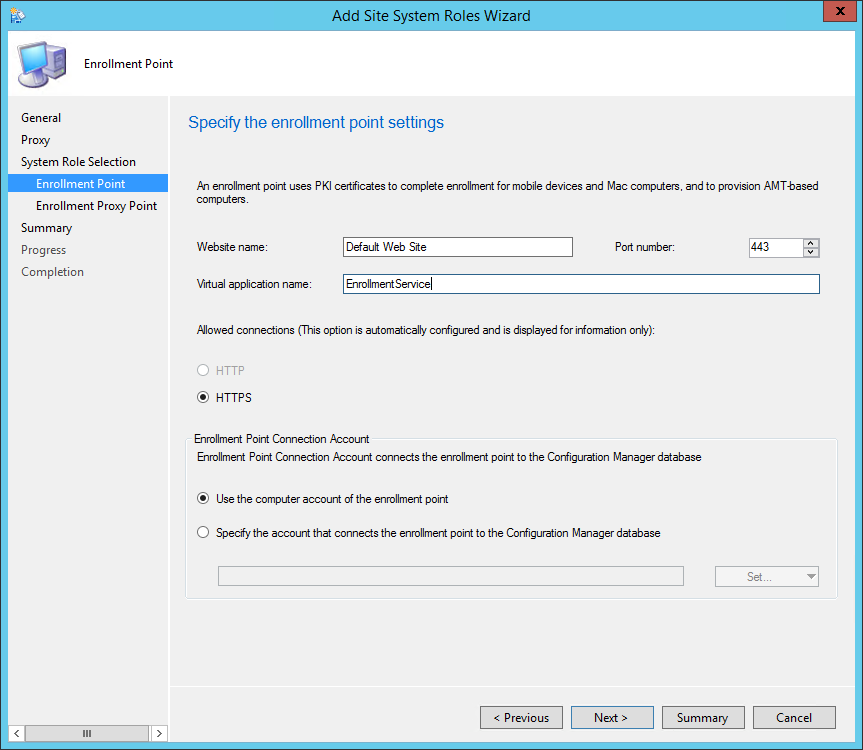
- On the Enrollment Point tab
- In the IIS Website and Virtualapplication name fields,leave both to the default values
- This is the names that you’ll see in IIS after the installation
- Enter the port number you want to use. The HTTPS setting is automatically selected and requires a PKI certificate on the server for server authentication to the Enrollment Proxy Point and for encryption of data over SSL. For more information about the certificate requirements, see PKI Certificate Requirements for Configuration Manager.
- In the IIS Website and Virtualapplication name fields,leave both to the default values
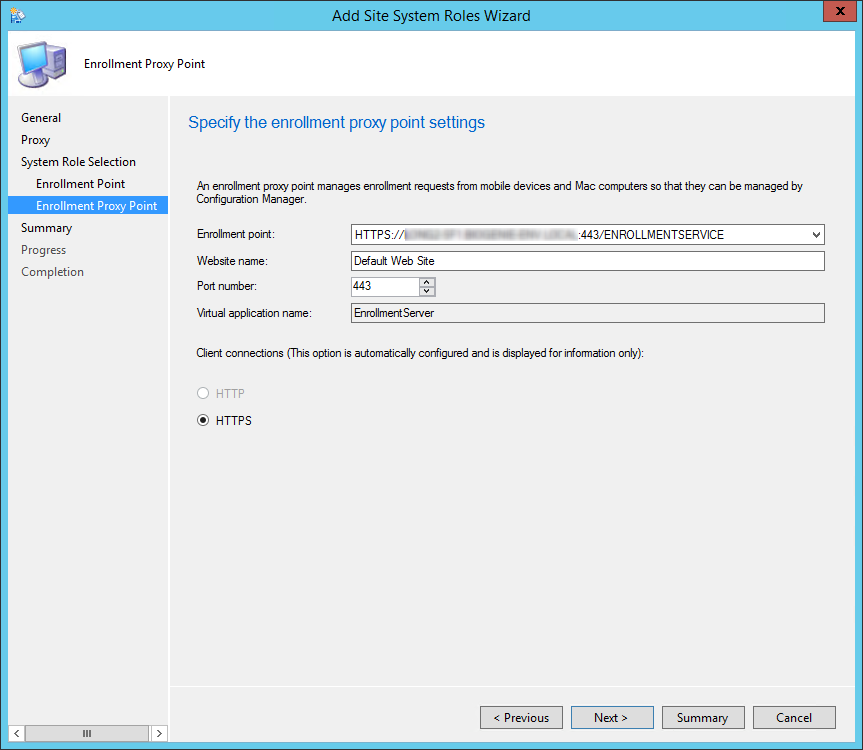
- On the Enrollment Proxy Point tab,
- The Enrollment point will be populated by default and can’t be changed
- Keep the Website name to it’s default value
- Enter the port and protocol that you want to use
- The Virtual application name can’t be changed. This will be used for client installation (https://servername/EnrollmentServer)
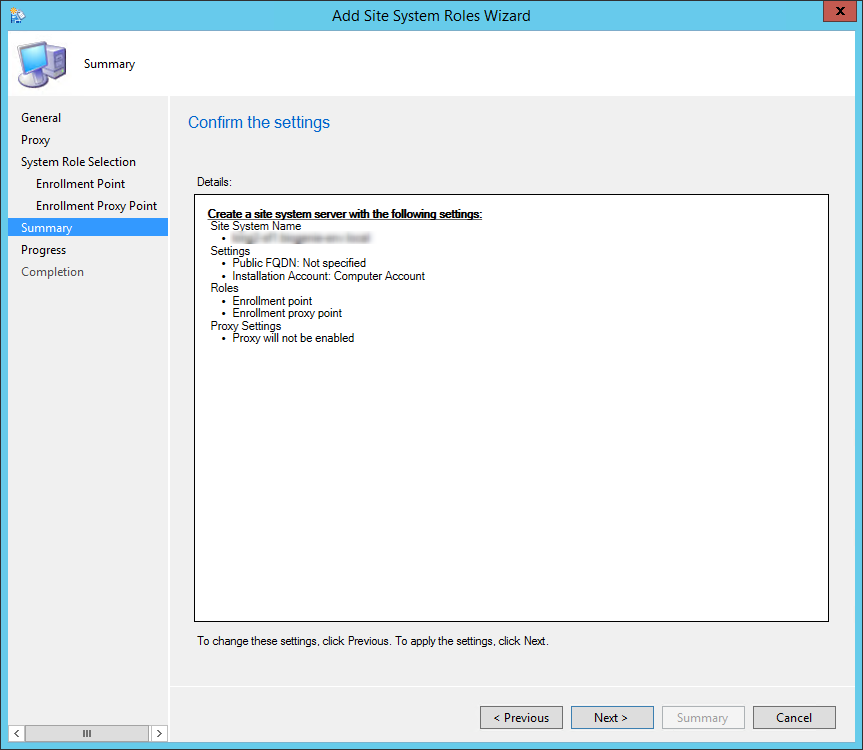
- On the Summary tab, review your settings, click Next and complete the wizard
Verification and Logs files
Logs
You can verify the role installation in the following logs:
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsenrollsrvMSI.log and enrollmentservice.log – Records details of about the Enrollment Point installation
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsenrollwebMSI.log – Records details of about the Enrollment Proxy Point installation
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsenrollmentweb.log – Records communication between mobile devices and the Enrollment Proxy Point
That’s it, you’ve installed your SCCM Enrollment Point, follow this Technet Guide if you want to proceed to next steps for Mac computers enrollment
Part 12 – Fallback Status Point
We will describe how to install SCCM Fallback Status Point (FSP).
Role Description
The FSP helps monitor client installation and identify unmanaged clients that cannot communicate with their management point.
This is not a mandatory Site System but we recommend to install a FSP for better client management and monitoring. This is the Site System that receive State Message related to client installation, client site assignment, and clients unable to communicate with their HTTPS Management Point.
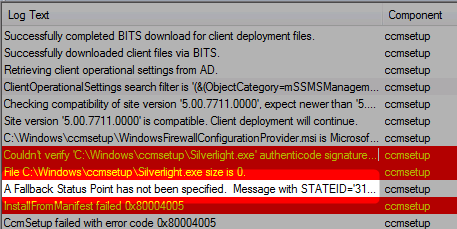
If the FSP is not configured properly you’ll end up having A fallback status point has not been specified errors in your logs.
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
This Site System is a hierarchy-wide option. It’s supported to install this role on a child Primary Site or stand-alone Primary Site but it’s not supported on a Central Administration site nor Secondary Site.
FSP Installation
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
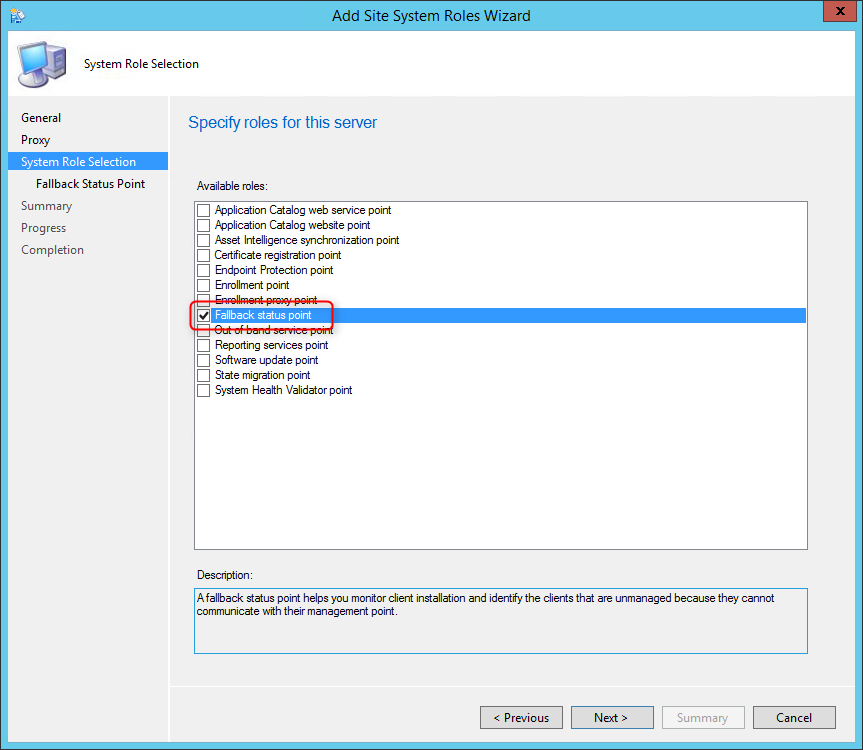
- Right click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
- On the Site System Role tab, select Fallback Status Point, click Next
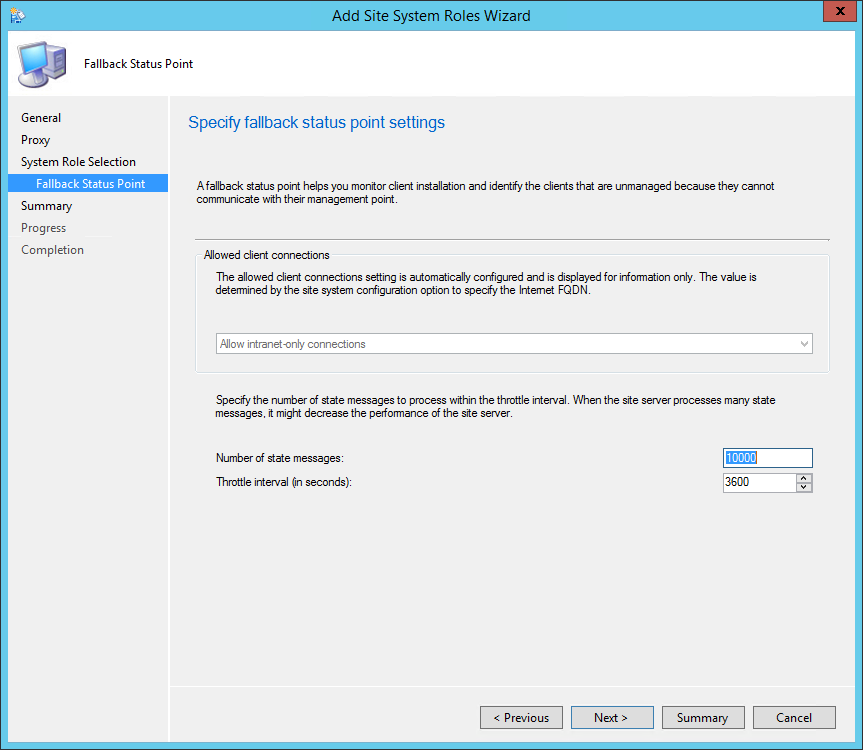
- On the Fallback Status Point tab, specify the number of state messages to process. We recommend to leave the default value, click Next
- On the Summary tab, review your setting and click Next
- Wait for the setup to complete and close the wizard
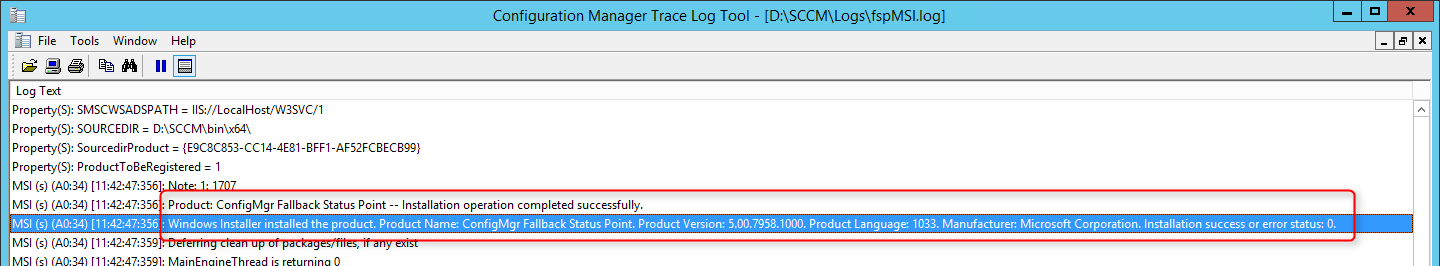
Verification and Logs files
- Smsfspsetup.log – DetailedFSP Installation status
- Fspmgr.log – Verify whether clients are successfully sending state messages to the FSP
You can also check if reports that depend on the FSP are populated with data. See the full list of reports that rely on the FSP here.
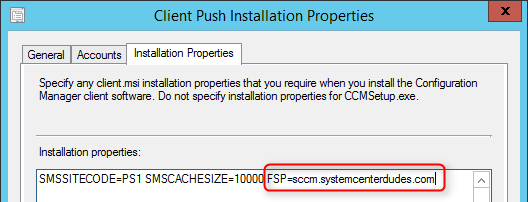
Configure clients
Use the FSP client properties to point your clients to your newly created FSP
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Site
- Click the Client Installation Setting icon on the ribbon
- Select Client Push Installation
- On the Installation Properties tab
- Enter your server FQDN in the FSP properties
Part 13 – Management Point Installation
We will describe how to install an SCCM Management Point (MP).
Role Description
Every SCCM hierarchy must have a Management Point to enable client communication. The Management Point is the primary point of contact between Configuration Manager clients and the site server. Management Points can provide clients with installation prerequisites, configuration details, advertisements and software distribution package source file locations. Additionally, Management Points receive inventory data, software metering information and state messages from clients.
Multiple Management Points are used for load-balancing traffic and for clients to continue receiving their policy after Management Point failure. Read about SCCM High-Availability options in this Technet article.
Prior to SCCM 2012 R2 SP1, it was not possible to assign client directly to a specific Management Point. It’s now possible using the new Preferred Management Point feature. Read about how clients choose their Management Point in this Technet article.
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
The Management Point is a site-wide option. It’s supported to install this role on a stand-alone Primary site, child Primary site or Seconday site. It’s not supported to install a Management Point on a Central Administration site.
Each primary site can support up to 10 Management Points.
By default, when you install a Secondary site, a Management Point is installed on the Secondary site server. Secondary sites do not support more than one Management Point and this Management Point cannot support mobile devices that are enrolled by Configuration Manager.
See the full Supported Configuration in the following Technet article.
Prerequisites
On Windows 2012, the following features must be installed before the Management Point Installation:
Features:
- .NET Framework 4.5
- BITS Server Extensions or Background Intelligent Transfer Services (BITS)
IIS Configuration:
- Application Development
- ISAPI Extensions
- Security
- Windows Authentication
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility
- IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility
- IIS 6 WMI Compatibility
SCCM Management Point Installation
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
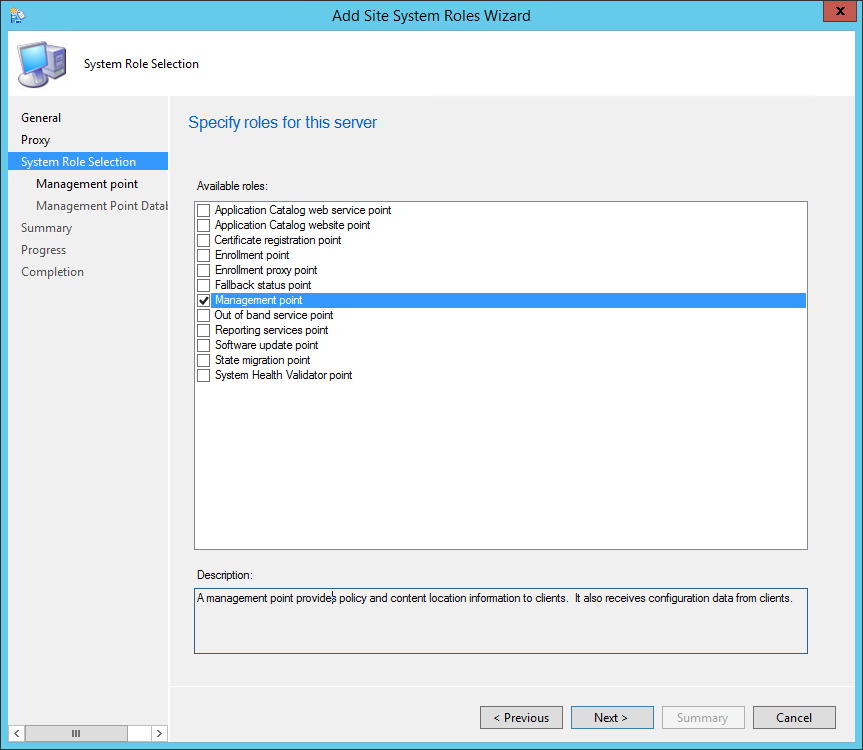
- Right click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
- On the Site System Role tab, select Management Point, click Next
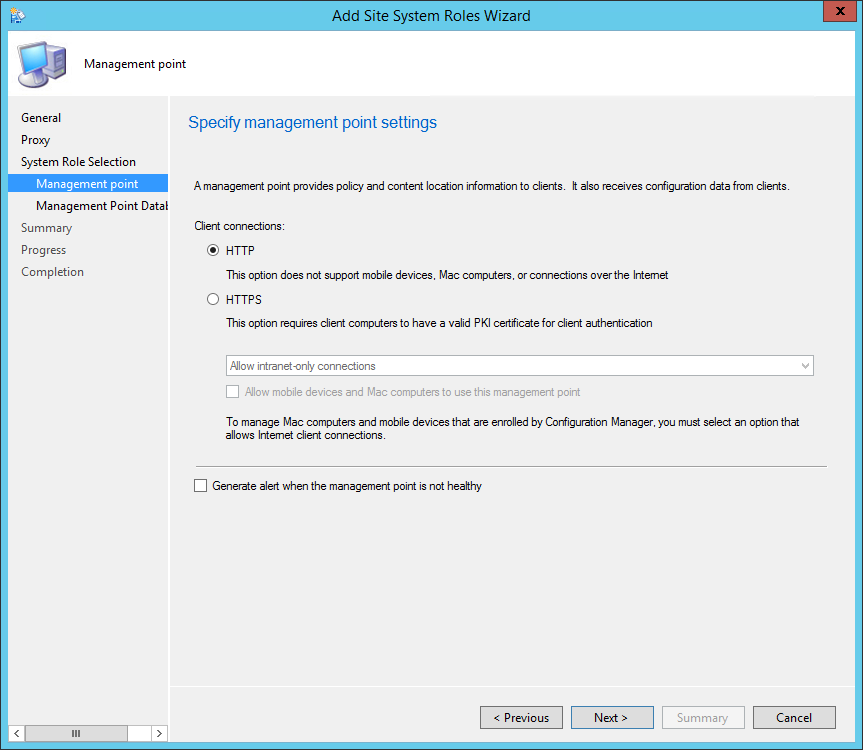
- On the Management Point tab
- Select the desired client connections methods. HTTPS required to have a valid PKI certificate for client authentication
- Click Next
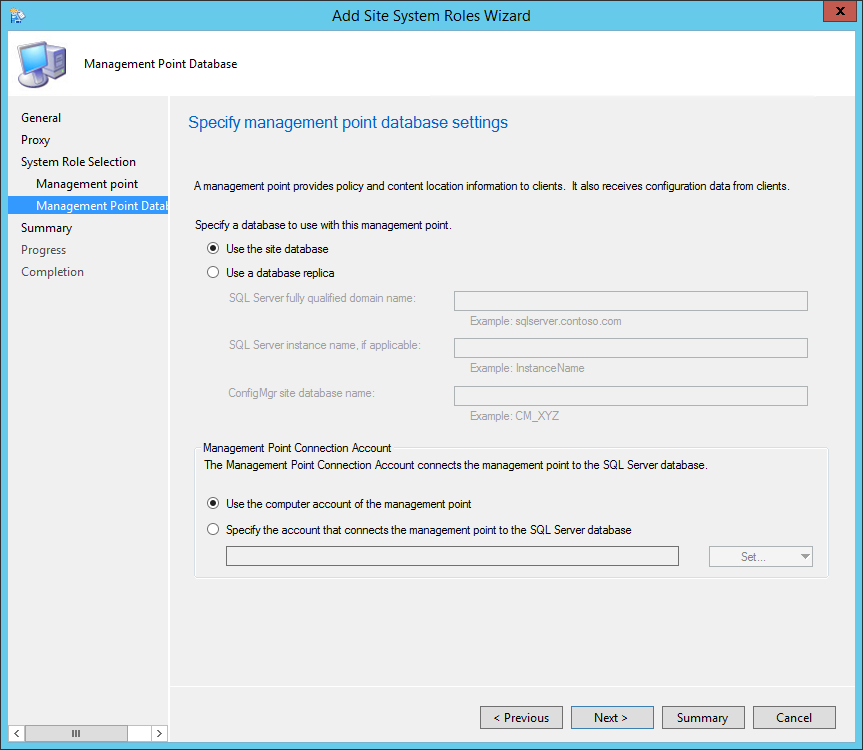
- On the Management Point Database tab, specify if you want to use the site database or a database replica. Read about database replica here
- Specify if you want to use the computer account of the Management Point to connect to the database or a specified account
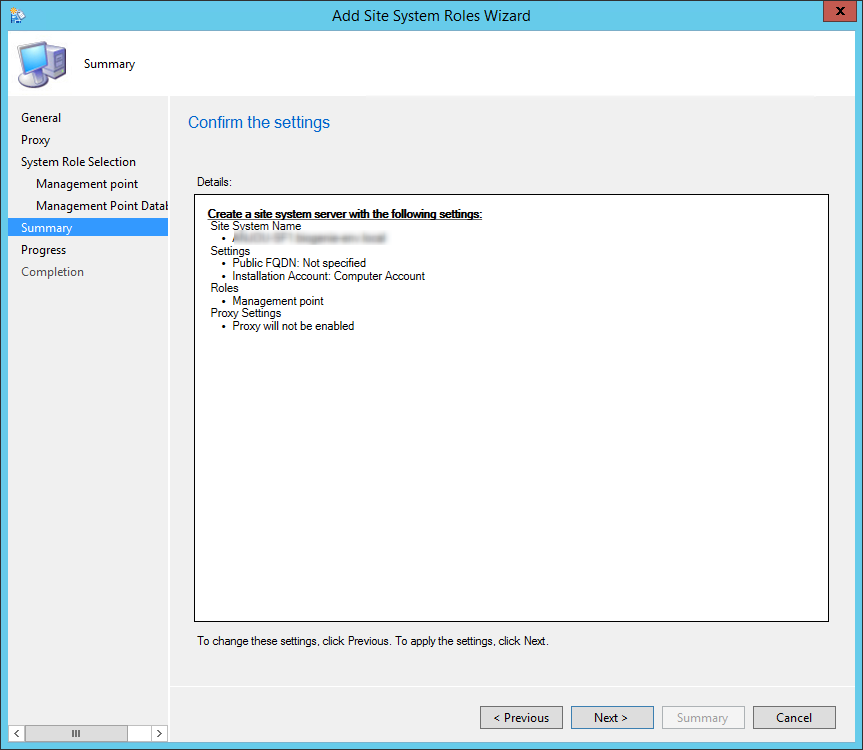
- On the Summary tab, review your settings, click Next and complete the wizard
Verification and Logs files
You can verify the installation in the following logs:
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsmpMSI.log – Records details of about the management point installation
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsMPSetup.log.log – Records the management point installation wrapper process
Part 14 – Reporting Point Installation
We will describe how to install a SCCM Current Branch reporting services point.
This role can be installed on a remote machine, the process is the same but the location of the logs is different.
Requirements
Before you can install the reporting services point role you must configure SQL correctly.
We’ll be using SQL 2012 on this post. We are assuming that SQL is already installed and that your SCCM site is up and healthy.
During the initial SQL installation, you must select Reporting Services.
If you have installed SQL Server, but have not installed Reporting Services follow the following steps. If Reporting Services is already installed, skip to the “Configure Reporting Services” section.
- Launch the SQL Server 2012 installation from the media.
- Click the Installation link on the left to view the Installation options.
- Click the top link, New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation.
- Follow the SQL Server Setup wizard until you get to the Installation Type screen.
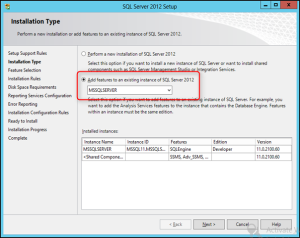
- Select Add features to an existing instance of SQL Server 2012.
- Click Next to move to the Feature Selection page.
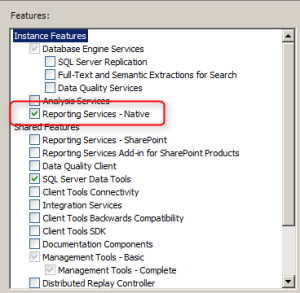
- Select Reporting Services – Native
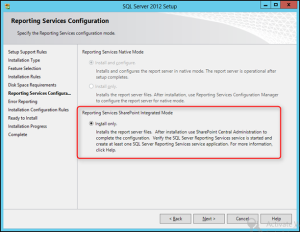
- At the Reporting Services Configuration page
- Select Install Only
Continue through the wizard and reboot the computer at the end of the installation if instructed to do so.
Configure Reporting Services
Before configuring the reporting point, some configuration needs to be made on the SQL side. The virtual instance needs to be created for SCCM to connect and store its reports.
If you installed Reporting Services during the installation of the SQL Server instance, SSRS will be configured automatically for you. If you install SSRS later, then you will have to go back and configure it as a subsequent step.
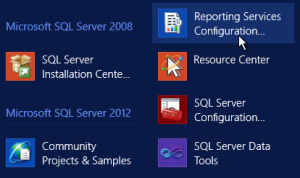
To configure, Open Reporting Services Configuration Manager
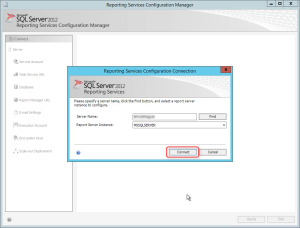
- Click Start > All Programs > Microsoft SQL Server > Configuration Tools > Reporting Services Configuration Manager
- Click Connect to connect to the SQL instance
- On the left-hand side of the Reporting Services Configuration Manager, click Database.
- Click the Change Database button
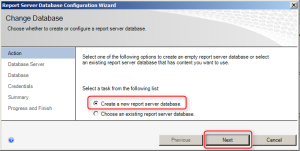
- Select Create a new report server database and click Next
This wizard creates two databases: ReportServer, used to store report definitions and security, and ReportServerTempDB which is used as scratch space when preparing reports.
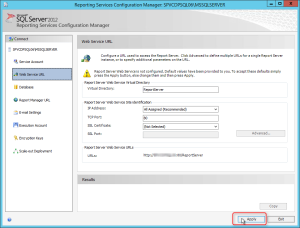
- Click the Web Service URL tab
- Click Apply
This step sets up the SSRS web service. The web service is the program that runs in the background that communicates between the web page, which you will set up next, and the databases.
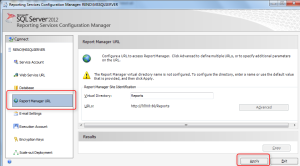
- Select the Report Manager URL
- Accept the default settings and click Apply.
If the Apply button was already grayed out, this means the SSRS was already configured. This step sets up the Report Manager web site where you will publish reports
Exit Reporting Service Configuration Manager.
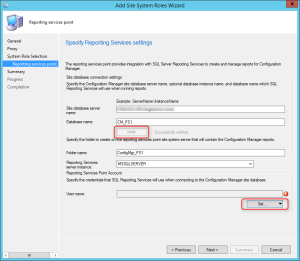
Add Reporting Services Point role in SCCM
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration/Site/Configuration/Servers and Site System Roles
- Right-click on your Site Server and click Add system Roles
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, Click Next
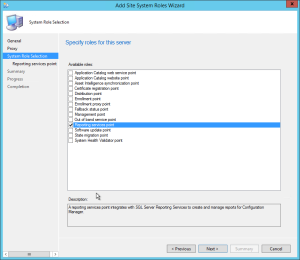
- On the Site System Role, select Reporting Services Point, Click Next
- On Rethe porting Services setting tab
- Click Verify
- At the bottom, Add an account to use for the reporting point. This account needs to have access to the SCCM DB
- Click Next
- Wait for the process to complete and close the wizard
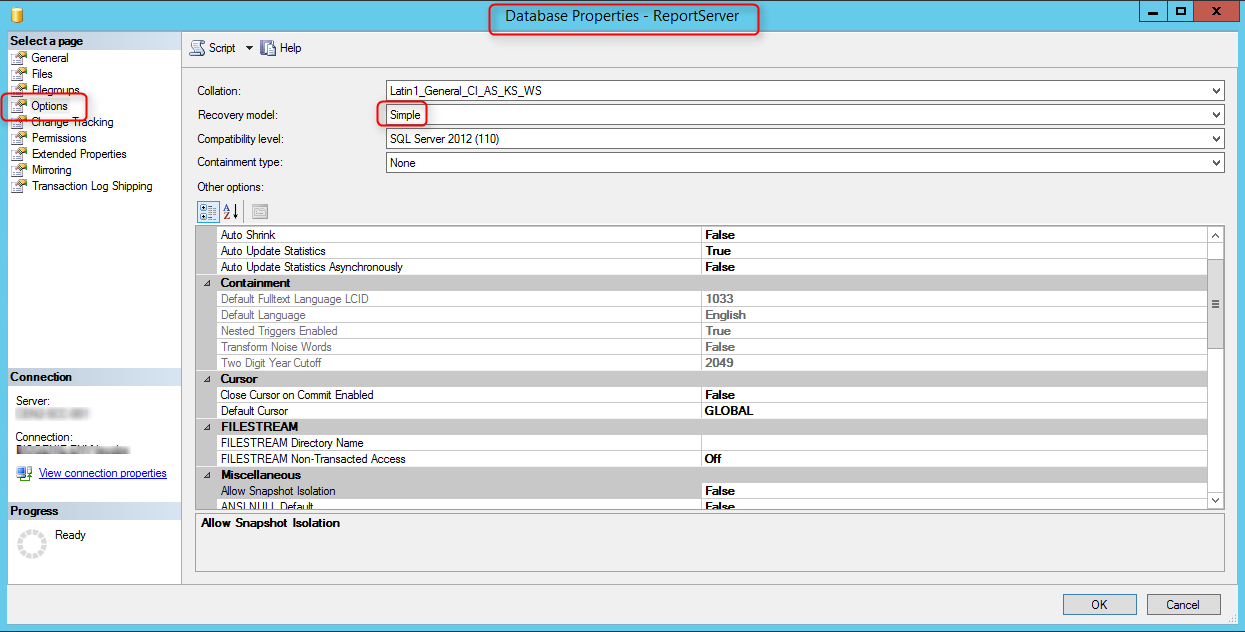
Recovery Model
Using the simple recovery model improves performance and saves your server hard drive and possibly a large transaction log file.
To change the Recovery Model of the ReportingDB to Simple
- Open SQL Management Studio
- Right-click on the ReportServer database and select Properties
- Go to the Options page
- Under Recovery model select Simple
- Click OK
Verification
Logs
Check for the following logs for reporting point installation status. Both logs are under the SCCM logs file locations.
- Srspsetup.log
- Srsrpmsi.log
If your reporting point is installed on a remote server look for the logs in :
Drive:SMSLogs
Console
Open Monitor/Reporting/Reports node. Verify that your reports are listed
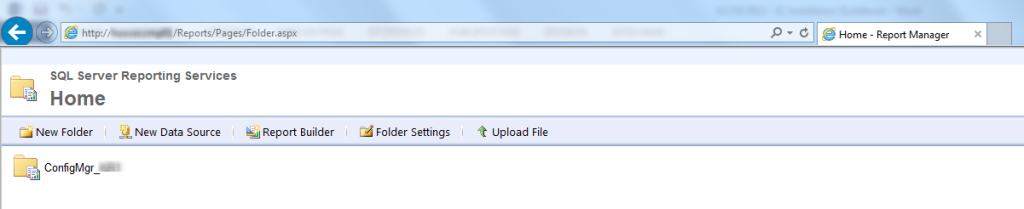
Web Browser
Open Internet Explorer, navigate to http://yourservername/Reports
If everything went well, you’ll have a folder Config_SiteCode containing your reports
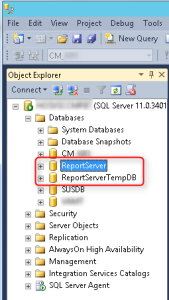
SQL
If you check your SQL instance, you’ll see the 2 new database which were created by the installation.
- Open SQL Management Studio
- Locate ReportServer and ReportServerTempDB
Happy reporting! 🙂
Part 15 – Software Update Point Installation
We will describe how to install SCCM Current Branch Software Update Point (SUP).
Role Description
The SUP integrates with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) to provide software updates to Configuration Manager clients.
This is not a mandatory Site System but your need to install a SUP if you’re planning to use SCCM as your patch management platform.
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
This Site System is a site-wide option. It’s supported to install this role on a Central Administration Site, child Primary Site, stand-alone Primary Site and Secondary Site.
When your hierarchy contains a Central Administration Site, install a Software Update Point and synchronizes with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) before you install a SUP at any child’s Primary Site.
When you install a Software Update Point at a child Primary Site, configure it to synchronize with the SUP at the Central Administration Site.
Consider installing a SUP in Secondary Site when data transfer across the network is slow.
Remote WSUS Warning
The WSUS Administration Console is required on the Configuration Manager site server when the software update point is on a remote site system server and WSUS is not already installed on the site server. The WSUS version on the site server must be the same as the WSUS version running on the software update points.
When using WSUS 3.0 (on server 2008, it was possible to install the console only). This has changed with 2012 and 2016. One way to do it is to add the Windows Software Update Services role and deselecting Database and WID Database. The problem is that will still cause some trouble with the post-install task.
The recommended way to do it :
- Start PowerShell Console (as Administrator)
- Run : Install-WindowsFeature -Name UpdateServices-Ui
This will install the console only and not run a post-install task.
Perform the following on the server that will host the SUP role.
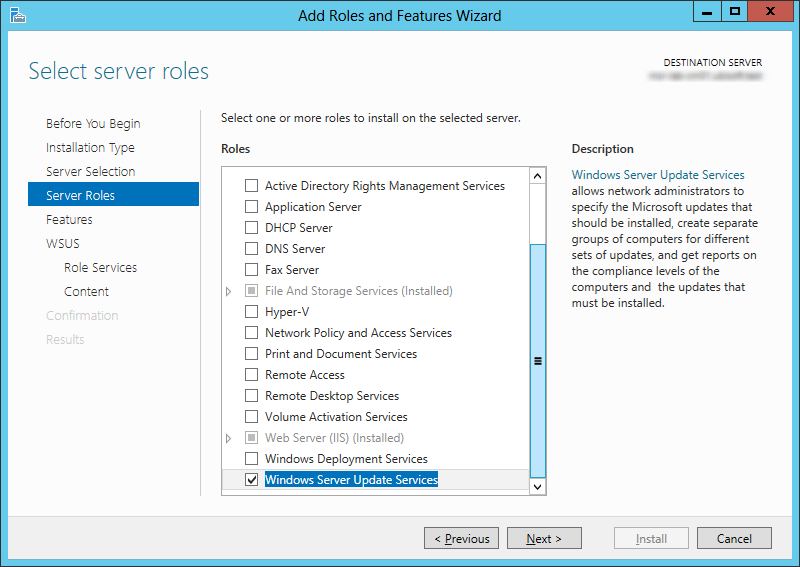
- Open Server Manager / Add Roles and Features
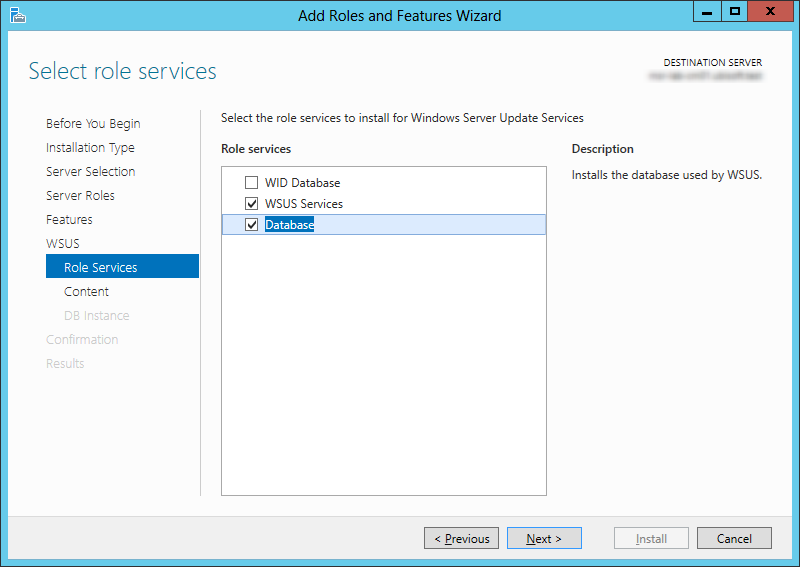
- Select the Windows Server Update Services Role, click Next
- Select WSUS Services and Database, click Next
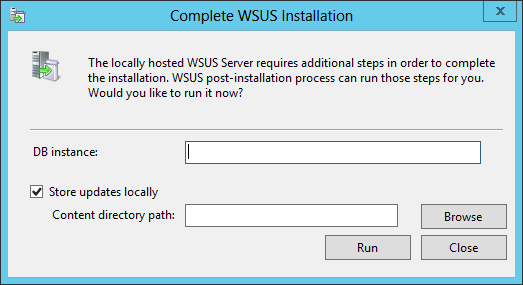
- Launch Windows Server Update Services from the Start Menu. You will be prompt with the following window :
- On the DB instance, enter your server name
- On Content directory path, use a drive with enough drive space. This is where your WSUS will store updates
- When the WSUS Configuration Wizard starts, click Cancel
- Open SQL Management Studio
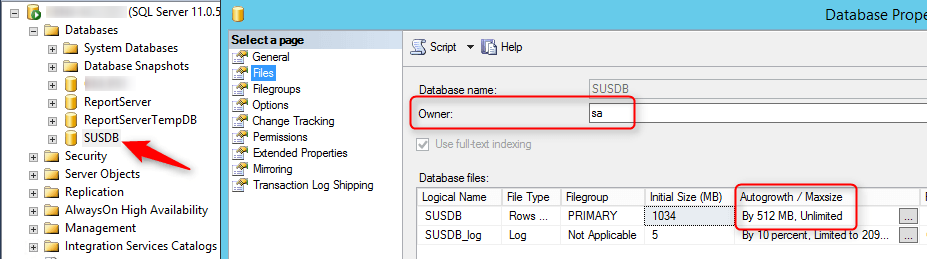
- Under Databases, Right-click SUSDB, select Properties and click Files
- Change Owner to SA
- Change the Autogrowth value to 512MB, click Ok and close SQL MS
Software Update Point Installation
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
- Right-click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
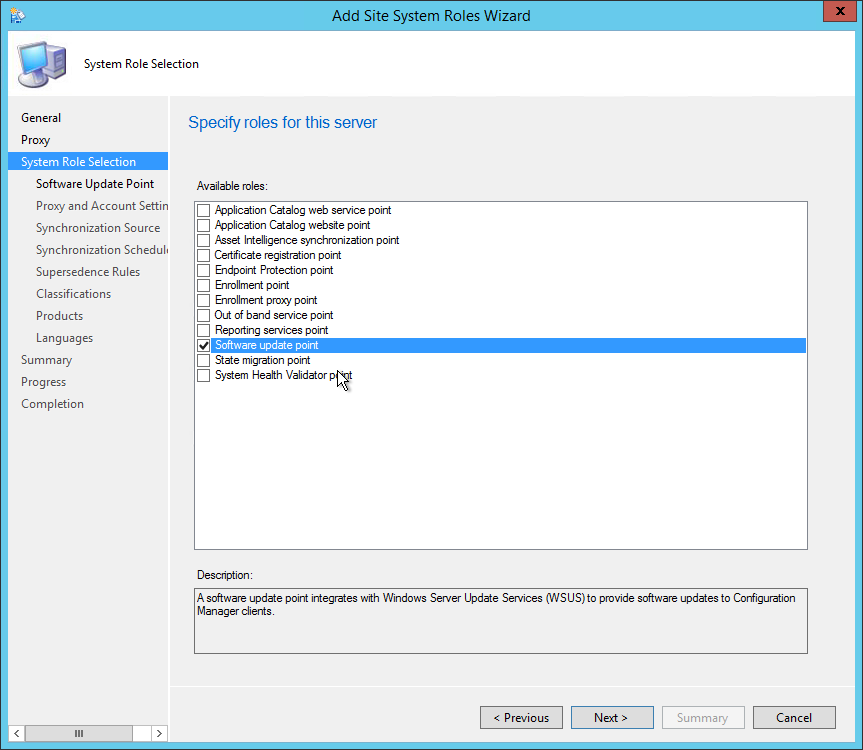
- On the Site System Role tab, select Software Update Point, click Next
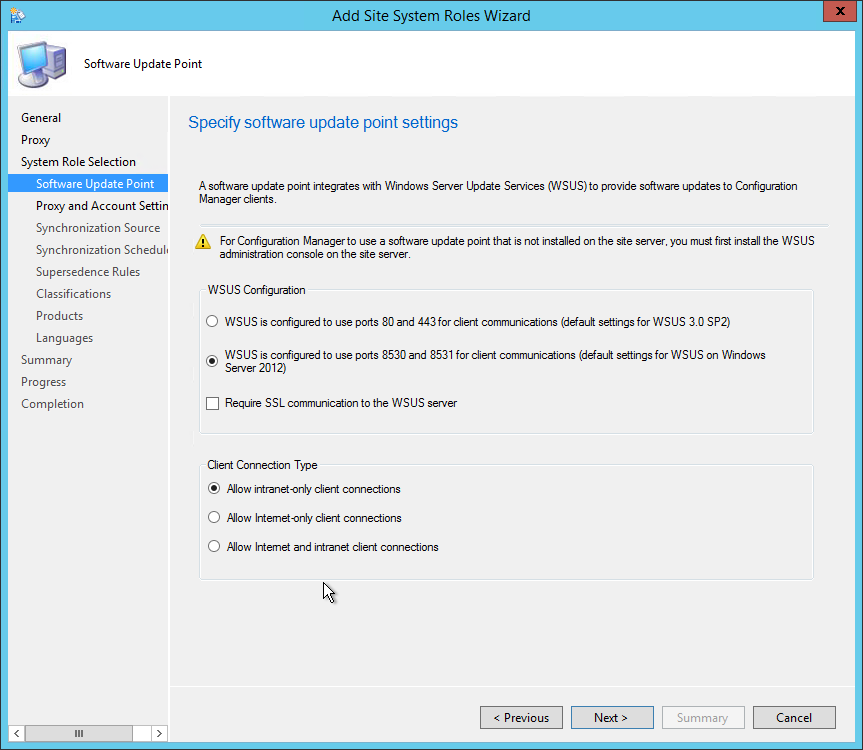
- On the Software Update Point tab, select WSUS is configured to use ports 8530 and 8531, click Next
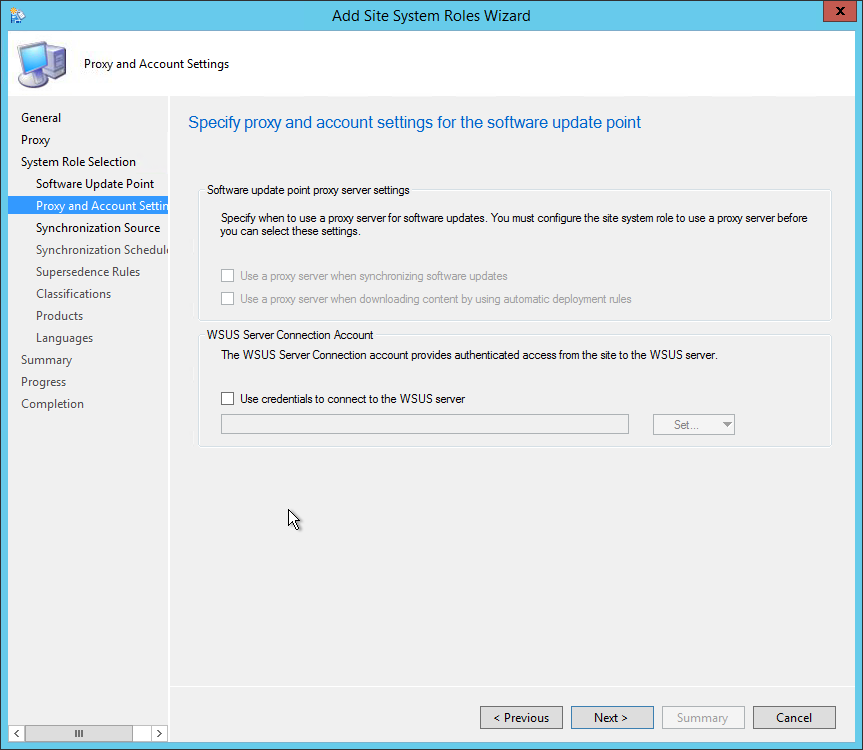
- On the Proxy and Account Settings tab, specify your credentials if necessary, click Next
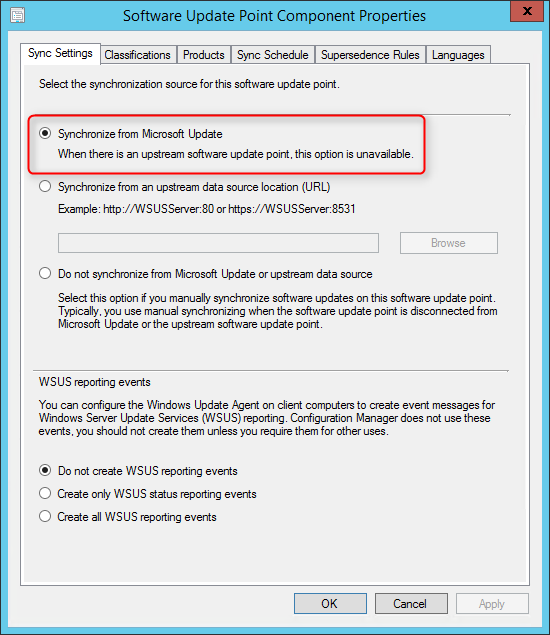
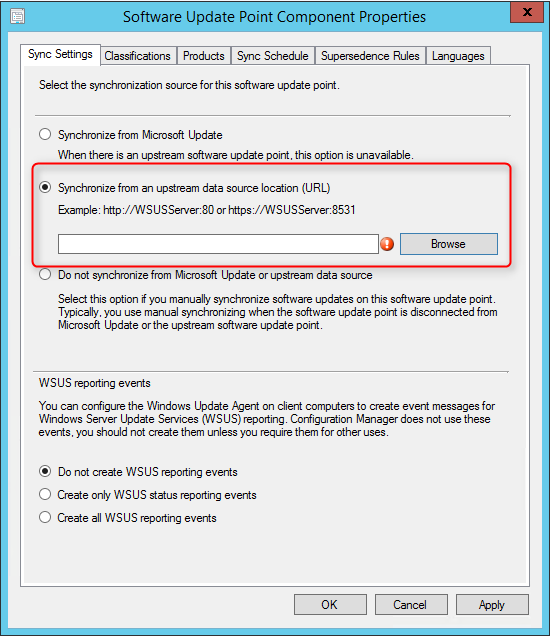
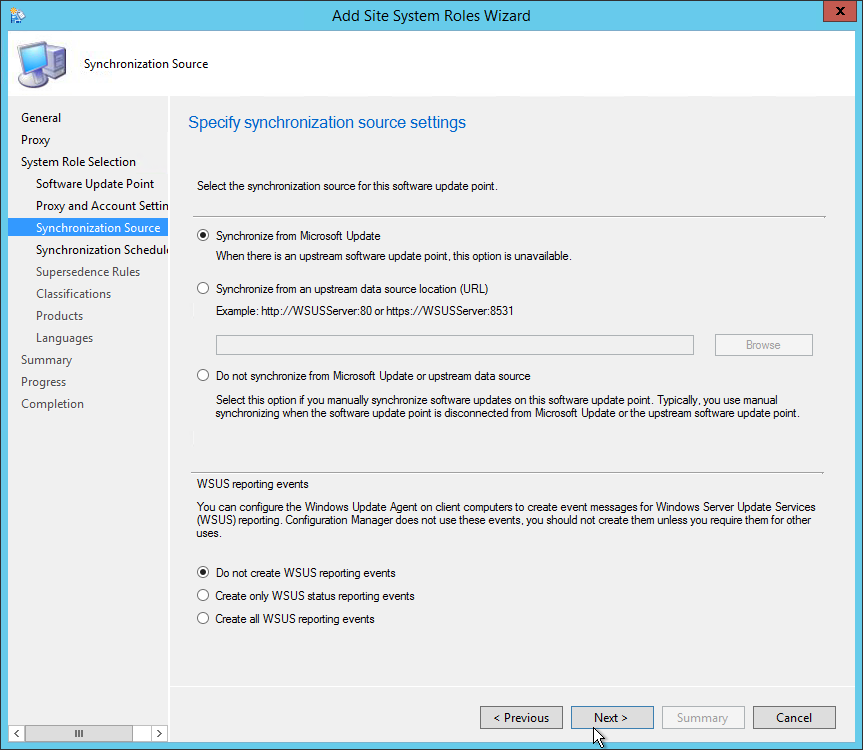
- On the Synchronization Source tab, specify if you want to synchronize from Microsoft Update or an upstream source. Refer to the Site System Placement section if you’re unsure. For a stand-alone Primary Site, select Synchronize from Microsoft Update, click Next
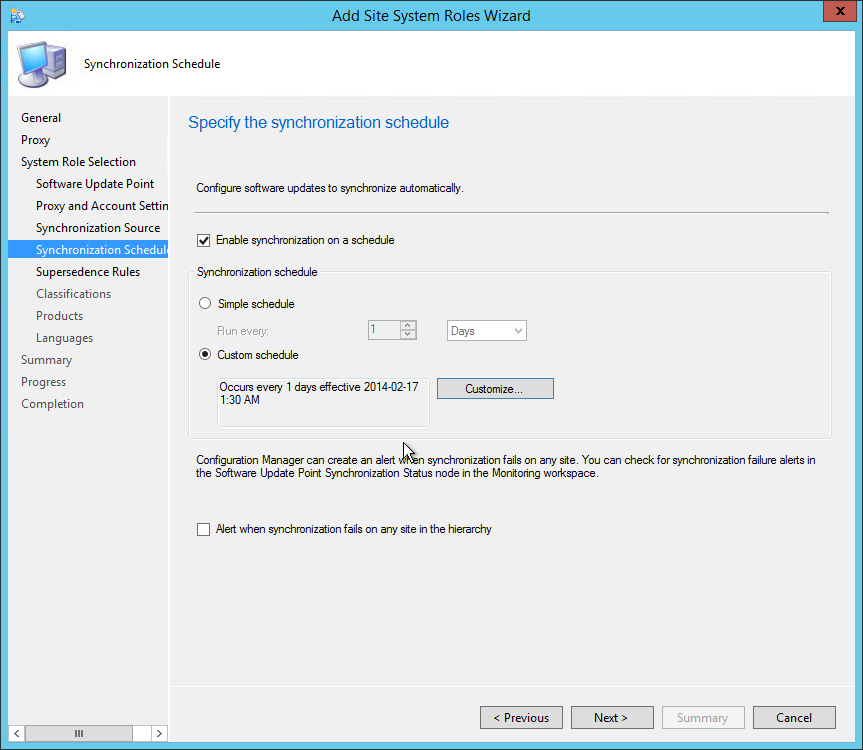
- On the Synchronization Schedule tab, check the Enable synchronization on a schedule checkbox and select your desired schedule. 1 day is usually enough but it can be lowered if you’re synchronizing Endpoint Protection definition files, click Next
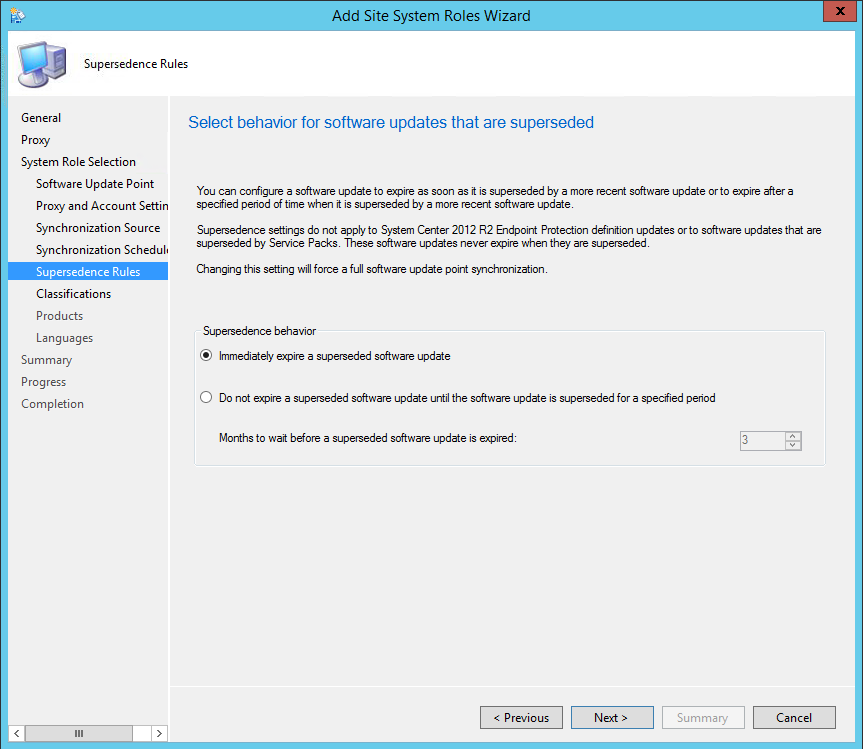
- On the Supersedence Rules tab, select Immediately expire a superseded software update, click Next
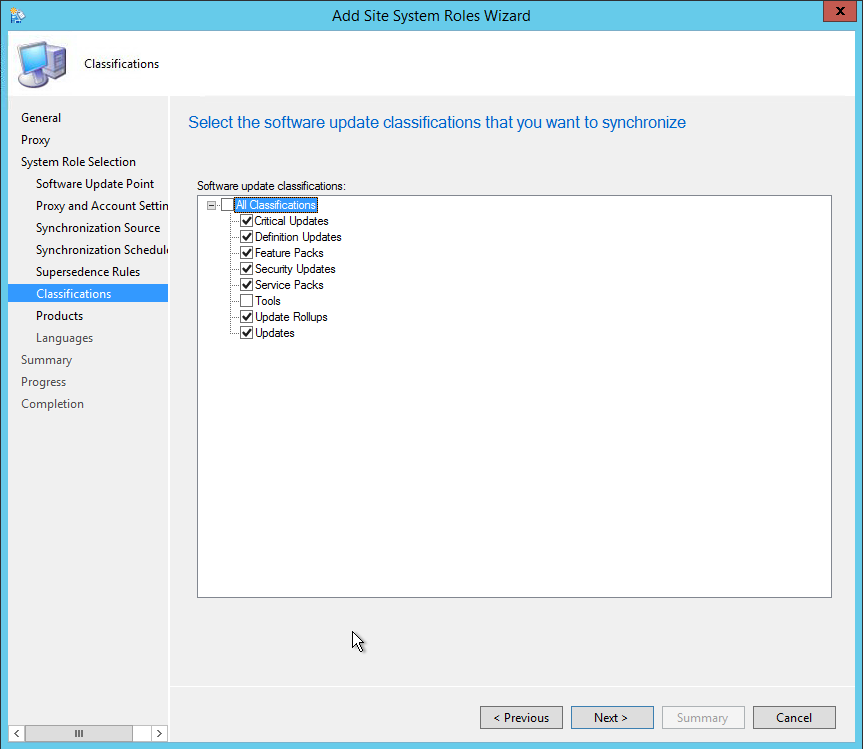
- On the Classifications tab, select your organization needs, click Next
- Full description on this Microsoft Support Article
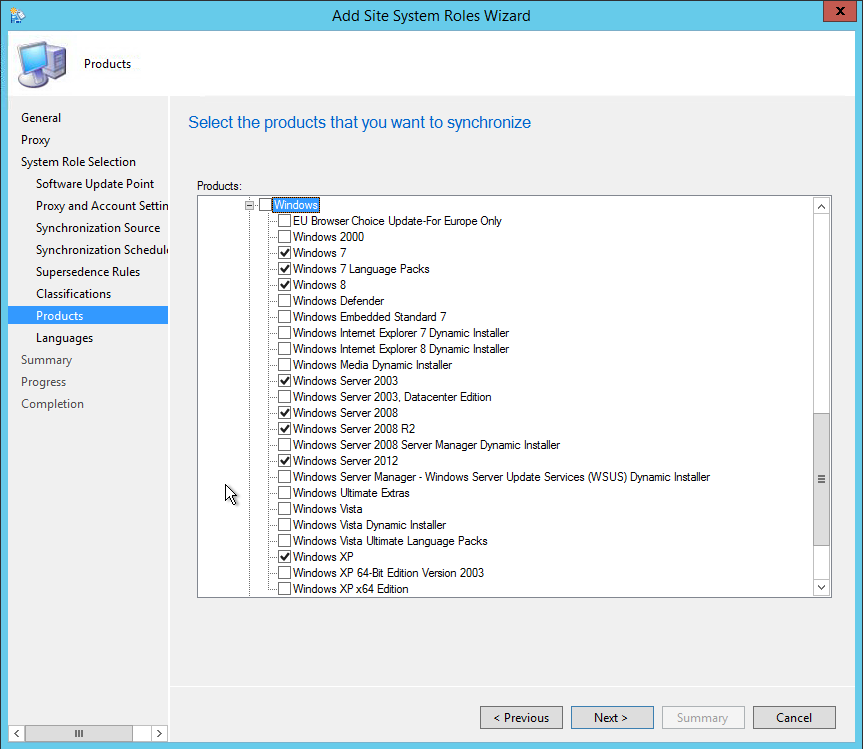
- On the Products tabs, select the products that you want to manage using SCCM, click Next
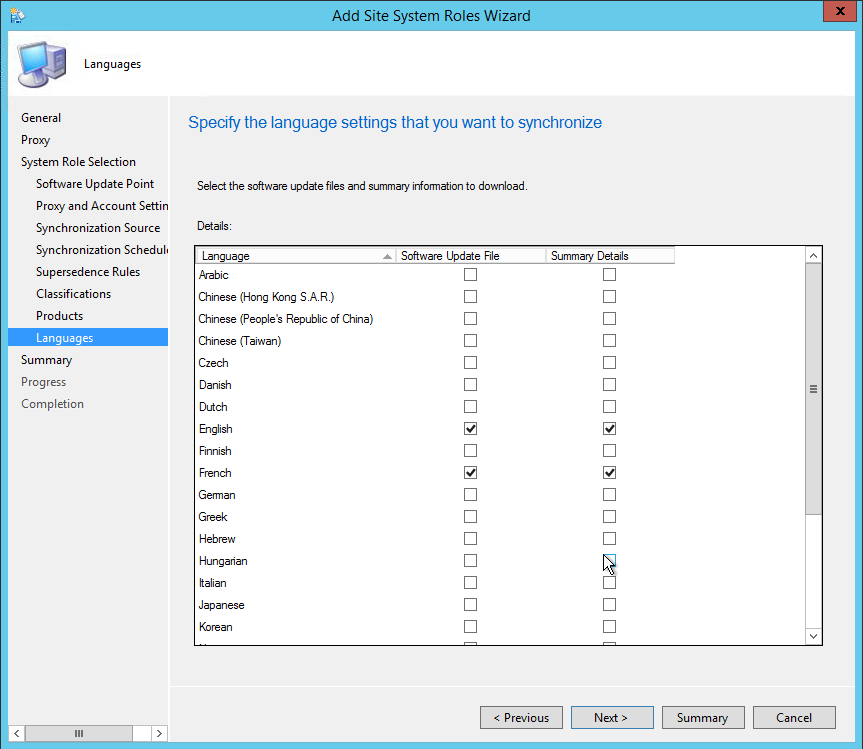
- On the Languages tab, select the desired language, click Next
- On the Summary tab, review your settings, click Next, wait for the setup to complete and click Close
Verification
- ConfigMgrSetupLogsSUPSetup.log -Provides information about the software update point installation. When the software update point installation completes, Installation was successful is written to this log file
- ConfigMgrSetupLogsWCM.log – Provides information about the software update point configuration and connecting to the WSUS server for subscribed update categories, classifications, and languages
- ConfigMgrSetupLogsWSUSCtrl.log – Provides information about the configuration, database connectivity, and health of the WSUS server for the site
- ConfigMgrSetupLogsWsyncmgr.log – Provides information about the software updates synchronization process
Bonus link : I suggest that you read the excellent article written by Kent Agerlund on how to avoid what he calls the House of Cards
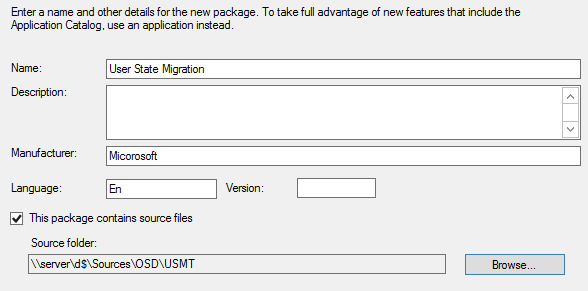
Part 16 – State Migration Point Installation
We will describe how to install SCCM Current Branch State Migration Point (SMP).
Role Description
The State Migration Point stores user state data when a computer is migrated to a new operating system.
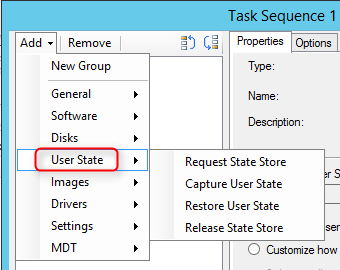
This is not a mandatory Site System but you need a State Migration Point if you plan to use the User State steps in your Task Sequence. These steps integrate with User State Migration Tools (USMT) to backup your user data before applying a new operating system to a computer.
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
The State Migration Point is a site-wide option. It’s supported to install this role on a child Primary Site, stand-alone Primary Site or Seconday Site. It’s not supported to install it on a Central Administration site.
The State Migration Point can be installed on the site server computer or on a remote computer. It can be co-located on a server that has the distribution point role.
SCCM State Migration Point Installation
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
- Right-click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
- On the Site System Role tab, select State Migration Point, click Next
- On the State Migration Point tab
- Click the star icon, specify the folder where you want the data to be stored and how much space must be reserved on the drive
- Specify the Deletion Policy. This is the delay to keep the data after a successful restore.
- Enable Restore-Only mode if needed. Use this setting if you want your SMP to be in read-only mode. This is useful if you replace or decommission an existing SMP
- On the Boundary Groups tab, add the boundary group that can access the State migration Point. If you add the role on a site system that already has the Distribution Point role, the boundary group of this DP will already be listed
- On the Summary tab, review your settings, click Next and complete the wizard
Verification and Logs files
You can verify the installation in the following logs:
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsSmssmpsetup.log – Detailed State Migration Point Installation status
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsSmpmsi.log – Provides information about the State Migration Point
If you have any error in the installation process refer to this post that explains the permission needed for the SMP to install correctly.
Create the USMT Package
To store the user state data on a State Migration Point, you must create a package that contains the USMT source files. This package is specified when you add the Capture User State step to your task sequence.
- On your SCCM Server where you installed Windows Deployment Toolkit, browse to : C:Program Files (x86)Windows Kits8.1Assessment and Deployment KitUser State Migration Tool
- If you don’t have this folder, it’s because you haven’t installed the USMT (included in Windows ADK) during your SCCM Installation
- Copy the folder content in your Content Library (In my example D:SourcesOSDUSMT)
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Software Library / Application Management / Packages
- Right-click Packages and select Create a new package
- Enter the Name, Manufacturer, Language
- Check the This package contains source files check-box and specify your source folder (D:SourcesOSDUSMT)
- Click Next
- On the Program Type tab, select Do not create a program and click Next
- Complete the Create Package wizard
The State Migration Point and the USMT package are now ready for use in an OSD Task Sequence using the Capture User State and Restore User State steps.
Part 17 – System Health Validator Point
We will describe how to install SCCM Current Branch System Health Validator Point (SHVP).
Role Description
The System Health Validator Point validates Configuration Manager Network Access Protection (NAP) policies.
This is not a mandatory site system but you need a System Health Validator Point if you plan to use NAP evaluation in your software update deployments. This site system integrates with an existing NAP server in your infrastructure.
