IP Addressing Commands
ip address
To define an IP
address for an interface, use the
ip address command in interface switch configuration
mode. Use the
no form of
this command to remove an IP address definition.
ip address ip-address mask
no ip address
Syntax Description
|
ip-address |
Specifies |
|
mask |
Specifies |
Command Default
No IP address is
defined for interfaces.
Command Modes
Interface (VLAN) switch configuration (config-switch-if)
Command History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.5.1 |
This |
Usage Guidelines
Use the
ip
address command to define a static IP address on an interface.
Defining a static
IP address on an interface stops the DHCP client running on the interface and
removes the IP address assigned by the DHCP client.
There is no
default IP address assigned to default VLAN.
Examples
The following
example configures VLAN 20 with the IP address 209.165.201.2 and the subnet
mask 255.255.255.0.
nfvis(config)# switch
nfvis(config-switch)# interface vlan 20
nfvis(config-switch-if)# ip address 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.0
nfvis(config-switch-if)# commit
nfvis(config-switch-if)# end
ip address
dhcp
To acquire the IP
address for an Ethernet interface from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) server, use the
ip address
dhcp command in interface configuration mode. To release the
acquired IP address, use the
no form of this
command.
ip address dhcp
no ip address dhcp
Syntax Description
| This command has no arguments or keywords. |
Command Default
None
Command Modes
Interface (VLAN) switch configuration (config-switch-if)
Command History
| Release | Modification
|
|---|---|
|
3.7.1 |
This command |
Usage Guidelines
This command
enables the DHCP client on the interface and removes all manually-configured
addresses on the interface. The
no form of
this command disables the DHCP client on the interface. The default route
(Default Gateway) received in DHCP Router option (Option 3) is assigned a
metric of 8.
Examples
The following
example acquires an IP address for VLAN 100 from DHCP.
nfvis(config-