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
The System Health Validator Point is a hierarchy-wide option. It’s supported to install this role on a Central Administration site, stand-alone Primary site, child Primary site. It’s not supported to install it on a Seconday site. The System Health Validator Point must be installed on a NAP health policy server.
SCCM System Health Validator Point Installation
- Open the SCCM console
- Navigate to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
- Right click your Site System and click Add Site System Roles
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
- On the Site System Role tab, select System Health Validator Point, click Next
- On the System Health Validator tab, click Next
- There are no properties to configure for this site system role
- On the Summary tab, review your settings, click Next and complete the wizard
Verification and Logs files
You can verify the installation in the following logs:
- ConfigMgrInstallationPathLogsSMSSHVSetup.log – Detailed System Health Validator Point installation status
Configure Client Settings
In order to enable Network Access Protection on your clients, you must configure your client settings :
- Open the SCCM console
- Browse to Administration / Client Settings
- Create a new client settings, select Network Access Protection on the left and choose Yes under Enable Network Access Protection on clients
- Select the desired NAP re-evaluation schedule and click Ok
In case you’re used to NAP in SCCM 2007 and looking for a Network Access Protection node in the console, the 2012 version of NAP is slightly different.
From Technet:
The New Policies Wizard is no longer available to create a NAP policy for software updates: The Network Access Protection node in the Configuration Manager console and the New Policies Wizard are no longer available in System Center 2012 Configuration Manager. To create a NAP policy for software updates, you must select Enable NAP evaluation on the NAP Evaluation tab in software update properties.
Part 18 – Service Connection Point Installation
We will describe how to perform an SCCM Service Connection Point Installation. The Service Connection Point is a new site system role that serves several important functions for the SCCM hierarchy.
It might affect how you configure this site system role:
- Manage mobile devices with Microsoft Intune– This role replaces the Windows Intune connector used by previous versions of SCCM, and can be configured with your Intune subscription details
- Manage mobile devices with on-premises MDM– This role provides support for on-premises devices you manage that do not connect to the Internet
- Upload usage data from your Configuration Manager infrastructure– You can control the level or amount of detail you upload
- Download updates that apply to your Configuration Manager infrastructure – Only relevant updates for your infrastructure are made available, based on usage data you upload
Site System Role Placement in Hierarchy
Each hierarchy supports a single instance of this role. The site system role can only be installed at the top-tier site of your hierarchy (On a Central Administration Site or a stand-alone Primary Site).
SCCM Service Connection Point Installation
The SCCM 1511 installation or upgrade wizard will ask to install the Service Connection Point. If you select to skip the role installation, you can manually add it to SCCM using the following steps.
- Go to Administration / Site Configuration / Servers and Site System Roles
- Right-click the Site System you wish to add the role
- Click Add Site System Role in the Ribbon
- On the General tab, click Next
- On the Proxy tab, click Next
- On the Site System Role tab, select Service Connection Point and click Next
- On the Service Connection Mode, select the desired option :
- In Online mode, the Service Connection Point automatically downloads updates that are available for your current infrastructure and product version, making them available in the SCCM console
- In Offline mode, the Service Connection Point does not connect to the Microsoft cloud service and you must manually use the service connection tool when your Service Connection Point is in Offline mode to import available updates
- On the Summary screen, wait for the setup to complete and close the wizard
Verification and Logs files
- ConnectorSetup.log –Information about role installation and that the Service Connection Point was created successfully
Now that all our site servers are installed, we are now ready to configure the various aspect of SCCM.
Part 19 – Plan and Configure Boundaries
We will start our configuration with the SCCM boundaries. First, let’s define what a boundary in SCCM is :
From Technet :
In MEMCM/SCCM, a boundary is a network location on the intranet that can contain one or more devices that you want to manage. Boundaries can be an IP subnet, Active Directory site name, IPv6 Prefix, or an IP address range, and the hierarchy can include any combination of these boundary types. To use a boundary, you must add the boundary to one or more boundary groups. Boundary groups are collections of boundaries. By using boundary groups, clients on the intranet can find an assigned site and locate content when they have to install software, such as applications, software updates, and operating system images.
A boundary does not enable clients to be managed at the network location. To manage a client, the boundary must be a member of a boundary group. Simple Boundaries on do nothing, they must be added to one or more boundary groups in order to work.
A boundary group is self-explanatory, it’s a group of boundaries used for site assignment and for content location. Beginning with SCCM 2012 R2 SP1, a boundary group can direct your clients to their Distribution Points for content, State Migration Point, Preferred Management Point and Software Update Point. Prior to R2 SP1, Content location is used by client to identify available Distribution Points or State Migration Point based on the client network location.
To resume :
- Site Assignment boundary group associate a resource to a site
- Content Location boundary group is used to retrieve its deployment content (applications, packages, images, etc)
Planning for SCCM Boundaries and Boundary Groups
Before designing your strategy choose wisely on which boundary type to use.
If you’re unsure of which type of boundary to use you can read Jason Sandys excellent post about why you shouldn’t use IP Subnet boundaries.
Microsoft recommends the following :
- When designing your boundary strategy, we recommend you use boundaries that are based on Active Directory sites before using other boundary types. Where boundaries based on Active Directory sites are not an option, then use IP subnet or IPv6 boundaries. If none of these options are available to you, then leverage IP address range boundaries. This is because the site evaluates boundary members periodically, and the query required to assess members of an IP address range requires a substantially larger use of SQL Server resources than queries that assess members of other boundary types
- It’s also recommended to split your Site Assignment and Content location group
Overlapping Boundaries
SCCM Current Branch supports overlapping boundary configurations for content location.
When a client requests content, and the client network location belongs to multiple boundary groups, Configuration Manager sends the client a list of all Distribution Points that have the content.
This behavior enables the client to select the nearest server from which to transfer the content or state migration information.
Real World Scenario
In our various SCCM installations, our clients are often confused about this topic. Let’s make an example to help you understand :
- Contoso has 1000 clients
- 1 Primary Site (Montreal)
- 3 remote offices with their local Distribution Point (New York, Chicago, Los Angeles)
- Active Directory Site are based on their site subnets (MTL,NY,CHI,LA)
In that scenario, we need to create 4 Boundary, 1 for each office :
| Boundary | Type |
|---|---|
| MTL | Active Directory Site |
| NY | Active Directory Site |
| CHI | Active Directory Site |
| LA | Active Directory Site |
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Administration / Hierarchy Configuration / Boundary
- Right-click Boundaries and select Create Boundary
- Create the boundary, in our example we’ll create 4 different boundary for my 4 locations using their Active Directory Sites
- Tip : If you have multiples Active Directory Sites, IP Ranges or Subnets, you can enable Active Directory Forest Discovery which can create them automatically
Create Boundary Group
Now, we’ll create a Site Assignment Boundary Group and add all those AD Site. That way, all my clients for my 4 locations will be assigned to my Montreal Primary Site.
For Content Location, we want clients to get their content locally at their respective location. We will create 4 Content Boundary groups, add only their AD Site Boundary and assign their local Distribution Point.
| Name | Boundary | Site System |
|---|---|---|
| MTL — Content Location | MTL | DPMTL01 |
| NY — Content Location | NY | DPNY01 |
| CHI — Content Location | CHI | DPCHI01 |
| LA — Content Location | LA | DPLA01 |
Here’s how to make this happen in SCCM :
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Administration / Hierarchy Configuration / Boundary Groups
- Right-click Boundary Groups and select Create Boundary Groups
Create Site Assignement Boundary Group
- We’ll start by creating a group for Site Assignment : SA – MTL
- Click the Add bouton on the bottom
- On the Add Boundaries screen, select all boundaries. This will direct all my clients to the Primary Site located in Montreal for Site Assignment
- On the References tab, check the Use this boundary group for site assignment box
- Select your assigned site. In my case : MTL
- Click Ok
Create Content Location Boundary Group
- Right-click Boundary Groups and select Create Boundary Groups
- We’ll name our group Content Location – MTL
- Click on Add
- Select only the MTL boundary
- The MTL boundary will be listed
- On the References tab, uncheck the Use this boundary group for site assignment box
- Click on Add at the bottom
- Select the Site System that host the Distribution Point role for the Montreal site. For our example DPMTL01
- Click Ok
- Repeat the steps for the other sites (New York, Chicago, Los Angeles)
- Once completed our clients are assigned to their local respective Site Systems
This is a simple but typical scenario. You can have multiples boundaries and Site System in your Boundary Groups if needed.
Part 20 – Configure Client Settings
This part will explain how to create a custom SCCM client settings and how to deploy it.
Client settings are used to configure your deployed agents. This is where you decide any configuration like :
- Enabling hardware inventory agent
- Enabling power settings options
- Enable cloud services
- Set scan schedules
- BITS throttling
- Ect..
In previous versions of SCCM, client settings were specific to the site. You had 1 client settings that applied to all your hierarchy. In SCCM you can specify clients setting at the collection level. You can have different settings for specific collections, overlapping settings are set using a priority setting.
When you modify the Default Client Settings, the settings are applied to all clients in the hierarchy automatically. You do not need to deploy the Default Client Settings to apply it. By default, it has a 10000 priority value (This is the lower priority). All other custom client settings can have a priority value of 1 to 9999 which will always override the Default Client Settings. (The higher Priority is 1).
We won’t explain each client’s settings and their descriptions. The Technet documentation is pretty clear and many of the client settings are self-explanatory. We cannot make any recommendations either as each environment has its own needs and limitations. If you have any questions concerning a specific setting, use the comment section and we’ll try to help you so you can make the right decision for your organization.
How to Create Custom Client Device Settings
When you deploy a custom client settings, they override the Default Client Settings.
Before you begin, ensure that you created a collection that contains the devices that require these custom client settings.
For our blog post, we will set the Client Policy polling interval to 15 minutes.
- Open the SCCM console
- Go to Administration / Client Settings
- On the top ribbon, click Create Custom Client Device Settings
- In the Create Custom Device Settings page, specify a name for the custom settings and description
- Select one or more of the available settings. We will select Client Policy
- On the left pane, Client Policy will be displayed, click on it
- We will set the Client Policy polling interval to 15 minutes
- Click Ok
- Your newly created setting will be displayed in the console
Set the Client Settings priority
When you create a new client setting, it automatically takes the next available priority. (Beginning with 1) Before deploying it, make sure that your priority is well set for your needs. A higher priority (1) will override any settings with a lower priority. (9999). Don’t get confused 1 is higher !
To change the priority number :
- On the top ribbon, select your client settings and click Increase Priority or Decrease Priority
- You can see each client settings priority and if they are deployed in the same section
How to deploy a client settings
Now that your client settings are created, you need to deploy it to a collection. This new client settings will apply to only this collection and depending on the priority, will override the settings.
- Select the custom client settings that you have just created
- On the top ribbon, click Deploy
- In the Select Collection dialog box, select the collection that contains the devices to be configured with the custom settings, and then click Ok
- You can verify the selected collection if you click the Deployments tab on the bottom of the console
How to apply
Client computers will apply your custom settings when they download their next client policy. You can trigger it manually to speed up the process.
Manually on the client
- In Control Panel, click on the Configuration Manager icon
- In the Action tab, select Machine Policy Retrieval & Evaluation Cycle
- Click Run now
Using the SCCM Console
To initiate client policy retrieval by using client notification (Configuration Manager SP1+ only)
- In the SCCM console
- Go to Assets and Compliance / Device Collections
- Select the device collection containing the computers that you want to download policy
- Right-click a single device or the whole collection and select Client Notification and then Download Computer Policy
How to verify your Client Settings
It’s possible to see which client settings are applied to a specific client. You must use the Resultant Client Settings function in the SCCM console.
We already cover this in a previous article.
Part 21 – Configure Discovery Methods
After you completed your SCCM installation, you certainly want to start managing some systems. The effective way to add them in SCCM is to configure SCCM discovery methods. This blog article will explain the various discovery methods and will describe how to configure it.
What is SCCM Discovery Methods
Here’s the official discovery methods definition from Technet :
SCCM discovery methods identifies computer and user resources that you can manage by using Configuration Manager. It can also discover the network infrastructure in your environment. Discovery creates a discovery data record (DDR) for each discovered object and stores this information in the Configuration Manager database.
When discovery of a resource is successful, discovery puts information about the resource in a file that is referred to as a discovery data record (DDR). DDRs are in turn processed by site servers and entered into the Configuration Manager database where they are then replicated by database-replication with all sites. The replication makes discovery data available at each site in the hierarchy, regardless of where it was discovered or processed. You can use discovery information to create custom queries and collections that logically group resources for management tasks such as the assignment of custom client settings and software deployments. Computers must be discovered before you can use client push installation to install the Configuration Manager client on devices.
In simple words, it means that SCCM needs to discover a device before it can manage them. It’s not mandatory to discover computers, if you manually install the client, it will appear in the console and it can be managed. The problem is that if you have a thousand computers, it can be a fastidious process. By using Active Directory System Discovery, all your computers will be shown on the console, from there you can choose to install the client using various SCCM methods. Of course, if you need information about your users and groups, you need to configure User and Group discovery, it’s the only way to bring this information in SCCM.
There are 5 Types of Discovery Methods that can be configured. Each one targets a specific object type (Computers, Users, Groups, Active Directory) :
Active Directory System Discovery
Discovers computers in your organization from specified locations in Active Directory. In order to push the SCCM client to the computers, the resources must be discovered first. You can specify to discover only computers that have logged on to the domain in a given period of time. This option is useful to exclude obsolete computer accounts from Active Directory. You also have the option to fetch custom Active Directory Attributes. This is useful if your organization store custom information in AD. You can read our blog post concerning this topic.
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Administration / Hierarchy Configuration / Discovery Methods
- Right-Click Active Directory System Discovery and select Properties
- On the General tab, you can enable the method by checking Enable Active Directory System Discovery
- Click on the Star icon and select the Active Directory container that you want to include in the discovery process
- On the Polling Schedule tab, select the frequency on which you want the discovery to happen
- A 7-day cycle with a 5 minutes delta interval is usually fine in most environment
- On the Active Directory Attribute tab, you can select custom attributes to include during discovery
- This is useful if you have custom data in Active Directory that you want to use in SCCM
- On the Options tab, you can select to discover only accounts that have logged or updated their passwords since a specific number of days
- This is useful if your Active Directory isn’t clean. Use this to discover only good records
Active Directory Group Discovery
Discovers groups from specified locations in Active Directory. The discovery process discovers local, global or universal security groups. When you configure the Group discovery you have the option to discover the membership of distribution groups. With the Active Directory Group Discovery, you can also discover the computers that have logged in to the domain in a given period of time. Once discovered, you can use group information for example to create deployment based on Active Directory groups.
Be careful when configuring this method: If you discover a group that contains a computer object that is NOT discovered in Active Directory System Discovery, the computer will be discovered. If the automatic client push is enabled, this could lead to unwanted clients’ computers.
To discover resources using this method:
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Administration / Hierarchy Configuration / Discovery Methods
- Right-Click Active Directory Group Discovery and select Properties
- On the General tab, you can enable the method by checking Enable Active Directory Group Discovery
- Click on the Add button on the bottom to add a certain location or a specific group.
- Remember : If you discover a group that contains a computer object that is NOT discovered in Active Directory System Discovery, the computer will be discovered.
- On the Polling Schedule tab, select the frequency on which you want the discovery to happen
- A 7-day cycle with a 5 minutes delta interval is usually fine in most environment
- On the Options tab, you can select to discover only accounts that have logged or updated their passwords since a specific number of days
- This is useful if your Active Directory isn’t clean. Use this to discover only good records
Active Directory User Discovery
The discovery process discovers user accounts from specified locations in Active Directory. You also have the option to fetch custom Active Directory Attributes. This is useful if your organization store custom information in AD about your users. Once discovered, you can use group information for example to create user-based deployment.
To discover resources using this method:
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Administration / Hierarchy Configuration / Discovery Methods
- Right-Click Active Directory User Discovery and select Properties
- On the General tab, you can enable the method by checking Enable Active Directory User Discovery
- Click on the Star icon and select the Active Directory container that you want to include in the discovery process
- On the Polling Schedule tab, select the frequency on which you want the discovery to happen
- A 7-day cycle with a 5 minutes delta interval is usually fine in most environment.
- On the Active Directory Attribute tab, you can select custom attributes to include during discovery
- This is useful if you have custom data in Active Directory that you want to use in SCCM
Active Directory Forest Discovery
Discovers Active Directory sites and subnets, and creates Configuration Manager boundaries for each site and subnet from the forests which have been configured for discovery. Using this discovery method you can automatically create the Active Directory or IP subnet boundaries that are within the discovered Active Directory Forests. This is very useful if you have multiple AD Site and Subnet, instead of creating them manually, use this method to do the job for you.
To discover resources using this method:
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Administration / Hierarchy Configuration / Discovery Methods
- Right-Click Active Directory Forest Discovery and select Properties
- On the General tab, you can enable the method by checking Enable Active Directory Forest Discovery
- Select the desired options
HeartBeat Discovery
Heartbeat Discovery runs on every client and to update their discovery records in the database. The records (Discovery Data Records) are sent to the Management Point in a specified duration of time. Heartbeat Discovery can force the discovery of a computer as a new resource record, or can repopulate the database record of a computer that was deleted from the database.
HeartBeat Discovery is enabled by default and is scheduled to run every 7 days.
To discover resources using this method:
- Open the SCCM Console
- Go to Administration / Hierarchy Configuration / Discovery Methods
- Right-Click Heartbeat Discovery and select Properties
- On the General tab, you can enable the method by checking Enable Heartbeat Discovery
- Make sure that this setting is enabled and that the schedule run less frequently than the Clear Install Flag maintenance task.
Network Discovery
The Network Discovery searches your network infrastructure for network devices that have an IP address. It can search the domains, SNMP devices and DHCP servers to find the resources. It also discovers devices that might not be found by other discovery methods. This includes printers, routers, and bridges.
We won’t go into detail of this discovery method as it’s old and depreciated methods. We never saw any customers using this method in production.
Part 22 – Configure Maintenance Tasks
Each
Configuration Manager site supports maintenance tasks that help maintain the
operational efficiency of the site database. By default, several maintenance
tasks are enabled in each site, and all tasks support independent schedules.
Maintenance tasks are set up individually for each site and apply to the
database at that site. However, some tasks, like Delete Aged Discovery Data,
affect information that is available in all sites in a hierarchy.
To
set up maintenance tasks for Configuration Manager :
- Go to Administration / Site Configuration / Sites
- On the Home tab, in the Settings group, choose Site Maintenance
- To set up the task, choose Edit, ensure the Enable this task checkbox is checked and set up a schedule for when the task runs.
To enable or disable the task without
editing the task properties, choose the Enable or Disable button.
The button label changes depending on the current configuration of the task.
When you are finished configuring the
maintenance tasks, choose OK to finish the procedure.
This topic lists
details for each of the SCCM site maintenance tasks :
Backup Site Server: Use this task to prepare for the recovery of critical data. You can create a backup of your critical information to restore a site and the Configuration Manager database. For more information, see our next section that covers it.
Check Application Title with Inventory Information: Use this task to maintain consistency between software titles that
are reported in the software inventory and software titles in the Asset Intelligence
catalog. Central administration site: Enabled
Clear Install Flag: Use this task
to remove the installed flag for clients that don’t submit a Heartbeat
Discovery record during the Client Rediscovery period. The installed flag prevents automatic client push
installation to a computer that might have an active Configuration Manager
client.
Delete Aged Application Request Data: Use this task to delete aged application requests from the
database.
Delete Aged Client Download History: Use this task to delete historical data about the download source
used by clients.
Delete Aged Client Operations:
Use this task to delete all aged data for client operations from the site
database. For example, this includes data for aged or expired client
notifications (like download requests for machine or user policy), and for
Endpoint Protection (like requests by an administrative user for clients to run
a scan or download updated definitions).
Delete Aged Client Presence History: Use this task to delete history information about the online
status of clients (recorded by client notification) that is older than the
specified time.
Delete Aged Cloud Management Gateway Traffic Data: Use this task to delete all aged data about the traffic that passes through the cloud management gateway from the site database. For example, this includes data about the number of requests, total request bytes, total response bytes, number of failed requests, and a maximum number of concurrent requests.
Delete Aged Collected Files: Use
this task to delete aged information about collected files from the database.
This task also deletes the collected files from the site server folder
structure at the selected site. By default, the five most-recent copies of
collected files are stored on the site server in the Inboxessinv.boxFileCol directory.
Delete Aged Computer Association Data: Use this task to delete aged Operating System Deployment computer
association data from the database. This information is used as part of
completing user state restores.
Delete Aged Delete Detection Data:
Use this task to delete aged data from the database that has been created by
Extraction Views. By default, Extraction Views are disabled. You only enable
them by using the Configuration Manager SDK. Unless Extraction Views are
enabled, there is no data for this task to delete.
Delete Aged Device Wipe Record:
Use this task to delete aged data about mobile device wipe actions from the
database.
Delete Aged Devices Managed by the Exchange Server Connector: Use this task to delete aged data about mobile devices that are
managed by using the Exchange Server connector. This data is deleted according
to the interval that is configured for the Ignore mobile
devices that are inactive for more than (days) option
on the Discovery tab of the Exchange
Server connector properties.
Delete Aged Discovery Data: Use
this task to delete aged discovery data from the database. This data can
include records that result from heartbeat discovery, network discovery, and
Active Directory Domain Services discovery methods (System, User, and Group).
This task will also remove aged devices marked as decommissioned. When this
task runs at a site, data associated with that site is deleted, and those changes
replicate to other sites.
Delete Aged Distribution Point Usage Data: Use this task to delete from the database aged data for
distribution points that has been stored longer than a specified time.
Delete Aged Endpoint Protection Health Status History Data: Use this task to delete aged status information for Endpoint
Protection from the database.
Delete Aged Enrolled Devices:
Beginning with the update for 1602, this task is disabled by default. You can
use this task to delete from the site database the aged data about mobile
devices that haven’t reported any information to the site for a specified time.
Delete Aged Inventory History:
Use this task to delete inventory data that has been stored longer than a
specified time from the database.
Delete Aged Log Data: Use this
task to delete aged log data that is used for troubleshooting from the
database. This data isn’t related to Configuration Manager component
operations.
Delete Aged Notification Task History: Use this task to delete information about client notification
tasks from the site database when it hasn’t been updated for a specified time.
Delete Aged Replication Summary Data: Use this task to delete aged replication summary data from the
site database when it hasn’t been updated for a specified time.
Delete Aged Passcode Records: Use
this task at the top-level site of your hierarchy to delete aged Passcode Reset
data for Android and Windows Phone devices. Passcode Reset data is encrypted,
but does include the PIN for devices. By default, this task is enabled and
deletes data that is older than one day.
Delete Aged Replication Tracking Data: Use this task to delete aged data about database replication
between Configuration Manager sites from the database. When you change the
configuration of this maintenance task, the configuration applies to each applicable
site in the hierarchy.
Delete Aged Software Metering Data: Use this task to delete aged data for software metering that has
been stored longer than a specified time from the database.
Delete Aged Software Metering Summary Data: Use this task to delete aged summary data for software metering
that has been stored longer than a specified time from the database.
Delete Aged Status Messages: Use
this task to delete aged status message data as configured in status filter
rules from the database.
Delete Aged Threat Data: Use this
task to delete aged Endpoint Protection threat data that has been stored longer
than a specified time from the database.
Delete Aged Unknown Computers:
Use this task to delete information about unknown computers from the site database
when it hasn’t been updated for a specified time.
Delete Aged User Device Affinity Data: Use this task to delete aged User Device Affinity data from the database.
Delete Aged CMPivot Results: Use this task to delete from the site database aged information from clients in CMPivot queries.
Delete Aged Cloud Management Gateway Traffic Data : Use this task to delete from the site database all aged data about the traffic that passes through the cloud management gateway. This data includes:
- The number of requests
- Total request bytes
- Total response bytes
- Number of failed requests
- Maximum number of concurrent requests
Delete Expired MDM Bulk Enroll Package Records: Use this task to delete old Bulk Enrollment certificates and
corresponding profiles after the enrollment certificate has expired.
Delete Inactive Client Discovery Data: Use this task to delete discovery data for inactive clients from
the database. Clients are marked as inactive when the client is flagged as
obsolete and by configurations that are made for client status.
This task operates only on resources that
are Configuration Manager clients. It’s different than the Delete Aged
Discovery Data task, which deletes any
aged discovery data record. When this task runs at a site, it removes the data
from the database at all sites in a hierarchy.
When it’s enabled, configure this task to
run at an interval greater than the Heartbeat Discovery schedule. This enables active clients to send a Heartbeat Discovery
record to mark their client record as active so this task doesn’t delete them.
Delete Obsolete Alerts: Use this
task to delete expired alerts that have been stored longer than a specified
time from the database.
Delete Obsolete Client Discovery Data: Use this task to delete obsolete client records from the database.
A record that is marked as obsolete has usually been replaced by a newer record
for the same client. The newer record becomes the client’s current record.
Delete Obsolete Forest Discovery Sites and Subnets: Use this task to delete data about Active Directory sites,
subnets, and domains that haven’t been discovered by the Active Directory
Forest Discovery method in the last 30 days. This removes the discovery data,
but doesn’t affect boundaries that are created from this discovery data
Delete Orphaned Client Deployment State Records: Use this task to periodically purge the table that contains client
deployment state information. This task will clean up records associated with
obsolete or decommissioned devices.
Delete Unused Application Revisions: Use this task to delete application revisions that are no longer
referenced.
Evaluate Collection Members: You
configure the Collection Membership Evaluation as a site component.
Monitor Keys: Use this task to
monitor the integrity of the Configuration Manager database primary keys. A
primary key is a column (or a combination of columns) that uniquely identifies
one row and distinguishes it from any other row in a Microsoft SQL Server
database table.
Rebuild Indexes: Use this task to
rebuild the Configuration Manager database indexes. An index is a database
structure that is created on a database table to speed up data retrieval. For
example, searching an indexed column is often much faster than searching a
column that isn’t indexed.
Summarize Installed Software Data:
Use this task to summarize the data for installed software from multiple
records into one general record. Data summarization can compress the amount of
data that is stored in the Configuration Manager database.
Summarize Software Metering File Usage Data: Use this task to summarize the data from multiple records for
software metering file usage into one general record. Data summarization can
compress the amount of data that is stored in the Configuration Manager
database.
Summarize Software Metering Monthly Usage Data: Use this task to summarize the data from multiple records for
software metering monthly usage into one general record. Data summarization can
compress the amount of data that is stored in the Configuration Manager
database.
Update Application Available Targeting: Use this task to have Configuration Manager recalculate the
mapping of policy and application deployments to resources in collections. When
you deploy policy or applications to a collection, Configuration Manager
creates an initial mapping between the objects that you deploy and the
collection members.
These mappings are stored in a table for
quick reference. When a collections membership changes, these stored mappings
are updated to reflect those changes. However, it’s possible for these mappings
to fall out of sync. For example, if the site fails to properly process a
notification file, that change might not be reflected in a change to the
mappings. This task refreshes that mapping based on current collection
membership.
Update Application Catalog Tables: Use this task to synchronize the Application Catalog website database cache with the latest application information. When you change the configuration of this maintenance task, the configuration applies to all primary sites in the hierarchy.
Part 23 – Backup your Server after SCCM Installation
In the last part of this SCCM Installation Guide, we will setup automation backup for Configuration Manager sites by scheduling the predefined Backup Site Server maintenance task. This task has the following features:
- Runs on a schedule
- Backs up the site database
- Backs up specific registry keys
- Backs up specific folders and files
- Backs up the CD.Latest folder
Plan to run the default site backup task at
a minimum of every five days. This schedule is because Configuration Manager
uses a SQL Server change tracking retention period of five days.
To simplify the backup process, you can
create an AfterBackup.bat file. This
script automatically runs post-backup actions after the backup task completes
successfully. Use the AfterBackup.bat file to archive the backup snapshot to a
secure location. You can also use the AfterBackup.bat file to copy files to
your backup folder, or to start other backup tasks.
Site backup status information is written
to the Smsbkup.log file. This file
is created in the destination folder that you specify in the properties of the
Backup Site Server maintenance task.
To enable the site backup maintenance task
- Go to the Administration workspace, expand Site Configuration
- Click Site Maintenance Tasks in the ribbon.
- Select the Backup Site Server task, and click Edit.
- Select the option to Enable this task. Click Set Paths to specify the backup destination. You have the following options:
- Local drive on site server for site data and database: Specifies that the task stores the backup files for the site and site database in the specified path on the local disk drive of the site server. Create the local folder before the backup task runs. The Local System account on the site server must have Write NTFS file permissions to the local folder for the site server backup. The Local System account on the computer that’s running SQL Server must have Write NTFS permissions to the folder for the site database backup.
- Network path (UNC name) for site data and database: Specifies that the task stores the backup files for the site and site database in the specified network path. Create the share before the backup task runs. The computer account of the site server must have Write NTFS and share permissions to the shared network folder. If SQL Server is installed on another computer, the computer account of the SQL Server must have the same permissions.
- Local drives on site server and SQL Server: Specifies that the task stores the backup files for the site in the specified path on the local drive of the site server. The task stores the backup files for the site database in the specified path on the local drive of the site database server. Create the local folders before the backup task runs. The computer account of the site server must have Write NTFS permissions to the folder that you create on the site server. The computer account of the SQL Server must have Write NTFS permissions to the folder that you create on the site database server. This option is available only when the site database isn’t installed on the site server.
Verify that the Backup Site Server maintenance task is
running
- Check the timestamp on the files
in the backup destination folder that the task created. Verify that the
timestamp updates to the time when the task was last scheduled to run.- Go to the Component
Status node of the Monitoring workspace. Review the status messages for SMS_SITE_BACKUP. When site backup completes successfully, you see message ID 5035. This message indicates that the site backup completed without any
errors. - When you configure the backup
task to create an alert when it fails, look for backup failure alerts in
the Alerts node of the Monitoring workspace. - Open Windows Explorer on the site server and browse to
<ConfigMgrInstallationFolder>Logs. Review Smsbkup.log for
warnings and errors. When site backup completes successfully, the log
showsBackupwith
completed
message IDSTATMSG: ID=5035.
- Go to the Component
SQL Backup
It’s also possible to backup your SCCM server using SQL Maintenance task. The biggest advantage of this method is that it offers compression. Please read this blog post if you prefer this method. Be aware that this backup method doesn’t backup the CD.Latest folder which is important. You could also have both backup methods enabled if needed.
More SCCM Ressources
System Center Dudes offers numerous
configurations guides and custom reports to ease your Configuration Manager
day-to-day operations.
Consult our product page to see the complete list.
That conclude this SCCM Installation Guide, we hope that it was hepful. Feel free to leave your comment in the section below.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Prerequisite Installation
- Install Windows ADK 10
- Create System Management Container in the Domain Controller System
- Extend Active Directory Schema
- Add IIS Server Role
- Install BITS and Remote Differential Compression features
- Install Windows Server Update Service
- Install System Center Configuration Manager
- Test System Center Configuration Manager
- Summary
- See Also
Introduction
The environment used for setting up System Center Configuration Manager is a two server farm with one server acting as the Domain Controller and the second one will act as the SCCM Server with SQL Server 2016 installation. We will install SCCM
on the same server as SQL Server for the time being. We can also extend the set up to a stand-alone SCCM server and SQL Server. The installation of SCCM is primarily divided into two sections:
- Prerequisite installation
- System Center Configuration Manager Installation
Prerequisite Installation
Before installing SCCM on the server we have to set up a few prerequisites on the server else we will get a few errors during the installation of SCCM. The prerequisites that we would be setting up are:
- Install Windows ADK 10
- Create System Management Container in the Domain Controller System
- Extend Active Directory Scheme
- Configure IIS Role
- Install BITS and Differential Compression
- Install Windows Server Update Service Role
Install Windows ADK 10
If we have not installed Windows ADK 10 we will get the below error while trying to install SCCM.
So let’s get the installation file from
here. Double-click the installation file and start the installer.
Specify the install location and continue.
Check the required features that have to be installed, We already have set up SQL Server 2016 on the server, so let’s uncheck the last option and install.
This will install Windows ADK 10 in the SCCM Server.
↑ Return
to Top
Create System Management Container in the Domain Controller System
Once Windows ADK 10 has finished the installation, we will set the System Management Container in the AD Server. In order to do that, let’s head over to the Server Manager and from tools select ADSI Edit.
Right-click on ADSI Edit option in the below window and select Connect to. This will open up the Connection Settings window. Click OK.
Right-click the Domain Controller name and select New->Object.
Specify the class as “container” and click Next.
Don’t create the container in the root directory (like the screenshot shows), but create it in the «CN=System»-Container.
(Thanks to the comments which led to this mistake)

Specify the values as “System Management”.
This will create the object in the AD. Now we have to assign object permissions to this container. Right-click the newly created container object and select properties.
Click Add to add the users.
Add the Admin Account of SCCM Server (here we are using SPFarmAccount) and the SCCM Computer (VM02-SQL2016) to this container object.
From advanced settings, change the permission entry from “This object” to “This object and all descendant objects”.
Now both SPFarmAccount and VM-2-SQL2016 has been granted Full Control to the Container Object.
↑ Return
to Top
Extend Active Directory Schema
Let’s download the SCCM Setup Files from
here.
It will contain the Zip file named SC_Configmr_SCEP which should be unzipped to a drive folder.
Go inside the extracted folder to the path C:SC_Configmgr_SCEP_1606SMSSETUPBINX64
From there, run the application extadsch
It will run the command line tool to extend the active directory schema. You can find the output file in the C Drive.
Opening it, we can see the success status of the operation.
↑ Return
to Top
Add IIS Server Role
From Server Manager, select Add Roles and Features option.
Select Role-based or feature-based installation option and continue.
Select the Role as WebServer(IIS) and continue.
Check the Role services that has to be installed as part of Web Server IIS and proceed.
This will start the installation of the Roles in the SCCM Server. Once completed, we can close the wizard and head to the next section.
↑ Return
to Top
Install BITS and Remote Differential Compression features
Just like we have installed Web Server (IIS), let’s install Background Intelligence transfer Service (BITS) and Remote Differential Compression in the SCCM Server.
Select BITS from the Features window.
Similarly, select Remote Differential Compression from the same window.
Install the selected features by clicking on Install.
Once the installation has completed we can close the window.
↑ Return
to Top
Install Windows Server Update Service
Now let’s add the last Role to the SCCM Server. It is the Windows Server Update Service Role.
Specify the folder location where the updates will be stored.
Click on Install to start the installation.
Install System Center Configuration Manager
From the downloaded installation files, start the installer present in the x64 folder.
↑ Return
to Top
Select “Install a Configuration Manager primary site” option.
If we have the product key we can enter it, else proceed with the evaluation option.
Accept the agreement and continue.
If you have already downloaded the required installation files we can specify the location of the installation media. Else we will have to download them to drive location first.
Here we will download them to a drive folder.
Specify the site code and site name and proceed.
We can choose to install the primary site as a stand-alone site or add it to an existing hierarchy. Even if we chose the stand alone option we can add it to the hierarchy at a later point.
Now we have to specify the Full Qualified name of the SQL Server where the SCCM databases will be created. Since we have chosen the SCCM to be installed on the same server as SQL Server, we don’t have to change the default value.
Specify the location for the SQL Server data file and transaction log to be saved and proceed.
Now we have to mention the location of the SMS provider which will be used to communicate with the site database. Let’s install it on the same SQL Server.
Check HTTPS communication option and proceed.
Chose to install a management point as well as installation point and proceed.
Finally, we are in the setting summary page. Click on Next to start the installation.
This will start the prerequisite check. Ensure that there are no errors. We can skip the warnings after checking for the severity. If there are errors we will have to resolve them before proceeding.
Once we click Begin Install, it would take around 45 minutes to complete the installation of System Center Configuration Manager.
↑ Return
to Top
Test System Center Configuration Manager
Once the installation has run to completion we go ahead and run the Configuration Manager Console.
This will open up the System Center Configuration Manager
Summary
Thus we saw how to set up the prerequisites required for setting up System Center Configuration Manager and how to set up SCCM in the Server.
↑ Return
to Top
See Also
This article can also be viewed from the below link:
- Step By Step Walkthrough To Set Up System Center Configuration Manager 2016
This is a complete SCCM install guide using baseline media. I will be going through the installation of SCCM 2103 using Baseline Media. To install and configure the Configuration manager there are lots of steps to be involved before actual configuration to begin.
This install guide for SCCM covers all the information related to download of correct ISO’s / files, server builds, pre-requisites required on servers, SQL database install, step by step SCCM install guide and all configuration required for it to make Configuration Manager fully functional
Table Of Contents
- Minimum Requirements (for Servers)
- Download required ISO’s & files
- Install Windows Server and configure Active Directory
- Prepare Active Directory for SCCM Installation
- Create Service account for SCCM
- Create container in “ADSI Edit”
- Extend the Schema
- Install SQL Server 2019 for SCCM
- Install SQL Server Management Studio
- Install Windows ADK 11 and WinPE add-on
- Install Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit
- Install Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit Windows Preinstallation Environment Add-ons
- Install Prerequisites on Configuration Manager Server
- Install Configuration Manager using Baseline Media
Minimum Requirements (for Servers)
Lets talk about the requirement, at a very basic minimum, we require 2 Servers:
- DC01 – Domain Controller – With Server 2019 or Server 2022.
I have assigned 4GB RAM with 128 GB of Disk attached with it with 1 single partition
2. SCCM01 – Member Server – With Server 2019 or Server 2022.
I have assigned 16 GB RAM with 3 disks.
c: drive for OS
d: for SCCM installation and Content library (for SCCM)
e: for SQL
Download required ISO’s & files
We need to have following ISO’s & files downloaded:
- Download Windows Server 2019 or 2022 – Can be downloaded from Evaluation Center which gives 180 days of evaluation.
- Download SQL Server 2019– SQL Server on-premises can be download from sql server downloads page.
Comes with 180 days of evaluation. - Download SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
- Download Windows ADK for Windows 11 – Use the page to download following:
- Download the Windows ADK
- Download the WinPE add-on for the Windows ADK
- Download Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager exe – Current Branch – version 2103
Comes with 180 days of evaluation. - Download Microsoft SQL Server 2019 Reporting Services (SSRS) –SQL Server Reporting Services can be download with evaluation version.
Install Windows Server and configure Active Directory
We can now proceed with installation of DC01 Server which is going to be our Domain Controller. This is a straight forward process, if you need complete guide for installation follow:
- Step by step Windows Server 2019 install guide
- Install and configure Active Directory
Once done, do the installation for SCCM01 Windows server as well, but don’t proceed with any SCCM installation.
Prepare Active Directory for SCCM Installation
Once Domain controller is ready, we need to make some configuration.
Create Service account for SCCM
It is always a good practice to have service account created for SCCM. This service account will be later be used for specific accounts used for SCCM such as Network Access account, Domain joining account, client push account, SQL Service account, and each account setting requires a specific permission. But for the purpose of configuration SCCM in LAB, I am going with Domain Admins Account permission. Hence went with creating SVC-SCCMAdmin account with Domain Admins account membership.
Create container in “ADSI Edit”
We need to create a container with name System Management under System, by default it is not created. This is a very important step as System Management container as SCCM Site and MP location will be published at this location only.
Launch adsiedit.msc, and create System Management container.
Once created, go to System Management Security and add SCCM01 server with Full control. Click on Advanced > Edit and provide following permission This object and all descendant objects.
Extend the Schema
We are going to extend the schema now which will create additional attributes in Active Directory which helps publishing the information of SCCM under this attributes. Schema files are available under SCCM Source files, location SMSSETUPBINX64extadsch.exe.
Open cmd prompt with elevated rights. Navigate to the folder containing extadsch.exe. Run extadsch.exe, we should get success message “Successfully extended the active Directory schema”
Install SQL Server 2019 for SCCM
Lets install SQL Serve 2019 on SCCM Server, ideally in production environment SQL Server is installed on a different box with multiple partitions configured for specific components required for SQL. However, for the sake of simplifying it, I am installing on SCCM Server.
Mount the SQL Server 2019 ISO and launch setup.exe to start SQL Server 2019 Setup.
Select New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation.
On Product Key page, specify free edition or enter the product key, click Next.
On Install Rules, it will verify the rules to makes sure everything is in place, you might see Windows Firewall as Warning status if Firewall ports are not configured properly.
Inbound TCP / UDP ports are required to be opened, such as ports 1433, 1434, 4022, 135.
If the named instance is the only instance of the Database Engine installed, it will probably use TCP port 1433
You can manually configure Firewall rules or can use following PowerShell commands:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “SQL Server” -Direction Inbound –Protocol TCP –LocalPort 1433 -Action allow
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “SQL Admin Connection” -Direction Inbound –Protocol TCP –LocalPort 1434 -Action allow
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “SQL Database Management” -Direction Inbound –Protocol UDP –LocalPort 1434 -Action allow
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “SQL Service Broker” -Direction Inbound –Protocol TCP –LocalPort 4022 -Action allow
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “SQL Debugger/RPC” -Direction Inbound –Protocol TCP –LocalPort 135 -Action allow
On Feature Selection page, select Database Enginer Services and Full-Text and Semantic Extractions.
On Instance Configuration, I am not going with Default instance, I will use Named instance, and specifying the name as INSTANCESCCM.
On Server Configuration, use the service account svc-SCCMAdmin which we created previously for the service SQL Server Agent and SQL Server Database Engine.
Under Authentication Mode, select Windows authentication mode and select Add Current User.
Click on tab Data Directories, and specify E drive rather than C drive for:
Data root directory
System database directory
User database directory
User database log directory
Backup directory
On tab TempDB, Data directories will be pointing to E drive now.
SQL Server 2019 setup is ready to install with ConfigurationFile.ini listed with all settings, click Install.
After waiting for few minutes, we see SQL installation completed, setup bootstrap logs can be viewed for installation logs.
It is always recommended to have latest version of patch applied. Hence, install latest version of cumulative update for SQL Server 2019 from Latest updates for SQL Server – SQL Server | Microsoft Docs
Install SQL Server Management Studio
As we have install SQL Server, but we cannot see or view the database without installing it. Download and install the SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Install Windows ADK 11 and WinPE add-on
This consists of 2 components:
- Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit
- Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit Windows Preinstallation Environment Add-ons
Windows ADK / Windows Assessment and deployment kit and WinPE add-on is a mandatory part of Configuration manager installation. Windows ADK is a set of tools required for Operating System deployment and other tasks related to deployment tools, deployment tools etc. This installation is required on SCCM Server.
Install Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit
Download adksetup.exe and initiate the installation. Adksetup.exe gives us the option to install it online and also to download it offline. Specify a Download Path to download the binaries, and once done initiate the installation.
We have following options to install:
- Application Compatibility Tools
- Deployment Tools
- Imaging And Configuration Designer (ICD)
- Configuration Designer
- User State Migration Tool (USMT)
- Volume Activation Management Tool (VAMT)
- Windows Performance Toolkit
- Microsoft User Experience Virtualization (UE-V) Template
- Microsoft Application Virtualization (App-V) Sequencer
- Microsoft Application Virtualization (App-V) Auto Sequencer
- Media eXperience Analyzer
We will be going with options marked in bold, rest others can be installed later on if it is required.
Install Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit Windows Preinstallation Environment Add-ons
Same way, download and install adkwinpesetup.exe, this component consists of Boot images required for OSD (operating system deployment) process. Download it to a path d:ADKWinPEAddons and initiate the installation.
Following boot images will be installed based upon various architecture:
Windows PE (x86)
Windows PE (AMD64)
Windows PE (ARM)
Windows PE (ARM64)
Under Program and features we will see the ADK & WinPE add-on is installed with version 10.1.22000.1
Install Prerequisites on Configuration Manager Server
Login to ConfigMgr server (SCCM Server) and launch Server Manager. Alternate way to launch Server Manager: On Windows + Run, type servermanager.exe.
From Server Manager Dashboard, click on Manage > Add Roles and Features. Under Server Roles select Web Server (IIS), selecting this will add additional features required for the components, click Add Features to continue.
On Add Roles and Features Wizard, Features page select few more components as those are not selected by default, make sure to select following:
- .NET Framework 3.5 Features
- Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)
- Remote Differential Compression
.NET framework 4.8 Features will be selected automatically, which is also a very important component for SCCM to work.
On Role Services page, select additional components, which is again very much important for Configuration Manager to work, and by default these components are not selected:
- Performance
- Dynamic Content Compression
- Security
- Windows Authentication
- Application Development
- .NET Extensibility 3.5
- .NET Extensibility 4.8 (or .NET Extensibility 4.7)
- ASP.NET 3.5
- ASP.NET 4.8 (or ASP.NET 4.7)
- ISAPI Filters
- Management Tools
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility
- IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility
- IIS 6 Management Console
- IIS Management Scripts and Tools
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility
On Confirmation page, you have to select the source path for .NET Framework 3.5 features which requires Windows Server source (ISO) and pointing to sourcesxs folder. Provide the path, in my case it was G:sourcesxs.
Installation will take a while, allow it to complete the install.
Create no_sms_on_drive.sms file.
What is no_sms_on_drive.sms ?
This is a file when created on root of the drive, configuration manager will no longer use the specific drive to install any component related to SCCM Site server, such as SCCM Content Library & other SMSPKG$, etc stuff.
How to create no_sms_on_drive.sms ?
Create an empty text file with name no_sms_on_drive.txt, rename the extension txt to sms so that it becomes no_sms_on_drive.sms
I created this file on C drive and E drive, hence will utilize D drive only for Config Mgr stuff.
This is the time now to do the actual stuff. We will be proceeding with installing the Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager using Baseline Media version 2103. Copy the binaries locally and launch splash to begin install SCCM 2103 using Baseline Media.
Click Install to initiate the process.
If don’t have .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 installed, we will see the error:
Setup requires .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 to continue
Hence, we need to make sure to install it before initiating the installation.
This will launch Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager Setup Wizard, click Next.
On Getting Started page, select Install a Configuration Manager primary site, along with other options we see here:
Install a Configuration Manager central administration site
Upgrade this Configuration Manager site
Recover a site
Perform site maintenance or reset this site
Uninstall this Configuration Manager site
On Product Key page, select Install the evaluation edition of this product, which gives us fully functional LAB for 180 days, we can later make it full licensed version as well.
On Product License Terms page, accept the conditions and click Next.
On Prerequisite Downloads page, provide the path to Download required files. We can Use previously downloaded files as well if it already exists.
We can download the prerequisite files from another system which has internet connectivity. Use Setupdl.exe which is located in folder SMSSETUPBINX64. Configuration Manager Setup downloader will be responsible to download the required binaries.
On Server Language Selection page, select any additional language you want, click Next.
On Client Language Selection page, select the language, click Next.
On Site and Installation Settings page, specify:
Site Code: <3 digit site code>
Site name: <Specify site name>
Installation folder: d:Program FilesMicrosoft Configuration Manager
Install the Configuration Manager console
On Primary Site Installation page, select Install the primary site as a stand-alone site. As there is no CAS site here, I am not selecting “Join the primary site to an existing hierarchy”
On Database Information page, select:
SQL Server name (FQDN):
Instance name: INSTANCESCCM
Database name: CM_MAN (created previously during SQL Server installation)
Service Broker Port: 4022 (default option elected automatically)
On Database Information page, I am using E drive for SQL Server data file and SQL Server log file, click Next.
On SMS Provider Settings page, specify SMS Provider (FQDN) which is going to be the SCCM server we are using, click Next.
On Client Computer Communication Settings page, select Configure the communication method on each site system role, click Next.
On Site System Roles, check the box Install a management point and Install a distribution point, click Next.
On Diagnostic and Usage Data page, click Next.
On Service Connection Point Setup page, select Yes if you have internet connection. This is an important step which connects on-premises infrastructure to cloud based solution such as mobile device management(MDM) / intune authority etc. With this step we are going to install Service Connection Point.
On Settings Summary page, verify Setup Component and Component Details and click Next.
Prerequisite Check will run and can be monitored through c:ConfigMgrPrereq.log. You might see SQL Server Tcp Port error with Status Failed. Follow the link to resolve the issue and Run Check.
You need to make sure to get rid of any Prerequisite Warning before initiating the install, I know these warnings won’t hamper SCCM installation setup hence I continued, but in production we need to get it resolved and setup properly.
Click on Begin Install to initiate the install.
This process will take time, you may monitor the installation through C:ConfigMgrSetup.log.
Conclusion
The installation is done for Configuration Manager but this is not in a fully functional configuration state which consists of enabling Discovery, configuring Boundary / Boundary groups, setting up Network Access Account and other settings.
1 — INTRODUCTION
2 — PREPARE FOR SCCM INSTALLATION
2.1 — SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS
2.2 — HARDWARE AND DISK LAYOUT REQUIREMENT
2.3 — IP CONFIGURATION
2.4 — SCCM NAMING CONVENTION
2.4.1 — Server Naming Convention
2.4.2 — Site Naming Convention
2.5 — CREATE SCCM VMS
3 — CREATE SCCM ACCOUNTS AND GROUPS
3.1 — CREATE SCCM ACCOUNTS
3.2 — CREATE SCCM GROUPS
3.3 — CREATE SCCM SERVER OU
4 — PREPARE THE FOREST
4.1 — WHY EXTEND THE ACTIVE DIRECTORY SCHEMA FOR SCCM
4.2 — EXTEND THE SCHEMA (MANUALLY)
4.2.1 — Identify Schema Admins Account
4.2.2 — Identify Forest Root Domain Controller Schema Master
4.2.3 — Log on to Forest Root Domain Schema Master
4.2.4 — Extend the Schema for SCCM 2019
4.2.5 — Verify Successful Schema Extension
4.2.6 — Verify DOMAIN Replication to Domain Controllers
5 — SYSTEM MANAGEMENT CONTAINER
5.1.1 — Create the System Management Container (Manaully)
5.1.2 — Set Security on the System Management Container (Manually)
6 — BUILD PRIMARY SCCM CB 1902 SITE (VP1)
6.1 — PRIMARY SITE SERVER NAMES AND ROLES
6.2 — PREP FOR SCCM AUTOMATED INSTALLATION
6.2.1 — Overview of SCCM PowerShell Install Script
6.2.2 — Create SCCM Staging Folders for Automated Deployment
6.2.3 — Create SCCMShare Folder
6.2.4 — Set Windows Firewall ports for SQL
6.2.5 — Create SQL Configuration file
6.2.6 — Create the SQL 2017 Reporting Service PS Scripts
6.2.7 — Create the Set Service Acct PS Scripts
6.2.8 — Create Report Server Encryption Key
6.2.9 — Download the Windows ADK 10 Files for Offline Use
6.2.10 — Download Windows PE_1903 as Separate Add-on
6.2.11 — Download SCCM CB v1902 Prerequisite Files
6.2.12 — Create the SCCM Setup.ini File for The Unattended Install
6.3 — INSTALL SCCM USING POWERSHELL
6.4 — INSTALL THE SCCM REPORTING SERVICES POINT
6.4.1 — Test SCCM Reports and SSRS Web site
6.4.2 — Configure Reporting Server Database Recovery Model
The sample scripts are not supported under any Microsoft standard support program or service. The sample scripts are provided AS IS without warranty of any kind. Microsoft further disclaims all implied warranties including, without limitation, any implied warranties of merchantability or of fitness for a particular purpose. The entire risk arising out of the use or performance of the sample scripts and documentation remains with you. In no event shall Microsoft, its authors, or anyone else involved in the creation, production, or delivery of the scripts be liable for any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of business profits, business interruption, loss of business information, or other pecuniary loss) arising out of the use of or inability to use the sample scripts or documentation, even if Microsoft has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
1 INTRODUCTION
The document outlines the steps required to install SCCM CB 1902 with SQL 2017 using PowerShell. These steps can be used on a disconnected network. The scripts included in this document can also be added to MDT to automate the install of SCCM CB 1902.
2 Prepare for SCCM Installation
2.1 Software Requirements
The following table outline the server specification that will be used to build the SRV-CM-01 server.
|
Application |
Where |
|
System Center Config Mgr (current branch 1902) |
From DVD or files on network share https://www.microsoft.com/Licensing/servicecenter/Downloads/DownloadsAndKeys.aspx |
|
SQL Server Enterprise Edition 2017 64 Bit |
From DVD or files on network share |
|
Cumulative Update Package 16 for SQL Server 2017 — KB4508218 |
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=56128 |
|
SQL Server Management Studio release (SSMS 18.3) |
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/ssms/download-sql-server-management-studio-ssms |
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2019, Standard |
From DVD or files on network share |
|
SCCM2019_PrereqCompFiles |
From URL…. From DVD or files on network share |
|
Visual C++ 2013 Redistributable Package Visual C++ Redistributable Packages for Visual Studio 2013 |
latest supported Visual C++ downloads https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4032938/update-for-visual-c-2013-redistributable-package https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40784 |
|
Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (WADK v1903) |
https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2086042 |
|
MDT 8456 |
Download the ADK from the following link: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=54259 |
2.2 Hardware and Disk Layout Requirement
Supported Configurations for Configuration Manager
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg682077.aspx
Note virtual servers will be used in the CONTOSO environment but the settings below applies to physical and virtual machines. The configuration below of a RAID 1 configuration is only a recommendation.
In this document ALL SCCM ROLES will be installed on a Single Server. The example below is for demonstration purposes only. The hardware used is outlined in the table below. Refer to SCCM hardware requirements for the best hardware configuration for your installation.
ROLES: ALL — (SRV-CM-01)
|
Component |
Specification |
|
CPU |
(4) 64 bit Single Processor 2.0 Ghz or Higher |
|
System Class |
VM/Server |
|
Memory |
16 GB or higher |
|
Network |
2 x Gigabit Ethernet network adapter (redundant) |
|
CD-ROM/DVD-ROM |
1 x CD-ROM/DVD-ROM |
|
Operating System |
Microsoft Windows Server 2019, Enterprise |
|
Disk |
(C:)(60gb+) RAID 1 for OS, page file (4k, NTFS) (D:)(100gb+) RAID 1 SCCM Inboxes, SCCMContentlib, (4k, NTFS) (E:)(150gb+) DP Content, SUP/WSUS, MDT, SCCMShare, WADK (4k, NTFS) (F:)(40gb+) RAID 5 for SQL DB (64k BlockSize, ReFS) (G:)(50gb+) RAID 1 for transaction logs,UserDBlog, SQL TempDB logs, SCCMBackup (64k BlockSize, ReFS) |
2.3 IP Configuration
SCCM IP Configuration
|
Server Name |
IP Numbers |
|
SRV-CM-01 |
192.168.x.x |
2.4 SCCM Naming Convention
2.4.1 Server Naming Convention
The following SCCM server naming convention will be used in the CONTOSO:
<TYPE>-<ROLE>-<INSTANCE>
Example: SRV-CM-01
2.4.2 Site Naming Convention
Site Naming Conventions
In the CONTOSO ConfigMgr hierarchy, a standard site naming convention will be used to ensure proper sorting of sites in the management console as well as to make troubleshooting processes faster and simpler.
Note if there are no current plans to have a central site, label the site as a primary (P) site.
The following SCCM server naming convention will be used in the CONTOSO:
<Network>-<Site>-<Instance>
Note the Central Administration Site name will be CAS.
Primary Site Naming conventions
Network:
· B=BALTIMORE
· C=CHICAGO
· N=NEWYORK
· V=VIRGINIA
Site:
· P=PRIMARY
Instance:
· The instance number
Examples:
· CAS=CAS SCCM site for organization
· VP1=First Primary SCCM site in Virginia
· CP1=First Primary SCCM site in Chicago
· CP2=Second Primary SCCM site in Chicago
· NP2=Second Primary SCCM site in New York
2.5 Create SCCM VMs
Create the VM for SCCM based on the specification above under Hardware and Disk Layout Requirement section.
3 Create SCCM Accounts and Groups
3.1 Create SCCM Accounts
Ensure that the following accounts have been created.
|
Account Name |
Location |
Description |
|
SVC-CM-Install |
AccountsInstall |
SCCM Install Account |
|
SVC-CM-CliPush |
AccountsService |
Client pus account that can be used to install the SCCM client. |
|
SVC-CM-RSP |
AccountsService |
Reporting Service Point SRS Execution account will be used to support the SCCM Reporting Services Point and SRS |
|
SVC-CM-NAA |
AccountsService |
SCCM Network Access account will be used to support OSD. |
|
SVC-SQLSC-01 |
AccountsService |
Account used as SQL service account for the SQL database that supports the SCCM server. |
3.2 Create SCCM Groups
Ensure that the following groups have been created and that the members listed are present in the listed groups.
|
Group Name |
Group Type |
Purpose |
Members |
|
ADM-SQL-ADMINS |
Domain Local |
Grants members SQL Administrative permission to SQL database |
TBD |
3.3 Create SCCM Server OU
Create the OU for The SCCM servers.
1. On a domain controller, create the following OU:
a. <CONTOSO.LOCALSERVERSCM>
2. All SCCM servers will be located in the OU above.
4 Prepare the Forest
4.1 Why Extend the Active Directory Schema for SCCM
When installing System Center Configuration Manager (ConfigMgr) you have to decide whether to extend the AD Schema or not.
ConfigMgr uses the Windows Active Directory (AD) environment to support many of the features it provides and can publish information to AD about sites and services. In this manner, the AD clients of ConfigMgr have this information easily accessible, but in order to use this feature the AD schema has to be extended in order to create the objects and the classes specific to ConfigMgr. Extending the schema is not required for the installation of ConfigMgr but it is recommended.
Extending the Active Directory Schema for ConfigMgr allows clients to retrieve many types of information related to Configuration Manager from a trusted source. In some cases, there are workarounds for retrieving the necessary information if the Active Directory schema is not extended, but they are all less secure than querying Active Directory Domain Services directly. Additionally, not extending the schema might incur significant workload on other administrators who might need to create and maintain the workaround solutions such as logon scripts and Group Policy objects (GPO) for computers and users in your organization. The Active Directory schema can be extended before or after running ConfigMgr Setup, however as a best practice, it’s best to extend the schema before you run Configuration Manager Setup. You have to extend the Active Directory schema only once for the forest that contains site servers; you do not have to extend the schema again if you upgrade the operating systems on the domain controllers or after you raise the domain or forest functional levels. Similarly, if you extended the schema for ConfigMgr with no service pack, you do not have to extend the schema again for ConfigMgr.
Extending the Active Directory schema is a forest-wide action and can only be done one time per forest. Extending the schema is an irreversible action and must be done by a user who is a member of the Schema Admins Group or who has been delegated sufficient permissions to modify the schema. If you decide to extend the Active Directory schema, you can extend it before or after setup. Only after the schema is AD extended and the steps needed to publish the ConfigMgr 2012 site information to AD, ConfigMgr can publish information to AD.
You can extend the AD Schema using either the extadsch.exe tool or the ConfigMgr_ad_schema.ldf file. When using the ldf file you will need to edit and configure this file. The extadsch.exe is easier to use and just needs a double click. The result of the extadsch.exe will write a log file in the root of C: of the computer from where the command was launched. You need to be a Schema Admin in order to make these changes and it is recommended to check with the AD administrator for permissions before extending the schema. If you need to see what happens and what changes are being made you can look at the ConfigMgr_ad_schema.ldf file.
While some Configuration Manager features depend on extending the schema, such as Network Access Protection in Configuration Manager and global roaming, there are workarounds for not extending the schema to enable other Configuration Manager features.
Four actions are required to successfully enable Configuration Manager clients to query Active Directory Domain Services to locate site resources:
· Extend the Active Directory schema.
· Create the System Management container.
· Set security permissions on the System Management container.
· Enable Active Directory publishing for the Configuration Manager site.
When extending the schema for Configuration Manager, several classes and attributes are added that any Configuration Manager site in the Active Directory forest can use. Because the global catalog is replicated throughout the forest, you must consider the network traffic that might be generated.
In Windows 2000 forests, extending the schema causes a full synchronization of the whole global catalog. For Windows 2003 forests, Windows 2008 forests, and Windows 2008 R2 forests, only the newly added attributes are replicated. You should plan to extend the schema during a time when the replication traffic does not adversely affect other network-dependent processes.
You can extend the Active Directory schema for ConfigMgr by running the ExtADSch.exe tool or by using the LDIFDE command-line tool to import the contents of the ConfigMgr_ad_schema.ldf LDIF file. Both the tool and the LDIF file are located in the SMSSETUPBINi386 directory of the Configuration Manager installation files. Regardless of the method that you use to extend the schema, two conditions must be met:
· The Active Directory schema must allow updates. On domains that are running Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, and Windows Server 2008 R2, by default the schema is enabled for updates. For domains that are running Windows 2000 Server, you must manually enable updates on the schema master for the Active Directory forest.
· The account that is used to update the schema must be either a member of the Schema Admins group or have been delegated sufficient permissions to modify the schema.
Using an LDIF file to extend the Active Directory schema instead of the ExtADSch.exe tool provides greater transparency about the changes being made to the Active Directory schema and also makes it easier to diagnose any problems encountered during the schema extension process.
You can use the LDIFDE command-line utility to import directory objects into Active Directory Domain Services using LDAP Data Interchange Format (LDIF) files. For greater visibility of the changes being made to the Active Directory schema than the ExtAdSch.exe utility provides, you can use the LDIFDE utility to import schema extension information using the ConfigMgr_ad_schema.ldf file is included on the Configuration Manager installation media in the .SMSSETUPBINi386 directory.
4.2 Extend the Schema (Manually)
Note PowerShell will not be used to extend the Schema.
SCCM uses AD to publish information about its sites and services, making it easily accessible to Active Directory clients. To leverage AD, we must extend the schema to create classes of objects specific to SCCM.
Client installation properties are published to Active Directory Domain Services if the schema is extended for Configuration Manager and read by client installations where CCMSetup is run without installation properties.
The System Management container is used to grant SCCM Permissions to Publish to the Active Directory. Each SCCM site requires explicit permissions to publish to the Active Directory. Child sites do not inherit permissions to the System Management container. Advanced clients use SCCM published information in active directory to find DPs, SLPs, and MPs.
Configuration Manager does not automatically create the System Management container in Active Directory Domain Services when the schema is extended. The container needs to be created once for each domain that includes any Configuration Manager site server that will publish site information to Active Directory Domain Services.
4.2.1 Identify Schema Admins Account
1. Log on a domain controller in the forest root domain.
2. Select Start, Run.
3. In the Run dialog box, type [dsa.msc].
4. In Active Directory Users and Computers, select the view menu, then activate (toggle) the Advanced Features.
5. Select the Users OU.
6. Right-click the Schema Admins global group icon.
7. Select Properties from the pop-up menu
8. Select the Members tab.
9. Double-click on the Domain Admins group to display the Properties screen.
10. Click on the Members tab.
11. Identify an account that is a member of Schema Admins and Domain Admins.
4.2.2 Identify Forest Root Domain Controller Schema Master
1. Log on a domain controller in the forest root domain.
2. Select Start, Run.
3. In the Run dialog box, type [cmd].
4. In the Command window, type dsquery server –forest –hasfsmo schema. The output displays the distinguished name of the server with the schema master role.
4.2.3 Log on to Forest Root Domain Schema Master
1. Locate the domain controller in the forest root domain with the Schema Master Role.
2. Log on with an account that is a member of Schema Admins and Domain Admins.
3. Verify Inbound Replication
4. Select Start, Run.
5. In the Run dialog box, type cmd.
6. In the Command window, type
i. repadmin /showreps.
ii. Note The output displays replication status in the INBOUND NEIGHBORS area of the screen.
7. Install the Active Directory Schema Snap-in
8. At the command prompt, type regsvr32 schmmgmt.dll to register the snap-in.
a. Note although the regsvr32 command shows that it is a 32-bit based command, it does run properly in the 64-bit versions of the supported operating systems.
9. Click OK.
10. At the command prompt, type mmc.
11. From the File menu, select Add/Remove Snap-in…
12. From the Add/Remove Snap-in screen, click the Active Directory Schema icon.
13. Click Add…then OK.
14. From the File menu, click Save to save the console.
15. From the Save in dropdown menu, locate the C:WINNTSystem32 directory.
16. In the File name field, type [schmmgmt.msc].
17. Click Save.
18. Close the Schema Management Console.
4.2.4 Extend the Schema for SCCM 2019
SCCM uses AD to publish information about its sites and services, making it easily accessible to Active Directory clients. To leverage AD, we must extend the schema to create classes of objects specific to SCCM.
Client installation properties are published to Active Directory Domain Services if the schema is extended for Configuration Manager and read by client installations where CCMSetup is run without installation properties.
The System Management container is used to grant SCCM Permissions to Publish to the Active Directory. Each SCCM site requires explicit permissions to publish to the Active Directory. Child sites do not inherit permissions to the System Management container. Advanced clients use SCCM published information in active directory to find DPs, SLPs, and MPs.
Configuration Manager does not automatically create the System Management container in Active Directory Domain Services when the schema is extended. The container needs to be created once for each domain that includes any Configuration Manager site server that will publish site information to Active Directory Domain Services.
Note: Only use the extadsch.exe file from the SCCM CD. If you use the extadsch.exe from active directory it will not create the proper attributes in Active Directory.
Schema extension must be done before any SCCM installation.
Note: ensure that the account used to extend the schema is in the Schema Admins group.
1. Locate the domain controller in the forest root domain with the Schema Master Role.
2. Logon to a domain controller as an account that is a member of the Schema Admins and domain admins.
3. Copy the following files to a folder on the local drive:
a. \SCCMShareSCCM_InstallFiles SCCM_2019SMSSETUPBIN<x64>
b. Note you must copy the entire …x64 folder to the domain controller to successfully run the extadsch.exe command. Coping the extadsch.exe along will fail.
4. At the command prompt, change directory to the local files
5. At the command prompt, type extadsch.exe and press Enter.
6. The following message displays:
Microsoft Systems Central xxx vX.00 (Build xxxx)
Copyright (C) 2011 Microsoft Corp.
a. Successfully extended the Active Directory Schema.
7. Finished.
4.2.5 Verify Successful Schema Extension
1. Review the Extadsch.log file located in the root of the C: drive on the Schema Master.
2. The output should be similar to the following:
<08-18-2012 14:20:19> Modifying Active Directory Schema — with SCCM extensions.
<08-18-2012 14:20:19> DS Root:CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=rko,DC=com
<08-18-2012 14:20:20> Defined attribute cn=MS-SMS-Site-Code.
<08-18-2012 14:20:20> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS -Assignment-Site-Code.
<08-18-2012 14:20:20> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS -Site-Boundaries.
<08-18-2012 14:20:20> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS -Roaming-Boundaries.
<08-18-2012 14:20:20> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS -Default-MP.
<08-18-2012 14:20:21> Defined attribute cn=mS- SMS -Device-Management-Point.
<08-18-2012 14:20:21> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS -MP-Name.
<08-18-2012 14:20:21> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS -MP-Address.
<08-18-2012 14:20:21> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS –Health-State.
<08-18-2012 14:20:21> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS –Source-Forest
<08-18-2012 14:20:21> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS -Ranged-IP-Low.
<08-18-2012 14:20:21> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS -Ranged-IP-High.
<08-18-2012 14:20:22> Defined class cn=MS- SMS -Management-Point.
<08-18-2012 14:20:22> Defined class cn=MS- SMS -Server-Locator-Point.
<08-18-2012 14:20:21> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS –Version
<08-18-2012 14:20:21> Defined attribute cn=MS- SMS -Capabilities
<08-18-2012 14:20:22> Defined class cn=MS- SMS -Site.
<08-18-2012 14:20:22> Defined class cn=MS- SMS -Roaming-Boundary-Range.
<08-18-2012 14:20:22> Successfully extended the Active Directory schema.
- Locate the entry Successfully extended the Active Directory Schema.
- If errors were reported, these should be resolved and the utility should be run again.
Verify SCCM Classes in the Active Directory
1. Open the Run dialog box by selecting Start, Run.
2. In the Run dialog box, type [schmmgmt.msc] then press [Enter].
Verify mSSMSSite Class
5. Expand the Active Directory Schema tree by clicking on the + symbol in the left pane.
6. Select the Classes folder to display the classes in the right pane.
7. From the right pane, locate the mSSMSSite class icon.
8. Right-click mSSMSSite icon, and select Properties from the pop-up menu.
9. From the mSSmSSite Properties screen, select the Attributes tab.
10. From the Attributes tab, verify the following attributes in the Optional area of the screen.
|
cn |
|
mSSMSAssignmentSiteCode |
|
mSSMSHealthState |
|
mSSMSRoamingBoundaries |
|
mSSMSSiteBoundaries |
|
MSSMSSiteCode |
|
mSSMSSourceForest |
|
serviceBindingInformation |
3.
4. Click the Cancel button to close the screen.
Verify mSSMSManagementPoint Class
- From the right pane, locate the mSSMSManagementPoint class icon.
- Right-click mSSMSManagementPoint class and select Properties from the pop-up menu.
- From the mSSMSManagementPoint Properties screen, select the Attributes tab.
- From the Attributes tab, verify the following attributes in the Optional area of the screen.
|
cn |
|
dNSHostName |
|
mSSMSCapabilities |
|
mSSMSDefaultMP |
|
mSSMSDeviceManagementPoint |
|
mSSMSMPAddress |
|
mSSMSMPName |
|
mSSMSSiteCode |
|
mSSMSSourceForest |
|
mSSMSVersion |
- Select Cancel.
Verify mSSMSServerLocatorPoint Class
- In the right pane, locate the mSSMSServerLocatorPoint class icon.
- Right-click mSSMSServerLocatorPoint class and select Properties from the pop-up menu.
- From the mSSMSServerLocatorPoint Properties screen, select the Attributes tab.
- From the Attributes tab, verify the following attributes in the Optional area of the screen.
|
cn |
|
dNSHostName |
|
mSSMSMPName |
|
mSSMSSiteCode |
|
mSSMSSourceForest |
- Select Cancel.
Verify mSSMSRoamingBoundaryRange Class
- In the right pane, locate the mSSMSRoamingBoundaryRange class icon.
- Right-click mSSMSRoamingBoundaryRange class and select Properties from the pop-up menu.
- Right-click mSSMSRoamingBoundaryRange class and select Properties from the pop-up menu.
- From the Attributes tab, verify the following attributes in the Optional area of the screen.
|
cn |
|
mSSMSAssignmentSiteCode |
|
mSSMSRangedIPHigh |
|
mSSMSSiteRangedIPLow |
|
mSSMSSiteCode |
|
mSSMSSourceForest |
- Select Cancel.
Verify SCCM Attributes in Active Directory Schema Snap-In
- In the left pane, click the Attributes folder.
- From the right pane, verify the following SCCM attributes are listed.
mSSMSAssignmentSiteCode
mSSMSCapabilities
mSSMSDefaultMP
mSSMSDeviceManagementPoint
mSSMSHealthState
mSSMSMPAddress
mSSMSMPName
mSSMSRangedIPHigh
mSSMSRangedIPLow
mSSMSRoamingBoundaries
mSSMSSiteBoundaries
mSSMSSiteCode
mSSMSSourceForest
mSSMSVersion
- Close the schmmgmt Console screen.
4.2.6 Verify DOMAIN Replication to Domain Controllers
- Login to another domain controller.
- In the elevated Command window, type [adsiedit.msc].
- In the ADSI Edit window, right-click on the ADSI Edit node icon.
- From the pop-up menu, click Connect to…
- In the Connection Settings screen, in the Select a well known Naming Context, select Schema and click Ok.
- From the ADSI Edit screen, expand Schema under the replication partner.
- Select the Schema folder.
- In the right pane, click the Class column to display the classSchema entries.
- Verify the following four SCCM schema classes are listed:
MS-SMS-Management-Point
MS-SMS-Roaming-Boundary-Range
MS-SMS-Server-Locator-Point
MS-SMS-Site
- Close the ADSI Edit window.
5 System Management Container
5.1.1 Create the System Management Container (Manaully)
The System Management container is used to grant SCCM Permissions to Publish to the Active Directory. Each SCCM site requires explicit permissions to publish to the Active Directory. Child sites do not inherit permissions to the System Management container. Advanced clients use SCCM published information in active directory to find DPs, SLPs, and MPs.
Configuration Manager does not automatically create the System Management container in Active Directory Domain Services when the schema is extended. The container needs to be created once for each domain that includes any Configuration Manager site server that will publish site information to Active Directory Domain Services.
Each domain maintains its own System Management container in Active Directory in its own domain partition. A domain controller does not replicate its System Management container to other domains in the forest.
In an Active Directory environment, the client queries Active Directory for a resident management point. It does this by searching the Active Directory global catalog for a site code, which has been registered (by a site server) with a matching Active Directory site name or IP address range.
NOTE
Remember that you create system management container one time in each domain that has a primary or secondary site. This will be used to publish data to Active Directory.
1. Logon to domain controller with an account that has permissions to create an Active Directory container.
2. Open the elevated command prompt.
3. Type adsiedit.msc, then press Enter.
4. Select Start, Run.
5. In the Run box, type adsiedit.msc.
6. Right click ADSI Edit and click Connect to.
7. On the Connection Settings window, the Name should be Default Naming Context. Click OK.
8. From the left pane, expand the Default naming context, expand Domain container <DC=CONTOSO,DC-COM>.
9. Right-click on CN=System.
10. Select New—Object from the pop-up menu.
11. From the Create Object screen, select container, then click Next.
12. From the next Create Object screen, in the Value text field type:
a. System Management.
13. Click Next.
14. Click Finish.
15. From the ADSI Edit screen, expand the CN=System node and visually verify that CN=System Management has been created.
16. Close the ADSI Edit screen.
5.1.2 Set Security on the System Management Container (Manually)
After you create System Management container, you must delegate SCCM server full permissions on System Management container.
For each site to create its site object, the System Management container must exist. The SCCM site server computer account must be granted full rights to the System Management container. After the site has generated its Active Directory site object, full rights to the Systems Management container can be removed and full permissions set only to the site object and all child objects, such as Management Points and Server Locator Points. Any time a secondary site is installed, the parent site will again need full permissions to the Systems Management container in order to create the secondary site’s site object.
Note: The SCCM Site server computer account will retain full control permission after the site object has been created to support the creation of subsequent SCCM secondary sites.
Note the ConfigMgr prerequisite checker displayed a warning when Verify site server permissions to Publish to Active Directory. Note the warning can be ignored. This is a warning, not an error, I’ve seen it on most of my SCCM installation. The setup application has no way to know if the site server can or cannot write to AD, so it throws the warning so you the admin should go and check to be sure. Confirm that the permissions are set promperly using a AD Group or the Site server compter account (It doesn’t matter which you use) and AD publishing works fine.
Note you can grant the site servers computer account Full Control permission to the System container in Active Directory Domain Services, which results in the site server automatically creating the System Management container when site information is first published to Active Directory Domain Services. However, it is more secure to manually create the System Management container.
Details:
- Logon to domain controller and launch Active Directory Users and Computers.
- From the Active Directory Users and Computers screen, select Advanced Features from the View menu.
- In the left pane, expand the Domain node (e.g., domain.com).
- Expand the System container.
- Right-click on the System Management container and select Properties from the pop-up menu.
- From the System Management Properties screen, select the Security tab.
- Click Add.
- In the Select Users, Computers, or Groups screen, type SRV-CM-01 in the Enter the object names to select text box.
- Click Check Names to verify the typed entry.
- Click OK.
- In the Permissions for SRV-CM-01, click the Full Control checkbox in the Allow column.
- Click the Advanced button.
- From the Advanced Security Settings for System Management screen, select SRV-CM-01.
- Click Edit.
- From the Permission Entry for System Management screen, click the Apply to: dropdown box.
- From the dropdown list, select This object and all desendant objects.
- In the Permissions pane under the Allow column, verify the Full Control checkbox is checked.
- At the Permission Entry for System Management screen, click OK.
- At the Advanced Security Settings for System Management screen, click OK.
- At the System Management Properties screen, click OK.
- Close the Active Directory Users and Computers screen.
==============================
Alternative Method of setting Permissions:
- Launch Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Click View and click Advanced Features.
- Expand System, right click System Management and click Delegate Control.
- On the Welcome page, click Next.
- Click Add.
- On select users, computers or groups window click on Object Types and check for Computers as object types. Click OK.
- Type the name of the primary site server computer account (SRV-CM-01) and click OK.
- This add primary site server computer account
- Click Next.
- On the Tasks to Delegate page, click Create a custom task to delegate. Click Next.
- On the Delegae Control Of page, Select This folder, existing objects in this folder and creation of new objects in this folder.
- Click Next.
- On the Permission page, Select General, Property Specific and Creation/deletion of specific child objects.
- Under Permissions, click Full Control. When you check the box Full Control, all the other permissions gets checked automatically.
- Click Next and click Finish to close the wizard.
6 BUILD PRIMARY SCCM CB 1902 SITE (VP1)
ALL SCCM ROLES will be install on One Server. This installation will be performed semi-automatically using PowerShell scripts.
6.1 Primary Site Server Names and Roles
SCCM Primary Site Server Names:
ROLES: ALL on One Server — (SRV-CM-01)
|
SCCM ROLE |
Server Name |
|
Site Server |
SRV-CM-01 |
|
Site Server Database |
SRV-CM-01 |
|
Reporting Point |
SRV-CM-01 |
|
Management Point |
SRV-CM-01 |
|
Distribution Point |
SRV-CM-01 |
|
PXE Service Point |
SRV-CM-01 |
|
Software Update Point |
SRV-CM-01 |
|
Fallback Status Point |
SRV-CM-01 |
|
EndPoint Protection Point |
SRV-CM-01 |
|
Application Catalog web service point |
SRV-CM-01 |
|
Application Catalog website point |
SRV-CM-01 |
6.2 Prep for SCCM Automated Installation
6.2.1 Overview of SCCM PowerShell Install Script
These scripts will be used to install SQL and SCCM on the SCCM Site server.
There will be two PowerShell script used:
· SCCM_CB_1902_PREP-11-15-2019.ps1
o The SCCM_CB_1902_PREP-11-15-2019.ps1 script will be use to create folders and set folder permission needed for the SCCM site server installation.
· SCCM_CB_1902_INSTALL-11-15-2019.ps1
o Use to install SCCM site server on local server.
The scripts will be running on the SCCM site server and will do the following:
- Set Folders permissions…
- Create the staging folders.
- Create the SQL folders.
- Grant the SVC-SQLSC-01 service account full control to these folders.
- Create the folders for the automated deployment of SCCM 2019.
6. Install IIS, BITS and .NET Framework 3.5.1
7. Install SQL Server 2017 Enterprise Edition.
a. Set SQL Service Accounts SPN
i. SVC-SQLSC-01 (VP1)
b. Install SQL Cummulative updates
c. Install SQL SSMS 18.3
i. **************
ii. Note the SQLCMD is included in the:
1. Microsoft ODBC Driver 13.1/17 for SQL Server
iii. Find out if it was installed with SQL 2017 or with SQL SSMS 18.3
iv. I believe its part of the SQL SSMS 18.3 install…Need to confirm…
v. ***********************
d. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
e. Configure SQL Memory
f. Install SQL 2017 Reporting Service
g. Set SQL 2017 Reporting Service Account
h. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
i. Configure SQL 2017 Reporting Service and Set Service Acct
8. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
9. Install ADK for Windows 1903
a. Install Windows ADK for Windows 10_1903
b. Install Windows PE_1903 as Separate Add-on
10. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
11. Configure NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS Files
12. Copy CMTrace
13. Install Remote Differential Compression
14. Install Microsoft Report Viewer 2012
a. Note Report Viewer 2012 is still needed for WSUS reports on a Windows 2019/2016 server.
15. Install and configure WSUS for SCCM (Unattended)
16. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
17. Run SCCM CB Prechecks
18. Install SCCM CB 1902 on Primary Site Server (VP1 Site)
- Finish.
Use the portions of the scripts when called for below.
===============================================
SCCM_CB_1902_PREP-11-15-2019.ps1
===========================================
1. See script below:
## Use the commands below to Install and Configure SCCM 2019 on a single server/PC.
##
## Create folders for the automatic deployment of SCCM 2019
## On the site server ensure these drives are present:
# (C:)(60gb+) RAID 1 for OS, page file (4k, NTFS)
# (D:)(100gb+) RAID 1 SCCM Inboxes, SCCMContentlib (4k, NTFS)
# (E:)(150gb+) DP Content, SUP/WSUS, MDT, SCCMShare (4k, NTFS)
# (F:)(40gb+) RAID 5 for SQL DB (64k BlockSize, ReFS)
# (G:)(50gb+) RAID 1 for transaction logs,UserDBlog, SQL TempDB logs, SCCMBackup (64k BlockSize, ReFS)
## On the Site server create the following folders on the outlined drives:
## Note copy the binary of all software that will be automated to this folder (SCCM,SQL, ADK Etc.. binaries):
# C:SCCM_STAGING
# W2019SourcesSxs
# SCCM_CB_1902
# SQL_2017_ENT
# SSMS_18.3
# Visual C++ 2013 Redistributable
# WADK_10_1809
# WINPE_FOR_ADK
## Create local folders for SCCM
### Create the SCCM Staging folder
New-Item C:SCCM_STAGING –Type Directory
New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGW2019SourcesSxs –Type Directory
New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902 –Type Directory
New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENT –Type Directory
New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_CU16 –Type Directory
New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_RS –Type Directory
New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGREPORT_VIEWER_2012 –Type Directory
New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGSSMS_18.3 –Type Directory
New-Item ‘C:SCCM_STAGINGVisual C++ 2013 Redistributable’ –Type Directory
New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGWADK_10_1903 –Type Directory
New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGWADK_10_WINPE_1903 –Type Directory
### STOP STOP STOP … Populate the above folders with the proper binaries ########
###############################################################################
### **** STOP ensure that folder above have been created and populated before proceeding ****
###############################################################################
# Create Folders for SQL Install:
# Grant the SQL service account (SVC-SQLSC-01) full control to the below folders.
# Note if SQL will be installed on a single storage/LUNS, then the folders can all be on the same drive letter.
# Note if this will be a multi-SQL instance, and all the SQL files will be place on a single storage/LUNS,
# -then create one drive letter per SQL instance. Meaning if you will have a SCCM and SCOM SQL instance then create a D:MSSQL and an E:MSSQL folder/VHDX.
# After folder creation, Grant the SQL service account (SVC-SQLSC-01) full control to the above folders.
New-Item F:MSSQL –Type Directory
New-Item F:MSSQLTempDB –Type Directory
New-Item F:MSSQLUserDB –Type Directory
New-Item G:MSSQL –Type Directory
New-Item G:MSSQLUserDBLOG –Type Directory
New-Item G:MSSQLTempDBLogs –Type Directory
New-Item G:MSSQLBackup –Type Directory
New-Item D:SRSReportKeys –Type Directory
###############################################################################
### **** STOP ensure that folder above have been created before proceeding to script #2 ****
###############################################################################
================================================
SCCM_CB_1902_INSTALL-11-15-2019.ps1
## Use the commands below to Install and Configure SCCM 2019 on a single server/PC.
##
## Do Not Proceed unless you have ran script # 1
###############################################################################################
############# Install SCCM 2019 Prerequisites #############################################
#### The script below assumes all SCCM and Prereqs files have been copied to the D:SCCM_STAGING folders.
# Install .NET Framework 3.5.1
# Ensure you copy the Windows 2019 DVDSourcesSxs folder in the staging folder
Dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:NetFx3 /All /Source:C:SCCM_STAGINGW2019SourcesSxs /LimitAccess
# Install BITS and IIS
# Bits is needed for the Distribution Point and Management Point.
Install-WindowsFeature BITS
Install-WindowsFeature Web-WMI
############# Install SQL 2017 #############################################
#### The script below assumes all SQL files have been copied to the D:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENT folders.
# Set SQL Service Accounts SPN
# Run on the Site Server or domain controller
setspn -A MSSQLSvc/SRV-CM-01.JCTECH.NET:1433 SVC-SQLSC-01
setspn -A MSSQLSvc/SRV-CM-01:1433 SVC-SQLSC-01
# Install SQL 2017 using SQL Configuration file
# Take a Snapshot/Checkpoint of VM.
#
# C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENTSetup.exe /QS /IACCEPTSQLSERVERLICENSETERMS /SQLSVCPASSWORD=»Password» /AGTSVCPASSWORD=»Password» /ASSVCPASSWORD=»Password» /ConfigurationFile=C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENTSQL2017ForSCCM1903.ini
C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENTSetup.exe /QS /IACCEPTSQLSERVERLICENSETERMS /SQLSVCPASSWORD=»Password» /AGTSVCPASSWORD=»Password» /ConfigurationFile=C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENTSQL2017ForSCCM1903.ini
# Install Latest Cumulative Update Package for SQL Server 2017
C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_CU16SQLServer2017-KB4508218-x64.exe /ACTION=INSTALL /QUIETSIMPLE /ALLINSTANCES /ENU /IACCEPTSQLSERVERLICENSETERMS /INDICATEPROGRESS
# Install SQL SSMS 18.3
# Note I install SSMS without the /norestart and it did not prompt for a restart. Need to determine if a reboot is required.
C:SCCM_STAGINGSSMS_18.3SSMS-Setup-ENU.exe /install /passive
# ******* Reboot the server here ******
# Configure SQL Memory
# Note you must reboot the server after the SSMS 18.3 install in order for the SQLCMD command to work.
# Note it is included in the Microsoft ODBC Driver 13/17 for SQL Server
# Set MAX to 8gb. Set MIN to 4gb
sqlcmd -S SRV-CM-01 -i C:SCCM_STAGINGSCRIPTSSetSQLMem.sql -o C:SCCM_STAGINGSCRIPTSSetSQLMem.log
# Install SQL 2017 Reporting Service
C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_RSSQLServerReportingServices.exe /passive /norestart /IAcceptLicenseTerms /PID=6GPYM-VHN83-PHDM2-Q9T2R-KBV83
# Configure SQL 2017 Reporting Service
& C:SCCM_STAGINGSCRIPTSConfigure-SQL2017RS.ps1
# Set SQL 2017 Reporting Service Account
& C:SCCM_STAGINGSCRIPTSSetReportServiceAcct.ps1
# ******* Reboot the server here ******
# Install Windows ADK for Windows 10_1903
# The command below will install Windows ADK version 1903 required features for SCCM.
# It will install the following features:
# • Deployment Tools
# • User State Migration Tool
C:SCCM_STAGINGWADK_10_1903adksetup.exe /quiet /installpath E:ADK /features OptionId.UserStateMigrationTool OptionId.DeploymentTools
# Sleep for 60 seconds to allow ADK for Windows 10_1903 to install
Start-Sleep -Seconds 60
# Install Windows ADK PE_1903
# Reboot the server after installation.
C:SCCM_STAGINGWADK_10_WINPE_1903adkwinpesetup.exe /quiet /ceip off /installpath E:ADK /Features OptionId.WindowsPreinstallationEnvironment /norestart
# Sleep for 60 seconds to all WINPE ADK PE_1903 to install
Start-Sleep -Seconds 60
# ******* Reboot the server here ******
############# Install SCCM 1902 #############################################
#### The script below assumes all SSCCM files have been copied to the D:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902 folders.
# Configure NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS Files
# Only configure on drive you DON’T want SCCM to install on. (C, F, G).
New-Item C:NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS -ItemType file
New-Item F:NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS -ItemType file
New-Item G:NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS -ItemType file
# Copy CMTrace
Copy C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902SMSSETUPTOOLSCMTrace.exe C:
# Remote Differential Compression for Windows Server 2019.
Install-WindowsFeature RDC
# Install REPORT VIEWER 2012 RUNTIME and Microsoft System CLR Types for Microsoft SQL Server 2012
# These are needed to read WSUS Reports.
msiexec /passive /norestart /i C:SCCM_STAGINGREPORT_VIEWER_2012SQLSysCLRTypes.msi
msiexec /passive /norestart /i C:SCCM_STAGINGREPORT_VIEWER_2012ReportViewer.msi
############# Install WSUS ##########################################
## When using a WID database for WSUS
## Install-WindowsFeature -Name UpdateServices -IncludeManagementTools
## & ‘C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesToolsWsusUtil.exe’ postinstall content_dir=E:WSUS
## When using a SQL database for WSUS
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Updateservices-Services,UpdateServices-DB -IncludeManagementTools
# If SQL server is installed on the default SQL instance (MSSQLSERVER) on the local server…run this:
& ‘C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesToolsWsusUtil.exe’ postinstall SQL_INSTANCE_NAME=»SRV-CM-01″ content_dir=E:WSUS
# If SQL server is installed on a remote SQL server instance (MSSQLSERVER or SCCM) include the remote server name and SQL instance:
# & ‘C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesToolsWsusUtil.exe’ postinstall SQL_INSTANCE_NAME=»SRV-CM-01″ content_dir=E:WSUS
# ******* Reboot the server here ******
# Run SCCM Precheck to confirm all prerequisites are in place
C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902SMSSETUPBINX64Prereqchk.exe /LOCAL
# Install SCCM unattended
C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902SMSSETUPBINX64Setup.exe /NOUSERINPUT /Script C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902SCCM_CB_1902_ALLROLES.ini
6.2.2 Create SCCM Staging Folders for Automated Deployment
These folders will be used to automate the SCCM installation. The PowerShell code below can be found in the SCCM_CB_1902_PREP-11-15-2019.ps1 script.
1. On the SCCM server create the following folders on the outlined drives by running this PowerShell command:
i. New-Item C:SCCM_STAGING –Type Directory
ii. New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGW2019SourcesSxs –Type Directory
iii. New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902 –Type Directory
iv. New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENT –Type Directory
v. New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_CU16 –Type Directory
vi. New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_RS –Type Directory
vii. New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGREPORT_VIEWER_2012 –Type Directory
viii. New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGSSMS_18.3 –Type Directory
ix. New-Item ‘C:SCCM_STAGINGVisual C++ 2013 Redistributable’ –Type Directory
x. New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGWADK_10_1903 –Type Directory
xi. New-Item C:SCCM_STAGINGWADK_10_WINPE_1903 –Type Directory
- *** STOP STOP STOP ****
- *** IMPORTANT copy the binaries to the folders above before prceeding.
*** BIG NOTE Populate the folders above with the proper binaries before proceeding.***
6.2.3 Create SCCMShare Folder
These folders will be used for files needed to operate SCCM. The PowerShell code below can be found in the SCCM_CB_1902_PREP-11-15-2019.ps1 script.
1. Logon to the server that will be used to house the files needed to support SCCM.
2. On the SCCM server create the following folders on the outlined drives by running this PowerShell command:
# Create the SCCM Share Folders
# These folders will be used for files needed to operate SCCM.
# This script creates the SCCM SHARE folder, Shares the folder and sets the NTFS and share permissions.
# Note the SVC-CM-NAA account is used for OSD.
# The SRV-CM-01$ computer account is optional and used to grant the server access to the share.
### Create the SCCM SHARE folder
New-Item D:SCCMSHARE –Type Directory
Get-Acl D:SCCMSHARE | Format-List
$acl = Get-Acl D:SCCMSHARE
$acl.SetAccessRuleProtection($True, $False)
# Applied to This Folder, Subfolders and Files
$rule = New-Object System.Security.AccessControl.FileSystemAccessRule(«Administrators»,»FullControl», «ContainerInherit, ObjectInherit», «None», «Allow»)
$acl.AddAccessRule($rule)
# Applied to This Folder, Subfolders and Files
# This group is used to grant the SVC-CM-NAA permissions to the SCCM folders.
$rule = New-Object System.Security.AccessControl.FileSystemAccessRule(«SVC-CM-NAA»,»FullControl», «ContainerInherit, ObjectInherit», «None», «Allow»)
$acl.AddAccessRule($rule)
# Applied to This Folder, Subfolders and Files
# Run these lines on a remote server (SRV-SC-01) that has the SCCM Share on it.
# These line grant the SCCM site server permission to the SCCM Share on a remote server.
# These line grant the SRV-CM-01$ computer account permissions to the SCCM folders on a remote server(SRV-SC-01).
# Remark these line out if the SCCM Share will be on the site server.
# $rule = New-Object System.Security.AccessControl.FileSystemAccessRule(«SRV-CM-01$»,»FullControl», «ContainerInherit, ObjectInherit», «None», «Allow»)
# $acl.AddAccessRule($rule)
# Applied to This Folder, Subfolders and Files
$rule = New-Object System.Security.AccessControl.FileSystemAccessRule(«System»,»FullControl», «ContainerInherit, ObjectInherit», «None», «Allow»)
$acl.AddAccessRule($rule)
# Apply the permision to the folder
Set-Acl D:SCCMSHARE $acl
### Share the folder…
# Use the method below to add multiple users/groups with the same permissions to the share
# Note do not add/include the domain name when setting the variables ($FullAccessAccts, $CHGAccessAccts, etc..)
# $CHGAccessAccts = (“SALEDPT”,”LOCALGRP”)
# $READAccessAccts=(“MARKGRP”,”BARKGRP”)
$FullAccessAccts = (“Administrators”,”SVC-CM-NAA”,»SRV-CM-01$»)
#New-SMBShare –Name “Shared” –Path “C:Shared” –FullAccess $FullAccessAccts –ChangeAccess $CHGAccessAccts –ReadAccess $READAccessAccts
#New-SMBShare –Name “Shared” –Path “C:Shared” –FullAccess “Administrators”
New-SMBShare –Name “SCCMSHARE” –Path “D:SCCMSHARE” –FullAccess $FullAccessAccts
# Create the SCCM Share sub Folders
# New-Item D:SCCMSHARE –Type Directory
New-Item D:SCCMShareImages –Type Directory
New-Item D:SCCMShareOSDDrivers –Type Directory
New-Item D:SCCMShareSCCM_InstallFiles –Type Directory
New-Item D:SCCMShareSMS_PkgSource –Type Directory
6.2.4 Set Windows Firewall ports for SQL
The default instance of SQL Server listens on Port 1433. Port 1434 is used by the SQL Browser Service which allows connections to named instances of SQL Server that use dynamic ports with out having to know what port each named instance is using, especially since this can change between restarts of the named instance.
Note the ports below open the firewall for SQL and SQL Reporting Services.
To Open the ports using PowerShell:
- Logon to the Site sever (SRV-CM-01).
- Open an administrative PowerShell prompt.
- Set Inbound Rules:
- New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “SQL TCP Ports” -Direction Inbound –Protocol TCP -Profile Domain –LocalPort 80,443,2382,2383,1433,1434,4022 -Action allow
- New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName “SQL UDP Ports” -Direction Inbound –Protocol UDP -Profile Domain –LocalPort 1434,4022 -Action allow
- Confirm ports has been opened in the firewall console.
6.2.5 Create SQL Configuration file
These steps are for SQL Server versions 2017 and later.
SQL Server Setup provides the ability to generate a configuration file based upon the system default and run-time inputs. You can use the configuration file to deploy SQL Server throughout the enterprise with the same configuration. You can also standardize manual installations throughout the enterprise, by creating a batch file that launches Setup.exe.
Set the following in the SQL Conifig INI File:
· SQL Service = CONTOSOSVC-SQLSC-01
· SQL Agent = CONTOSOSVC-SQLSC-01
· Do not install Analysis Service, it is not needed for SCCM.
Use the selections in the article below as a reference when selecting options for the SQL INI file.
Reference:
· Step 9 – Install SQL Server 2017
o https://www.prajwaldesai.com/sccm-1902-install-guide-using-baseline-media/#Step_9_Install_SQL_Server…
· Supported SQL Server versions for Configuration Manager
o https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/configmgr/core/plan-design/configs/support-for-sql-server-versions
· Install SQL Server using a configuration file
o https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/install-windows/install-sql-server-using-a-conf…
·
How to generate a configuration file
- Insert the SQL Server installation media. From the root folder, double-click Setup.exe.
- Note to install from a network share, locate the root folder on the share, and then double-click Setup.exe.
- Note SQL Server Express Edition setup does not create a configuration file automatically. The following command will start setup and create a configuration file.
c. SETUP.exe /UIMODE=Normal /ACTION=INSTALL
- Follow the wizard through to the Ready to Install page.
- The path to the configuration file is specified in the Ready to Install page in the configuration file path section.
- Cancel the setup without actually completing the installation, to generate the INI file.
a. The setup infrastructure writes out all the appropriate parameters for the actions that were run, with the exception of sensitive information such as passwords.
b. The /IAcceptSQLServerLicenseTerms parameter is also not written out to the configuration file and requires either a modification of the configuration file or a value to be supplied at the command prompt.
c. For more information, see Install SQL Server from the Command Prompt. In addition, a value is included for Boolean parameters where a value is usually not supplied through the command prompt.
4. SQL Progress NOTE — Edit the new SQL configuration file with notepad. Comment out the UIMODE = “NORMAL” line.
a. Note with the UIMODE = NORMAL, the SQL install stops on each setup page. It is not automated.
b. Note we will use the /QS switch on the SQL Setup.exe command line so we can see the progress.
5. Copy the SQL Configuration file to the C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENT<SQL2017ForSCCM1903.ini> folder.
SQL2017ForSCCM1903.ini
;SQL Server 2017 Configuration File
[OPTIONS]
; By specifying this parameter and accepting Microsoft R Open and Microsoft R Server terms, you acknowledge that you have read and understood the terms of use.
IACCEPTPYTHONLICENSETERMS=»False»
; Specifies a Setup work flow, like INSTALL, UNINSTALL, or UPGRADE. This is a required parameter.
ACTION=»Install»
; Specifies that SQL Server Setup should not display the privacy statement when ran from the command line.
SUPPRESSPRIVACYSTATEMENTNOTICE=»False»
; By specifying this parameter and accepting Microsoft R Open and Microsoft R Server terms, you acknowledge that you have read and understood the terms of use.
IACCEPTROPENLICENSETERMS=»False»
; Use the /ENU parameter to install the English version of SQL Server on your localized Windows operating system.
ENU=»True»
; Setup will not display any user interface.
QUIET=»False»
; Setup will display progress only, without any user interaction.
QUIETSIMPLE=»False»
; Parameter that controls the user interface behavior. Valid values are Normal for the full UI,AutoAdvance for a simplied UI, and EnableUIOnServerCore for bypassing Server Core setup GUI block.
; UIMODE=»Normal»
; Specify whether SQL Server Setup should discover and include product updates. The valid values are True and False or 1 and 0. By default SQL Server Setup will include updates that are found.
UpdateEnabled=»False»
; If this parameter is provided, then this computer will use Microsoft Update to check for updates.
USEMICROSOFTUPDATE=»False»
; Specify the location where SQL Server Setup will obtain product updates. The valid values are «MU» to search Microsoft Update, a valid folder path, a relative path such as .MyUpdates or a UNC share. By default SQL Server Setup will search Microsoft Update or a Windows Update service through the Window Server Update Services.
UpdateSource=»MU»
; Specifies features to install, uninstall, or upgrade. The list of top-level features include SQL, AS, IS, MDS, and Tools. The SQL feature will install the Database Engine, Replication, Full-Text, and Data Quality Services (DQS) server. The Tools feature will install shared components.
FEATURES=SQLENGINE,CONN
; Displays the command line parameters usage
HELP=»False»
; Specifies that the detailed Setup log should be piped to the console.
INDICATEPROGRESS=»False»
; Specifies that Setup should install into WOW64. This command line argument is not supported on an IA64 or a 32-bit system.
X86=»False»
; Specify a default or named instance. MSSQLSERVER is the default instance for non-Express editions and SQLExpress for Express editions. This parameter is required when installing the SQL Server Database Engine (SQL), or Analysis Services (AS).
INSTANCENAME=»MSSQLSERVER»
; Specify the root installation directory for shared components. This directory remains unchanged after shared components are already installed.
INSTALLSHAREDDIR=»F:MSSQL»
; Specify the root installation directory for the WOW64 shared components. This directory remains unchanged after WOW64 shared components are already installed.
INSTALLSHAREDWOWDIR=»F:MSSQLx86″
; Specify the Instance ID for the SQL Server features you have specified. SQL Server directory structure, registry structure, and service names will incorporate the instance ID of the SQL Server instance.
INSTANCEID=»MSSQLSERVER»
; TelemetryUserNameConfigDescription
SQLTELSVCACCT=»NT ServiceSQLTELEMETRY»
; TelemetryStartupConfigDescription
SQLTELSVCSTARTUPTYPE=»Automatic»
; Specify the installation directory.
INSTANCEDIR=»F:MSSQL»
; Agent account name
AGTSVCACCOUNT=»CONTOSOsvc-sqlsc-01″
; Auto-start service after installation.
AGTSVCSTARTUPTYPE=»Automatic»
; CM brick TCP communication port
COMMFABRICPORT=»0″
; How matrix will use private networks
COMMFABRICNETWORKLEVEL=»0″
; How inter brick communication will be protected
COMMFABRICENCRYPTION=»0″
; TCP port used by the CM brick
MATRIXCMBRICKCOMMPORT=»0″
; Startup type for the SQL Server service.
SQLSVCSTARTUPTYPE=»Automatic»
; Level to enable FILESTREAM feature at (0, 1, 2 or 3).
FILESTREAMLEVEL=»0″
; Set to «1» to enable RANU for SQL Server Express.
ENABLERANU=»False»
; Specifies a Windows collation or an SQL collation to use for the Database Engine.
SQLCOLLATION=»SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS»
; Account for SQL Server service: DomainUser or system account.
SQLSVCACCOUNT=»CONTOSOsvc-sqlsc-01″
; Set to «True» to enable instant file initialization for SQL Server service. If enabled, Setup will grant Perform Volume Maintenance Task privilege to the Database Engine Service SID. This may lead to information disclosure as it could allow deleted content to be accessed by an unauthorized principal.
SQLSVCINSTANTFILEINIT=»False»
; Windows account(s) to provision as SQL Server system administrators.
SQLSYSADMINACCOUNTS=»CONTOSOadministrator» «BUILTINAdministrators» «CONTOSOsvc-sqlsc-01» «CONTOSOADM-SQL-ADMINS»
; The number of Database Engine TempDB files.
SQLTEMPDBFILECOUNT=»2″
; Specifies the initial size of a Database Engine TempDB data file in MB.
SQLTEMPDBFILESIZE=»8″
; Specifies the automatic growth increment of each Database Engine TempDB data file in MB.
SQLTEMPDBFILEGROWTH=»64″
; Specifies the initial size of the Database Engine TempDB log file in MB.
SQLTEMPDBLOGFILESIZE=»8″
; Specifies the automatic growth increment of the Database Engine TempDB log file in MB.
SQLTEMPDBLOGFILEGROWTH=»64″
; Default directory for the Database Engine backup files.
SQLBACKUPDIR=»G:MSSQLBackup»
; Default directory for the Database Engine user databases.
SQLUSERDBDIR=»F:MSSQLUserDB»
; Default directory for the Database Engine user database logs.
SQLUSERDBLOGDIR=»G:MSSQLUserDBLOG»
; Directories for Database Engine TempDB files.
SQLTEMPDBDIR=»F:MSSQLTempDB»
; Directory for the Database Engine TempDB log files.
SQLTEMPDBLOGDIR=»G:MSSQLTempDBLogs»
; Provision current user as a Database Engine system administrator for %SQL_PRODUCT_SHORT_NAME% Express.
ADDCURRENTUSERASSQLADMIN=»False»
; Specify 0 to disable or 1 to enable the TCP/IP protocol.
TCPENABLED=»1″
; Specify 0 to disable or 1 to enable the Named Pipes protocol.
NPENABLED=»0″
; Startup type for Browser Service.
BROWSERSVCSTARTUPTYPE=»Disabled»
6.2.6 Create the SQL 2017 Reporting Service PS Scripts.
After installing SSRS 2017, it will be completely unconfigured. Configuration can be done using the Reporting Service Configuration Manager GUI. In the steps below we will use a PowerShell script to automate the configuration of the reporting service.
Downloaded from Github:
https://gist.github.com/SvenAelterman/f2fd058bf3a8aa6f37ac69e5d5dd2511
The Configure-Sql2017RS.ps1 PowerShell Script
The Configure-Sql2017RS.ps1 script itself has comments that will hopefully allow you to follow the flow, but here is a quick overview of the different steps:
- Get a WMI object with the configuration settings for the SSRS 2017 instance.
- Get a SQL script to create the ReportServer and ReportServerTempDB databases.
- Establish a connection to the default SQL Server instance on the same machine.
- Execute the SQL script.
- Get and execute a second SQL script, this time to set the permissions for the SSRS 2017 service account.
- Set the SSRS database connection to this newly created database.
- Configure the virtual directory name and URL of the web service.
- Configure the virtual directory name and URL of the report manager web app.
- Initialize the report server with encryption for sensitive data.
- Restart the service.
- Output the new configuration.
Details:
1. Create a PowerShell script name Configure-Sql2017RS.ps1 using the code below.
2. After creating the script, copy the script to the following folder on the SQL Reporting Service server:
a. C:SCCM_STAGINGSCRIPTSConfigure-Sql2017RS.ps1
3. Note this script will be called from the SCCM_CB_1902_INSTALL-11-15-2019.ps1 script below.
4. Finish.
=========== POWERSHELL SCRIPTS ==================
Configure-Sql2017RS.ps1
<#
#>
function Get-ConfigSet()
{
return Get-WmiObject –namespace «rootMicrosoftSqlServerReportServerRS_SSRSv14Admin» `
-class MSReportServer_ConfigurationSetting -ComputerName localhost
}
# Allow importing of sqlps module
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Force
# Retrieve the current configuration
$configset = Get-ConfigSet
$configset
If (! $configset.IsInitialized)
{
# Get the ReportServer and ReportServerTempDB creation script
[string]$dbscript = $configset.GenerateDatabaseCreationScript(«ReportServer», 1033, $false).Script
# Import the SQL Server PowerShell module
Import-Module sqlps -DisableNameChecking | Out-Null
# Establish a connection to the database server (localhost)
$conn = New-Object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Common.ServerConnection -ArgumentList $env:ComputerName
$conn.ApplicationName = «SSRS Configuration Script»
$conn.StatementTimeout = 0
$conn.Connect()
$smo = New-Object Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server -ArgumentList $conn
# Create the ReportServer and ReportServerTempDB databases
$db = $smo.Databases[«master»]
$db.ExecuteNonQuery($dbscript)
# Set permissions for the databases
$dbscript = $configset.GenerateDatabaseRightsScript($configset.WindowsServiceIdentityConfigured, «ReportServer», $false, $true).Script
$db.ExecuteNonQuery($dbscript)
# Set the database connection info
$configset.SetDatabaseConnection(«(local)», «ReportServer», 2, «», «»)
$configset.SetVirtualDirectory(«ReportServerWebService», «ReportServer», 1033)
$configset.ReserveURL(«ReportServerWebService», «http://+:80», 1033)
# For SSRS 2016-2017 only, older versions have a different name
$configset.SetVirtualDirectory(«ReportServerWebApp», «Reports», 1033)
$configset.ReserveURL(«ReportServerWebApp», «http://+:80», 1033)
$configset.InitializeReportServer($configset.InstallationID)
# Re-start services?
$configset.SetServiceState($false, $false, $false)
Restart-Service $configset.ServiceName
$configset.SetServiceState($true, $true, $true)
# Update the current configuration
$configset = Get-ConfigSet
# Output to screen
$configset.IsReportManagerEnabled
$configset.IsInitialized
$configset.IsWebServiceEnabled
$configset.IsWindowsServiceEnabled
$configset.ListReportServersInDatabase()
$configset.ListReservedUrls();
$inst = Get-WmiObject –namespace «rootMicrosoftSqlServerReportServerRS_SSRSv14» `
-class MSReportServer_Instance -ComputerName localhost
$inst.GetReportServerUrls()
}
6.2.7 Create the Set Service Acct PS Scripts
Create the SetReportServiceAcct.ps1 PowerShell Script
This script will be used to:
· Set the Reporting Service Service Account to a specific domain account:
Downloaded from Github:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/34769856/change-ms-sql-reporting-service-account-to-built-in-net…
Note run this after you have configured the Reporting Service above.
1. Login to the SQL reporting service server.
2. Create a PowerShell script name SetReportServiceAcct.ps1 using the code below.
3. Edit the script and set the following variables for your environment:
a. $serviceAccount = <«CONTOSOsvc-cm-rsp»>
b. $servicePW = <«PASSWORD99»>
4. After downloading script, copy the script to the following folder on the SQL Reporting Service server:
a. C:SCCM_STAGINGSCRIPTSSetReportServiceAcct.ps1
5. Note this script will be called from the SCCM_CB_1902_INSTALL-11-15-2019.ps1 script below.
6. Finish.
=========== POWERSHELL SCRIPTS ==================
SetReportServiceAcct.ps1
$ns = «rootMicrosoftSqlServerReportServerRS_SSRSv14Admin»
$RSObject = Get-WmiObject -class «MSReportServer_ConfigurationSetting» -namespace «$ns»
# Set service account
$serviceAccount = «CONTOSOsvc-cm-rsp»
$servicePW = «PASSWORD99»
$useBuiltInServiceAccount = $false
$RSObject.SetWindowsServiceIdentity($useBuiltInServiceAccount, $serviceAccount, $servicePW) | out-null
# Need to reset the URLs for domain service account to work
$HTTPport = 80
$RSObject.RemoveURL(«ReportServerWebService», «http://+:$HTTPport», 1033) | out-null
$RSObject.RemoveURL(«ReportServerWebApp», «http://+:$HTTPport», 1033) | out-null
$RSObject.SetVirtualDirectory(«ReportServerWebService», «ReportServer», 1033) | out-null
$RSObject.SetVirtualDirectory(«ReportServerWebApp», «Reports», 1033) | out-null
$RSObject.ReserveURL(«ReportServerWebService», «http://+:$HTTPport», 1033) | out-null
$RSObject.ReserveURL(«ReportServerWebApp», «http://+:$HTTPport», 1033) | out-null
# Restart SSRS service for changes to take effect
$serviceName = $RSObject.ServiceName
Restart-Service -Name $serviceName -Force
6.2.8 Create Report Server Encryption Key
- Click on Encryption Keys, then click on Restore.
- File Location: D:SRSReportKeys
- File name: SRSReportkey2017.snk
- Password: xxxxxx
6.2.9 Download the Windows ADK 10 Files for Offline Use
Note if you’re installing the ADK files to a system that does not have Internet access, you’ll need to download the files to a system that has Internet access first.
Note the step below will make the ADK files available for an offline PC so it does not download 1-3 GB every time.
Download the ADK v1903 from the following link:
https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2086042
What’s new in ADK tools for Windows 10, version 1903
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/get-started/what-s-new-in-kits-and-tools
Make the ADK files available for an offline PC so it does not download 1-3 GB every time:
- On an Internet connected PC, Download the executable for Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (ADK for Windows 10_v1903) from:
- https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2086042
- Open an administrative command prompt and type:
- adksetup /quiet /layout D:WADK_10_1903_Offline
- Note this download the required files, and can take a while depending on internet connection as it is a 1.1GB download.
- Note the above command downloads it to:
i. (D:WADK_10_1903_Offline)
3. After downloading the files, copy the downloaded Windows Kit files to the following folder on the SCCM server:
- C:SCCM_STAGINGWADK_10_1903
- Finish.
6.2.10 Download Windows PE_1903 as Separate Add-on
Note as you realize the Windows PE feature is not in Windows ADK 1903. You must download a separate add-on to install.
Download the Windows PE add-on for the ADK
https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2087112
DOWNLOAD:
- On the SCCM Primary site server, run the following file (Run as Administrator):
- adkwinpesetup.exe /quiet /layout D:WADK_10_WINPE_1903_Offline
- Note this download the required files, and can take a while depending on internet connection as it is a 3.1GB download.
- Note the above command downloads it to:
i. (D:WADK_10_WINPE_1903_Offline)
2. After downloading the files, copy the downloaded Windows PE files to the following folder on the SCCM server:
- C:SCCM_STAGINGWADK_10_WINPE_1903
- Finish
6.2.11 Download SCCM CB v1902 Prerequisite Files
In order to install SCCM on a network not connected to the Internet you first need to download the SCCM Updated Prerequisite Files. The files can only be downloaded from a machine connected to the Internet.
Ensure that the directory used to store prerequisite update files does not contain previously downloaded files. Previous prereq downloads cannot be used for current site installations.
To download the files:
1. On a machine which has connection to the internet insert the SCCM CB v1902 source media.
2. Run the following command:
a. “<sccm source media>SMSSETUPBINx64setupdl.exe <path to be stored>”
i. Note: Where is <path to be stored> you could use a network share if that is an option. Otherwise USB storage media’s
b. Example:
i. X: SMSSETUPBINx64setupdl.exe D:SCCM_CB_1902_PREQCOMP
3. Note if you receive an error about prerequisite can’t be downloaded check IE settings as follows:
a. Go into Internet Explorer-Tools-Connections-LAN Settings.
b. Check the «Automatically Detect Settings«.
c. Try the download again..
4. After downloading the files, copy the downloaded files to the following folder on the SCCM SITE server:
- C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902_PREQCOMP
5. Finish.
6.2.12 Create the SCCM Setup.ini File for The Unattended Install
The installation script is automatically created when you run Setup to install a site using the user interface. When you confirm the settings on the Summary page of the wizard, the following happens:
- Setup creates the script %TEMP%ConfigMgrAutoSave.ini. You can rename this file before you use it, but it must retain the .ini file extension.
- The unattended installation script contains the settings that you selected in the wizard.
- After the script is created, you can modify the script to install other sites in your hierarchy.
- You can then use this script to perform an unattended setup of Configuration Manager.
This script file provides the same information that the Setup Wizard prompts for, except that there are no default settings.
You must specify all values for the Setup keys that apply to the type of installation that you are using.
Note we will not install SCCM. We are only walking through these steps to capture the settings to the .INI file. We will not click Begin Install on the last screen.
Note after creating the SCCM unattend file (setup.ini) below, you can further customize it using the following link:
· Use the following information to configure scripts or to install Configuration Manager from a command line.
· Command-line options for Configuration Manager setup
o https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/servers/deploy/install/command-line-options-for-setup
o https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/servers/deploy/install/use-a-command-line-to-install-site…
Create Setup.ini File:
1. Log on to the site server (SRV-CM-01) with the ConfigMgr install account(SVC-CM-Install). The account must have local administrator permissions on the system and Full Control within the SCCM database upon installation of SCCM.
2. Launch the ConfigMgr CB 1902 installation program.
a. Note the install files are located at C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902
- Launch the splash.hta file.
- Note If presented with an Internet Explorer Script Error then click Yes.
- Click Install on the Configuration Manager Setup Splash screen.
- On the Before You Begin screen make sure you have done the listed steps and click Next.
- On the Getting Started —Available Setup Options screen select:
- Install a Configuration Manager primary Site
- Click Next.
- On the Product Key screen, enter the product key. then select:
- Note I did not select a Software Assurance Date.
- Click Next.
- On the Product License Terms screen check the boxes I accept the terms and click Next.
- On the Prerequisite Downloads screen, click Use Previously downloaded files, then click Browse and select:
- C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902_PRECOMP
- On the Server Language Selection screen click Next.
- Note English is installed/selected by default.
- Note you can modify the server languages if you run setup again and select the Site Maintenance option.
- On the Client Language Selection screen click Next.
- Note English is installed/selected by default.
- Note you can modify the client languages if you run setup again and select the Site Maintenance option.
- On the Site and Installation Settings screen:
a. In the Site Code box:
i. <VP1>
b. In the Site Name box, type:
i. SCCM CB <VP1> Site
c. In the Installation Folder box, type:
i. D:SCCM.
d. Select the Install the Configuration Manager console box.
- Click Next.
- On the Primary Site Installation page, select:
- Install the primary site as a standalone.
- Note on the pop up dialog box that says ….expand this site into a hierarch at a later time by installing central administration…click Yes.
- Click Next.
- On the Database Information screen, enter the following:
- SQL Server Name (FQDN): SRV-CM-01.JCTECH.LOCAL
i. Note if SQL on a remote system:
1. SQLSC-01.contoso.local
- Instance Name:
i. If SQL is local:
1. Leave blank for default local SQL Instance
ii. If SQL is Remote:
1. Instance Name: SCCM
- Database name: CM_VP1
- Service Broker Port: 4022
i. Note specify the information for the site database server and the SQL Server Service Broker (SSB) port used by the SQL Server
- Click Next.
- On the next Database Information screen, enter:
- Path to the SQL Server data file:
i. F:MSSQLUserDB
ii. Note these path are on the remote SQL server
- Path to the SQL Server log file:
i. G:MSSQLUserDBLogs
ii. Note these path are on the remote SQL server.
- Click Next.
- On the SMS Provider Settings page, type:
- SMS Provider (FQDN): SRV-CM-01.JCTECH.LOCAL
- Click Next.
- On the Client Computer Communication Settings page, select:
- Configure the communication method on each site system role.
- Note do not select Clients will use HTTPS when they have a valid PKI….
- Click Next.
- On the Site System Roles page,
- For a all role on one SCCM server:
i. Select the Install a management point
ii. Select the Install a distribution point
- On the Diagnostic and Usage Data page, click Next.
- On the Service Connection Point Setup page, click:
- Yes, lets’get connected (Recommended)
- Select a server to use as the service connection point (Requires Internet Access)
- Note selecting this option works on a disconnected network install of SCCM CB 1902. After the installation is complete you can change the SCP Mode to Offline. On-demand connection.
- Setting this option prevents the SCP error message when opening the SCCM console on an disconnected network.
- Click Next.
- On the Settings Summary screen review the summary of the settings click Next.
- On the Prerequisite Check screen, ensure that all tests have passed:
- WSUS on site Server … Warning
i. This can be ignored for now if you’re planning to install WSUS on this server later.
- Verify site server permissions to publish to Active Directory…Warning
i. Note the ConfigMgr prerequisite checker displayed a warning when Verify site server permissions to Publish to Active Directory. Note the warning can be ignored. This is a warning, not an error, I’ve seen it on most of my SCCM installation. The setup application has no way to know if the site server can or cannot write to AD, so it throws the warning so you the admin should go and check to be sure. Confirm that the permissions are set promperly using a AD Group or the Site server compter account (It doesn’t matter which you use) and AD publishing works fine.
ii. I’ve noticed that you can not avoid this message regardless if you use the Site server computer account or an AD group.
- SQL Server process memory allocaton…Warning
i. Note this warning is because the Minimum amount of memory set on the SQL server is less than 8gb. To clear this error set the minimum memory setting in SQL to a minimum of 8gb. If you have less than 8gb you can ignore this warning.
- DO NOT click Begin Install.
- Collect the SCCM Installation Setup.ini file:
- Navigate to %TEMP% or C:Users<LOGINUSER>AppDataLocalTemp
i. Note the installation script is automatically created when you run Setup to install a site using the user interface. When you confirm the settings on the Summary page of the wizard, the following happens:
1. Setup creates the script %TEMP%ConfigMgrAutoSave.ini. You can rename this file before you use it, but it must retain the .ini file extension.
- Copy the ConfigMgrAutoSave.ini file to:
- C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902SCCM_CB_1902_ALLROLES.ini
- Cancel the SCCM Install.
- Follow steps in the next section to launch SCCM installation.
SCCM_CB_1902_ALLROLES.ini
[Identification]
Action=InstallPrimarySite
[Options]
ProductID=xxxx-xxxx-xxx-xxx-xxx
SiteCode=VP1
SiteName=VP1 Site
SMSInstallDir=D:SCCM
SDKServer=SRV-CM-01.CONTOSO.LOCAL
RoleCommunicationProtocol=HTTPorHTTPS
ClientsUsePKICertificate=0
PrerequisiteComp=1
PrerequisitePath=C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902_PRECOMP
MobileDeviceLanguage=0
ManagementPoint=SRV-CM-01.CONTOSO.LOCAL
ManagementPointProtocol=HTTP
DistributionPoint=SRV-CM-01.CONTOSO.LOCAL
DistributionPointProtocol=HTTP
DistributionPointInstallIIS=0
AdminConsole=1
JoinCEIP=0
[SQLConfigOptions]
SQLServerName=SRV-CM-01.CONTOSO.LOCAL
SQLServerPort=1433
DatabaseName=CM_VP1
SQLSSBPort=4022
SQLDataFilePath=F:MSSQLUserDB
SQLLogFilePath=G:MSSQLUserDBLOG
[CloudConnectorOptions]
CloudConnector=0
CloudConnectorServer=SRV-CM-01.CONTOSO.LOCAL
UseProxy=0
ProxyName=
ProxyPort=
[SystemCenterOptions]
SysCenterId=QQ08RZLD2hnzmBTdavcwZl4Yjpv6vJZOrNN4rOfEpLg=
[SABranchOptions]
SAActive=1
CurrentBranch=1
[HierarchyExpansionOption]
6.3 Install SCCM Using PowerShell
Use this script to install the SCCM site server.
The SCCM_CB_1902_INSTALL-11-15-2019.ps1 script will be ran on the local SCCM Site server and will do the following:
1. Install IIS, BITS and .NET Framework 3.5.1
2. Install SQL Server 2017 Enterprise Edition.
a. Set SQL Service Accounts SPN
i. SVC-SQLSC-01 (VP1)
b. Install SQL Cummulative updates
c. Install SQL SSMS 18.3
3. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
a. Configure SQL Memory
4. Install SQL 2017 Reporting Service
a. Set SQL 2017 Reporting Service Account
5. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
6. Configure SQL 2017 Reporting Service and Set Service Acct
7. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
8. Install ADK for Windows 1903
a. Install Windows ADK for Windows 10_1903
b. Install Windows PE_1903 as Separate Add-on
9. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
10. Configure NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS Files
11. Copy CMTrace
12. Install Remote Differential Compression
13. Install Microsoft Report Viewer 2012
a. Note Report Viewer 2012 is still needed for WSUS reports on a Windows 2019/2016 server.
14. Install and configure WSUS for SCCM (Unattended)
15. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
16. Run SCCM CB Prechecks
17. Install SCCM CB 1902 on Primary Site Server (VP1 Site)
18. *** REBOOT THE SERVER ***
DETAILS:
The SCCM_CB_1902_INSTALL-11-15-2019.ps1 script has all the commands in it to install SCCM CB. Reboots are required after certain steps in the script. Review the script before running it to determine when to reboot the server. Run the script a portion at a time. Ensure that you reboot the server when mentioned.
On the SCCM Site Server, run the SCCM_CB_1902_INSTALL-11-15-2019.ps1:
1. On the SCCM Site server, open a PowerShell command prompt with administrative permissions.
2. Open the script and review its content. Pay attention to REBOOT SERVER entries.
3. Run the following PowerShell script a portions at a time honoring the server reboots:
a. SCCM_CB_1902_INSTALL-11-15-2019.ps1
4. Vertify the Install:
a. Option#1) Verify verson SCCM CB v1902
i. View the C:ConfigMgrSetup.log check for the following line:
1. === Completed Configuration Manager Server Setup ===
b. (Option#2) Verify verson SCCM CB v1902
i. Launch the SCCM console.
ii. In the upper left corner, click the dropdown arrow and select About Configuration Manager.
iii. The Console versions should be: 5.1902.1085.1700
iv. The Site version should be: 5.0
5. See script content below:
SCCM_CB_1902_INSTALL-11-15-2019.ps1
## Use the commands below to Install and Configure SCCM 2019 on a single server/PC.
##
## Do Not Proceed unless you have ran script # 1
###############################################################################################
############# Install SCCM 2019 Prerequisites #############################################
#### The script below assumes all SCCM and Prereqs files have been copied to the D:SCCM_STAGING folders.
# Install .NET Framework 3.5.1
# Ensure you copy the Windows 2019 DVDSourcesSxs folder in the staging folder
Dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:NetFx3 /All /Source:C:SCCM_STAGINGW2019SourcesSxs /LimitAccess
# Install BITS and IIS
# Bits is needed for the Distribution Point and Management Point.
Install-WindowsFeature BITS
Install-WindowsFeature Web-WMI
############# Install SQL 2017 #############################################
#### The script below assumes all SQL files have been copied to the D:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENT folders.
# Set SQL Service Accounts SPN
# Run on the Site Server or domain controller
setspn -A MSSQLSvc/SRV-CM-01.JCTECH.NET:1433 SVC-SQLSC-01
setspn -A MSSQLSvc/SRV-CM-01:1433 SVC-SQLSC-01
# Install SQL 2017 using SQL Configuration file
# Take a Snapshot/Checkpoint of VM.
#
# C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENTSetup.exe /QS /IACCEPTSQLSERVERLICENSETERMS /SQLSVCPASSWORD=»Password» /AGTSVCPASSWORD=»Password» /ASSVCPASSWORD=»Password» /ConfigurationFile=C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENTSQL2017ForSCCM1903.ini
C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENTSetup.exe /QS /IACCEPTSQLSERVERLICENSETERMS /SQLSVCPASSWORD=»Password» /AGTSVCPASSWORD=»Password» /ConfigurationFile=C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_ENTSQL2017ForSCCM1903.ini
# Install Latest Cumulative Update Package for SQL Server 2017
C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_CU16SQLServer2017-KB4508218-x64.exe /ACTION=INSTALL /QUIETSIMPLE /ALLINSTANCES /ENU /IACCEPTSQLSERVERLICENSETERMS /INDICATEPROGRESS
# Install SQL SSMS 18.3
# Note I install SSMS without the /norestart and it did not prompt for a restart. Need to determine if a reboot is required.
C:SCCM_STAGINGSSMS_18.3SSMS-Setup-ENU.exe /install /passive
# ******* Reboot the server here ******
# Configure SQL Memory
# Note you must reboot the server after the SSMS 18.3 install in order for the SQLCMD command to work.
# Note it is included in the Microsoft ODBC Driver 13/17 for SQL Server
# Set MAX to 8gb. Set MIN to 4gb
sqlcmd -S SRV-CM-01 -i C:SCCM_STAGINGSCRIPTSSetSQLMem.sql -o C:SCCM_STAGINGSCRIPTSSetSQLMem.log
# Install SQL 2017 Reporting Service
C:SCCM_STAGINGSQL_2017_RSSQLServerReportingServices.exe /passive /norestart /IAcceptLicenseTerms /PID=6GPYM-VHN83-PHDM2-Q9T2R-KBV83
# Configure SQL 2017 Reporting Service
& C:SCCM_STAGINGSCRIPTSConfigure-SQL2017RS.ps1
# Set SQL 2017 Reporting Service Account
& C:SCCM_STAGINGSCRIPTSSetReportServiceAcct.ps1
# ******* Reboot the server here ******
# Install Windows ADK for Windows 10_1903
# The command below will install Windows ADK version 1903 required features for SCCM.
# It will install the following features:
# • Deployment Tools
# • User State Migration Tool
C:SCCM_STAGINGWADK_10_1903adksetup.exe /quiet /installpath E:ADK /features OptionId.UserStateMigrationTool OptionId.DeploymentTools
# Sleep for 60 seconds to allow ADK for Windows 10_1903 to install
Start-Sleep -Seconds 60
# Install Windows ADK PE_1903
# Reboot the server after installation.
C:SCCM_STAGINGWADK_10_WINPE_1903adkwinpesetup.exe /quiet /ceip off /installpath E:ADK /Features OptionId.WindowsPreinstallationEnvironment /norestart
# Sleep for 60 seconds to all WINPE ADK PE_1903 to install
Start-Sleep -Seconds 60
# ******* Reboot the server here ******
############# Install SCCM 1902 #############################################
#### The script below assumes all SSCCM files have been copied to the D:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902 folders.
# Configure NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS Files
# Only configure on drive you DON’T want SCCM to install on. (C, F, G).
New-Item C:NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS -ItemType file
New-Item F:NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS -ItemType file
New-Item G:NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS -ItemType file
# Copy CMTrace
Copy C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902SMSSETUPTOOLSCMTrace.exe C:
# Remote Differential Compression for Windows Server 2019.
Install-WindowsFeature RDC
# Install REPORT VIEWER 2012 RUNTIME and Microsoft System CLR Types for Microsoft SQL Server 2012
# These are needed to read WSUS Reports.
msiexec /passive /norestart /i C:SCCM_STAGINGREPORT_VIEWER_2012SQLSysCLRTypes.msi
msiexec /passive /norestart /i C:SCCM_STAGINGREPORT_VIEWER_2012ReportViewer.msi
############# Install WSUS ##########################################
## When using a WID database for WSUS
## Install-WindowsFeature -Name UpdateServices -IncludeManagementTools
## & ‘C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesToolsWsusUtil.exe’ postinstall content_dir=E:WSUS
## When using a SQL database for WSUS
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Updateservices-Services,UpdateServices-DB -IncludeManagementTools
# If SQL server is installed on the default SQL instance (MSSQLSERVER) on the local server…run this:
& ‘C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesToolsWsusUtil.exe’ postinstall SQL_INSTANCE_NAME=»SRV-CM-01″ content_dir=E:WSUS
# If SQL server is installed on a remote SQL server instance (MSSQLSERVER or SCCM) include the remote server name and SQL instance:
# & ‘C:Program FilesUpdate ServicesToolsWsusUtil.exe’ postinstall SQL_INSTANCE_NAME=»SRV-CM-01″ content_dir=E:WSUS
# ******* Reboot the server here ******
# Run SCCM Precheck to confirm all prerequisites are in place
C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902SMSSETUPBINX64Prereqchk.exe /LOCAL
# Install SCCM unattended
C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902SMSSETUPBINX64Setup.exe /NOUSERINPUT /Script C:SCCM_STAGINGSCCM_CB_1902SCCM_CB_1902_ALLROLES.ini
6.4 Install the SCCM Reporting Services Point
In this step you will install the SCCM Reporting service point on the site server.
1. Log on to the site server (SRV-CM-01) with the ConfigMgr 2019 install account (SVC-CM-Install).
2. Configure NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS Files
a. Start Windows Explorer.
i. Note Only configure on drive you DON’T want SCCM to install on. (C, D, E).
b. Select drive letter:
c. C, D, E
d. From the root of the drive, select File, New, Text Document.
e. Name the file NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS.
f. At the Rename screen, click Yes
- In the Configuration Manager console, click Administration.
- In the Administration workspace, expand Site Configuration, and then click Servers and Site System Roles
- Right click SRV-CM-01 and select Add Site System Role.
- The Add Site System Roles Wizard opens.
- If this is a new site system, On the Home tab, select Create Site System Server.
- On the General page, specify the general settings for the site system server. Click Next.
- Note when you add the reporting services point to an existing site system server, verify the values that you previously configured.
- On the Proxy page, click Next.
- On the System Role Selection page, select Reporting Services Point in the list of available roles, and then click Next.
- On the Reporting Services Point page, configure the following settings:
- Site database server name: SRV-CM-01.CONTOSO.NET
i. Specify the name of the server that hosts the Configuration Manager site database. Typically, the wizard automatically retrieves the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the server. To specify a database instance, use the format <Server Name><Instance Name>.
- Database name: CM_VP1
i. Specify the Configuration Manager site database name, and then click Verify to confirm that the wizard has access to the site database.
ii. Security Note The user account that is creating the reporting services point must have Read access to the site database. If the connection test fails, a red warning icon appears. Move the cursor over this icon to read details of the failure. Correct the failure, and then click Test again.
iii. Click Verify.
- Folder name: ConfigMgr_VP1
i. Specify the folder name that is created and used to host the Configuration Manager reports in Reporting Services.
- Reporting Services server instance: SSRS
i. Select in the list the instance of SQL Server for Reporting Services. When there is only one instance found, by default, it is listed and selected. When no instances are found, verify that SQL Server Reporting Services is installed and configured, and that the SQL Server Reporting Services service is started on the site system.
ii. Security Note configuration Manager makes a connection in the context of the current user to Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) on the selected site system to retrieve the instance of SQL Server for Reporting Services. The current user must have Read access to WMI on the site system, or the Reporting Services instances cannot be retrieved.
- User Name:
i. CONTOSOSVC-CM-RSP
ii. Note Select an account that is used when SQL Server Reporting Services on the reporting services point connects to the Configuration Manager site database to retrieve the data displayed in a report.
iii. Note Select Existing account to specify a Windows user account that has previously been configured as a Configuration Manager account, or select New account to specify a Windows user account that is not currently configured as a Configuration Manager account. Configuration Manager automatically grants the specified user access to the site database. The user is displayed in the Accounts subfolder of the Security node in the Administration workspace with the ConfigMgr Reporting Services Point account name. The specified Windows user account and password is encrypted and stored in the Reporting Services database. Reporting Services retrieves the data for reports from the site database by using this account and password.
- Click Next.
- On the Summary page, verify the settings and click Next to install the reporting services point.
11. After the wizard is completed, report folders are created, and the Configuration Manager reports are copied to the specified report folders. When report folders and reports are copied to the report server, they are copied in the same language as the operating system that is running on the report server.
a. To monitor the installation progress for the reporting services point, on the Reporting Service Point (SRV-CM-01) open in <F:>SMSLogs or <F:>SCCMLogs
1. SRSRPSETUP.log
2. SRSRP.log.
3. SRSRPMSI.log
ii. Note in the SRSRP.log you should see the SCCM reports being copied to the SRS database.
iii. Note if you see the following in the SRSRP.LOG:
1. ERROR:
a. Failure reported during periodic health check by the SRS Server SRV-CM-01.contoso.local
b. Error: SRS not detected as running
2. FIX:
a. When configuring SQL Server 2017 Reporting Services for SCCM, on the Database page, if using a SQL NAMED Instance (JCT-SQLSC-01SCCM) make sure the SQL Server Name includes the SQL instance:
i. SQL Server Name: JCT-SQLSC-01SCCM
iv. Note the reports should be written to D:SMS_SRSRPReports
b. When the installation completes, you should see in the SRSRP.LOG:
i. Successfully checked that the SRS web service is healthy on server <SRV-CM-01>
c. Note: you can verify that the role installs successfully navigate to Monitoring—System Status—Component Status. Right click on the following and select Show Messages-All-1 Day Ago.
i. SMS_SRS_REPORTING_POINT
ii. Look for Message ID 1015 which indicates that the Reporting Services point was successfully installed
12. Done.
6.4.1 Test SCCM Reports and SSRS Web site
- On SRV-CM-01, in the Configuration Manager console, navigate to Monitoring, Reporting.
- Click Reports.
- You should see reports in the right window.
3. (After Installation) On the SRV-CM-01 server launch IE.
4. Type in the following URL:
a. http:// SRV-CM-01/reports_SCCM
b. Or
c. http:// SRV-CM-01/reports
i. Note if prompted for credentials
1. Launch Server Manager.
2. Click Local Server. To the right of IE Enhanced Security Configuration click the ON hyperlink/option.
3. Under Administrators click Off. Click Ok to save.
4. For IE8, navigate to the Tools-Internet Options-Security-Local intranet-Sites.
5. Add the add the following:
a. Http://SRV-CM-01
ii. Note this will display the SQL Server Reporting Services home page
iii. Note you should see the ConfigMgr_VP1
d. http:// SRV-CM-01/Reportserver_SCCM
e. Or
f. http:// SRV-CM-01/Reportserver
g.
i. Note this should return the Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services Version 13.0.4001.0.
5. Done.
6.4.2 Configure Reporting Server Database Recovery Model
Set the Reporting server database recovery model to Simple. In the step you will set the database recovery Model to Simple. This is done to allow the database transaction logs to be shrink after the database is backed up.
Note if you don’t change this or backup the Reporting server database on a regular basis, the ReportServer_log.ldf file will grow extremely large.
1. On the SQL database server (JCT-SQLSC-01), Launch SQL Studio Manager 18.3.
2. Expand Databases and right click ReportServer and select properties.
3. Click Options.
4. Set the Recovery model to Simple.
5. Click Ok to save the setting.
This post will show the step-by-step process on how to install System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1902 as a Standalone Primary Server in a Windows Server 2019 lab environment from scratch and later on we will upgrade it to SCCM Current Branch version 1906.
I have broken down this post in a series of steps:
- Step 1. Primary Site Server Installation Prerequisites
- Virtual Environment
- Installation Media
- AD Accounts
- Server Configuration
- Create System Management Container and Delegate of Permission
- Extend Active Directory Schema for SCCM 1902
- Configure Windows Firewall
- Step 2. Install Web Server (IIS) Role and other Features
- Step 3. Installing and Configuring SQL Server 2017
- SQL Server 2017 Installation
- MS SQL Server Management Studio Installation
- Configure SQL Server Memory Allocation
- Step 4. Windows ADK Installation
- Installing Windows ADK for Windows 10
- Installing Windows PE add-on
- Step 5. Install Windows Server Update Services
- Step 6. Configuration Manager 1902 Installation
- Step 7. Configuration Manager 1906 Upgrade Installation
- Step 8. Optional: MDT 8456 Installation and ConfigMgr Integration
Step 1. Primary Site Server Installation Prerequisites
Virtual Environment
For the virtual environment I usually use Hyper-V in Windows 10/Windows Server 2016/2019 or VMWare Workstation.
- A host computer with enough disk space (1TB to 2TB SSD recommended) and RAM (32GB or higher)
- Virtual Machines:
- DC01 = Domain Controller (I have a server core setup)
- C: | Windows | 80 GB
- 2GB RAM
- CM01 = Primary Site Server (Domain joined)
- Recommend Partition setup:
- C: | Windows | 100 GB
- D: | SCCM / SQL /Logs | 200 GB
- 16 GB RAM or higher is recommended (70% to be allocated for the database)
- Recommend Partition setup:
- DC01 = Domain Controller (I have a server core setup)
Installation Media
What you need:
- Windows Server 2019
- SCCM 1902
- SQL Server 2017
- MS SQL Management Studio
- Windows ADK 1903 and Windows PE add-on
Download the iso files from your Visual Studio Subscription or Microsoft Evaluation Center
AD Accounts
For this installation I have created accounts
- SCCMAdmin – account to be used for administering ConfigMgr
- SQLSvrAgent – account to be used as the SQL Server Account

You can go ahead and create the rest of the required SCCM Accounts
- SCCM Network Access Account
- SCCM Client Push Install Account
- SCCM Domain Join Account (for OSD)
- SCCM Admins Group
- SCCM SQL Reporting Account (If you’re uninstalling Reporting Services)
Server Configuration
Add LABSCCMAdmin and LABCM01 to the local Administrators group for CM01.

Create System Management Container and Delegate of Permission
Open ADSI Edit to create the System Management container
In the left pane, browse the Default naming context > expand DC and look for CN=System > make a right-click > in the context menu select New > Object…

In the Create Object window, scroll and select container and click Next.

In the Value: type System Management (it’s important to take note of the spelling, capitalization and the space between the two words).

click Finish to close the window.
Launch Active Directory Users and Computers and on the View tab, click on Advance Features

Browse for System > System Management > Right-click and select Delegate Control.

In the Delegation of Control Wizard click Next.

Add the Primary Site Server, CM01 once the server is added, click Next.

In the Task to Delegate, select Create a custom task to delegate click Next.

In the Active Directory Object Type select This folder, existing objects in this folders, and creation of new objects in this folder and click Next.

Tick on the 3 permissions General, Property-specific and Creation/deletion of specific child objects. Under Permissions tick on Full Control and click Next.

Click Finish to close the wizard.

Back in the System Management Properties, confirm that the Primary Site Server has Full Control Permission.

Note: As my Domain Controller was installed as a Server Core, I installed the Remote Server Administrator Tool (RSAT) for ADDS in the Primary Site Server to have access to the Active Directory Services Interface (ADSI Edit) tooland Active Directory Users and Computers.
Extend Active Directory Schema for SCCM 1902
In the Primary Site Server, mount the installation file of System Center Configuration Manager 1902 and browse to its directory <Drive>:SMSSETUPBINX64 you’ll find the extadsch.exe file.

You can either double click on it or run it from your command prompt

When you run the Extadsh.exe its actually running ConfirMgr_ad_schema.ldf, this LDF file contains the instructions for what needs to be changed in Active Directory to support the schema extensions.
You can examine its content by opening ConfirMgr_ad_schema.ldf in Notepad.

If you’re curious go and browse through the SMS Schema Attributes. This will give you better understanding on how Active Directory schema extensions work for Configuration Manager.

From the LDF file:
# ———————————————————————-
# This section adds a new attribute for SMS Capabilities information. This is a
# new attribute for SMS V4.
#
# This attribute updates the MS-SMS-Management-Point class.
# ———————————————————————-
dn: CN=mS-SMS-Capabilities,CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=x ← this is the path of where the change is going to happen
changetype: add ← it’s going to add something
objectClass: top
objectClass: attributeSchema ← theres an obect class that attributes schema
cn: mS-SMS-Capabilities ←in this folder location
attributeID: 1.2.840.113556.1.6.29.2.1.14 ← here is the ID
attributeSyntax: 2.5.5.4 ←Syntax value
#schemaIDGUID:: y1C8EEwlBkWgB+T2V+XESA== ← here its showing the GUID
isSingleValued: TRUE
oMSyntax: 20
searchFlags: 0
isMemberOfPartialAttributeSet: TRUE
dn:
changetype: modify
replace: schemaupdatenow ← this portion will update the schema
schemaupdatenow: 1
For more information about Extending the Schema in Configuration Manager go to this link
In the root directory for your Primary Site Server, you’ll see a small text file ExtADSch.txt and when you open it, you’ll find the line: Successfully extended the Active Directory schema.

Configure Windows Firewall
To open TCP port 1433 and 4022 for SQL replication you need to launch the Windows Defender Firewall and Advance Security to do that, press Windows logo key, type wf.msc and click on it
In the Windows Defender Firewall and Advance Security right-click Inbound Rules, and then click New Rule.

In the Rule Type dialog box, select Port and then click Next.

In the Protocol and Ports dialog box, select TCP. Select Specific local ports, and then type port numbers 1433 for SQL Server default instance and 4022 for Inter-site communications use the SQL Server Service Broker. Click Next.

In the Action dialog box, select Allow the connection, and then click Next.

In the Profile dialog box, select Domain and then click Next.

In the Name dialog box, type a profile name,like SQL ports for ConfigMgr and then click Finish.

Step 2. Install Web Server (IIS) Role and other Features
In the Primary Site Server we will need to install the follow Roles and Features from the Server Manager:
In the Server Roles, select Web Server (IIS)
When prompted to “Add features that are required for Web Server (IIS)?” click the Add Features button.and click Next.

In Features, select .NET Framework 3.5 Feature and Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS)
Note: BITS – is the technology that allows us to throttle all the network communication that occurs between servers to client where it utilizes idle bandwidth to transfer data.

Still in the Features page, scroll down and select Remote Differential Compression (RDC) and click Next.
Note: RDC – is a client–server synchronization algorithm which BITS leans on to ensure that the files goes in the most efficient way possible.
In the Web Server Role (IIS) > Role Services select the following:
Web Server (IIS)
- Web Server
- Common HTTP Features: Default Document, Directory Browsing, HTTP Errors Static Content, HTTP Redirection
- Health and Diagnostics: HTTP logging, Logging tools, Request Monitor Tracing, Tracing
- Performance: Static Content Compression
- Security: Windows Authentication
- Application Development: .NET Extensibility 3.5, .NET Extensibility 4.7, ASP.NET 3.5, ASP.NET 4.7, ISAPI Extensions, ISAPI Filters
- Management Tools
- IIS Management Console
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility: IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility, IIS 6 WMI Compatibility
- IIS Management Scripts and Tools

In the Add Roles and Feature Wizard > Confirm installation selection page, review the Roles and Features selected:
- NET Framework 3.5 Features
- .NET Framework 4.7 Features
- Background Intelligent Transfer (BITS)
- Remote Differential Compression
- Web Server (IIS)
- Web Server
- Common HTTP Features: Default Document, Directory Browsing, HTTP Errors Static Content, HTTP Redirection
- Health and Diagnostics: HTTP logging, Logging tools, Request Monitor Tracing, Tracing
- Performance: Static Content Compression
- Security: Windows Authentication
- Application Development: .NET Extensibility 3.5, .NET Extensibility 4.7, ASP.NET 3.5, ASP.NET 4.7, ISAPI Extensions, ISAPI Filters
- Management Tools
- IIS Management Console
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility: IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility, IIS 6 WMI Compatibility
- IIS Management Scripts and Tools
- Web Server
Click the Install button to complete the installation of the Web Server Roles and Features.
Verify that the installation is successful from this point you can now click the Close button to proceed to the next step.
Step 3. Installing and Configuring SQL Server 2017
SQL Server 2017 Installation
In this section we will install and configure the Primary Site’s database server and it’s components. Go a head an mount the SQL Server 2017 installer and run the setup.exe.
In the SQL Server Installation Center > Installation, click on the New Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation.

In the Product Key page, choose for the Evaluation or enter a product key then click Next to continue.
Agree to the License Terms then click Next.
In the Microsoft Update we’ll skip the check updates for now, click Next.
In the Install Rules, make sure that everything pass else rectify by clicking the Status links, as for Windows Firewall we’ll ignore the Warning as the required ports for SQL replication was previously configured. We will now and proceed to the Feature Selection page.
In the Feature Selection, tick the Database Engine Services then click Next.
In the Instance Configuration, leave the default instance ID, MSSQLSERVER click Next to continue.
In the Server Configuration, Service Accounts tab, make sure to configure ALL SQL services to run under a domain user account (e.g., LABSQLSvrAgent) instead of the local system or network services.
Note: Best practice in Production, the SQL Server Agent and SQL Server Database Engineer should each have a domain accounts. For their account’s passwords should be configured not to expire and cannot be changed (so make sure these service accounts are restricted not have an interactive logon rights as well).
…Moving on, in the same window click the Collation tab.
In the Database Engine Configuration, click Add Current User or add another user/SCCM Admin groups and click Next.
SQL Server 2017 is ready to install, click the Install button.
Note: Notice the Configure file path, you can go to the directory and explore the ConfigurationFile.ini if you’re interested to install SQL Server using the configuration file.
Confirm that SQL Server 2017 is successfully installed, click the Close button to complete the installation.
MS SQL Server Management Studio Installation
Beginning SQL Server 2016 the release of SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) was a stand-alone install outside of the SQL Server release. That is why we need to do a separate install of the SSMS.
Download and install SSMS
After the installation is complete you are required to restart the Primary Server.
Configure SQL Server Memory Allocation
Launch the SQL Server Management Studio, Right-click on the CM01 (SQL Server) and select Properties.
In the Server memory options I have set the Minimum and Maximum memory size to 12288 if it’s not set to at least 8192 you’ll have a little warning during the installation of Config Manager. Setting the Memory b/w 2048 to 4096 will still work.
By default the Minimum server memory (in MB) is set to 0 and the Maximum server memory (in MB) is set to 2147483647.
Click OK to close the Server Properties window and complete the SQL configuration.
Step 4. Windows ADK Installation
In any Configuration Manager deployment I strongly recommend to install the lasted Windows 10 ADK in preparation for Windows 10 Operating Systems Deployment with Configuration Manager, the Windows ADK is a required external dependency.
Note: As of this blog post, the latest version of ADK is 1903.
From docs.microsoft.com: The following table lists the versions of the Windows 10 ADK that you can use with different versions of Configuration Manager.

In this section we will install Windows ADK 1903 and Windows PE add-on for ADK
Installing Windows ADK for Windows 10
Download and run the adksetup.exe
The installation is very straight forward, in the Specify Location leave the default and click Next.
In the Select the features you want to install, as for this installation we will only select the following:
- Deployment Tools
- Imaging and Configuration Designer – this can be used later on for provisioning packages.
- Configuration Designer
- User State Migration Tool
After selecting the features to to install, click Install button.
You’ll get the Welcome screen to Windows 10 ADK once the installation is completed. Click Close to finish the installation.

Installing Windows PE add-on
Starting Windows 10 1809, Windows Preinstallation Environment (PE) has been released separately from the Windows ADK.
To add Windows PE to the ADK installation, we need to download the Windows PE add-on and run the included installer after installing the ADK.
Similarly to Windows ADK the WinPE Add-on is a straight forward install. Download and run the adkwinpesetup.exe
In the Specify Location, click Next.

There’s nothing else to select in the Select the features you want to install other than Windows PE. Click the Install button to complete the installation.

Step 5. Install Windows Server Update Services
For us to deploy software updates using Configuration Manager we need to install the WSUS Server Role. WSUS will be later on be integrated with the Software Update Point (SUP) Site System Role.
In the Server Manager select Windows Server Update Services and click Next.

In the Role Services, tick WSUS Services and SQL Server Connectivity, in this example we will make use of the SQL Server database that we just installed in Step 3 instead of Windows Internal Database (WID).

In the Content location selection define a local or network share to store the updates. In this example I have pointed it to C:WSUS.

For the Database Instance Selection we’ll use the Primary Site’s database CM01.sg,lab.demo.
Click Install to proceed installing the WSUS role.
In the Installation progress once you see the installation succeeded go and click on the Launch Post-Install task then click on the Close button.
You can see the status of the Post-deployment Configuration from the Server Manager. Verify that the Configuration is completed.
We can also verify from SSMS that SUSDB has been created under the Databases.
Step 6. Configuration Manager 1902 Installation
Finally after all the preparation we are now ready to the install SCCM 1902. Go and mount the SCCM 1902 ISO and run the Setup.exe.
Download Required Prerequisite Files
Optional: We can download the required prerequisite files prior to the installation of Configuration Manager. This is usually done if your server is in an isolated network.
After click the Download required prerequisite files the Configuration Manager Setup Downloader will pop-up, select a directory where to download the file and click Download.


The downloader tool will close automatically after the download is complete, for this download I got 56 files in my Prereqs folder.
Install SCCM v1902
In the SCCM installation screen click Install
Click Next.
Select Install a Configuration Manager primary and tick the Use typical installation options for stand-alone primary site box.
A pop-up box will appear, read through and click on the Yes button.
In the Product Key. select an option and click on Next.
In the Product License Terms, tick all the 3 boxes and click Next.
For the Prerequisite Downloads we’ll be using the Use previously downloaded file option and point it the folder where we downloaded the files.

Let wizard finish verifying the files

In the Site and Installation Settings , enter a 3 character site code and site name that normally pertains to the site location and click Next.

In the Diagnostic and Usage Data click Next.

In the Service Connection Point Setup in this example, we will select the Yes, let’s go connected (recommended) as my server has internet connectivity, if you’re server is in an isolated network select the Skip this for now option.

Click the Next button for the final Prerequisite Check.

In the Prerequisite Check page, make sure there’s no problem found and if there is fix it first before clicking the Begin Install button.

After clicking the Begin Install you’ll be brought to the Install page to see the over all progress. You may want to grab a coffee or a beer at this point (you deserve it) and come back after an hour.

To see the detailed progress you can click the View log button, make sure to set and use CM Trace.exe as the default log viewer.
Note: CMTrance can be found in the SCCM installer’s directory e.g., D:SMSSETUPTOOLS

After an hour later, your Configuration Manager 1902 installation core setup is completed – Congratulations!

There’s a Post-Setup-Configuration Tasks link in the wizard which will lead you this Post-update checklist link: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/p/?LinkId=626562 go ahead an open the link

for version 1902 here’s the post-update check list: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/servers/manage/checklist-for-installing-update-1902#post-update-checklist
Now go ahead launch the SCCM Console and open the About window
and verify that the SCCM version is on 1902.

Don’t configure the Configuration Manager server yet as we will update it first to version 1906 in the next step.
Step 7. Configuration Manager 1906 Upgrade Installation
Before we begin to upgrade our SCCM 1902 to 1906 you may want go through on the what’s new in version 1906 of SCCM Current branch https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/plan-design/changes/whats-new-in-version-1906
Support for Configuration Manager current branch versions
Also its good to get to know about the Servicing Support/end of support dates for Configuration Manager versions from this link: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-ca/sccm/core/servers/manage/current-branch-versions-supported
SCCM 1906 Prerequisite Check
Launch the SCCM console and go to Administration > Updates and Servicing and verify that the Configuration Manager 1906 is in Ready to install State. (This will appear if your SCCM is connected to the internet for sometime)

Highlight Configuration Manager 1906 and Run prerequisite check

You will see that the Status is now Checking prerequisites.
We can see the progress by opening the C:ConfigMgrPrereq.log with CMTrace.

Alternatively we can also view the progress from the Monitoring workspace > Updates and Servicing Status right-click on the Configuration Manager 1906 and select Show Status.

The Update Pack Installation Status window will pop-up. At anytime you can click the OK button to close the window.

Back in the SCCM Console wait until the Prerequisite check passed
Select and right-click the Configuration Manager 1906 update and select Install Update Pack
SCCM 1906 Update
The Configuration Manager Updates Wizard will launch and in the General click on Next.

In the Features, select the feature you need to install, in my case the check boxes are pre-selected already I just needed to click Next.
Note: if you don’t want to select any of the features you can always enable it later, from the SCCM console Administration workspace > Updates and Servicing > Features.

In the Client Update Options, I will select Upgrade without validating as I don’t have any active client yet.

In the License Terms tick and accept the license terms box and click Next and in the Summary click on Next.

Click Close and go back to the SCCM Console to monitor the progress of the update.

In the Monitoring workspace > Updates and Servicing Status you can see that the status is Installing, go and right-click on the Configuration Manager 1906 and select Show Status to further view the detailed status.

It will take something for the installation to complete. Once completed, click the OK button to close the Status window.

In the SCCM Console, you will get a notification that “A new version of the console is available…. ” go and click on the Install the new console version link.

The SCCM console will close and go through the installation process.


You can view the progress from the log files C:ConfigMgrAdminUISetup.log and C:ConfigMgrAdminUISetupVerbose.log and after the installation is completed the new SCCM Console will automatically launch.
In the console, go and verify that the SCCM version is now in 1906.
We can refer the Configuration Manager versions from this link: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/servers/manage/updates#supported-versions
We can further confirm the Primary Site version from its Properties you can see that the Version and Build number refers back from the table above.

Later on you may see a Configuration Manager 1906 Hotfix Rollup, you can go a head and install it as at this point our SCCM Lab is still empty, the procedure of install the hotfix is the same as the SCCM 1906 Update do Run prerequisite check and Install Update Pack.
That concludes our SCCM 1906 installation process. Congratulation you made it this far!
Step 8. Optional: MDT 8456 Installation and ConfigMgr Integration
This section will show how to integrate the Microsoft Deployment Toolkit with Configuration Manager 1906 and understand the benefits of integrating MDT with SCCM.
I strongly recommend that you always include MDT to your SCCM infrastructure as this will add many enhancements (280 to be exact) in the Windows Operating System Deployment with Configuration Manager. enhancements that MDT adds to Configuration Manager.
Note: as of writing the latest version used is MDT 8456
Install MDT
After you download MDT copy it over to your Primary Site Server and run the MicrosoftDeploymentToolkit_x64.msi file.
In the MDT Setup Wizard click Next
Accept the License Agreement and click on Next
In the Custom Setup leave the defaults (as we will not be using MDT as the deployment tool) and click Next.
In the CEIP click Next
In the next page, click Install.
Once the MDT setup is complete click the Finish button to close the window.
Integrate MDT 8456 with SCCM 1906
To integrate MDT with SCCM we need to run the Configure ConfigMgr Integration as administrator from the Start Menu > Microsoft Deployment Toolkit
In the Options, the Install the MDT extensions for Configuration Manager is selected by default. The check boxes have been ticked, the Site server name and Site code boxes have been automatically populated with the SCCM server details. Click Next to proceed.
Verify that the integration is successful. Click Finish to close the window.
In the SCCM 1906 Console, go to the Software Library workplace > Overview > Operating Systems > Task Sequences
You will that there will a Create MDT Task Sequence available in ribbon.
Summary
In this post we have completed the following
- Build a SCCM 1902 lab environment
- Upgrade SCCM 1902 to 1906
- Integrate MDT with SCCM
Now you are ready to perform Software Deployment Services and Operating System Deployment with the lab that we’ve built. Thanks for taking time to read this post.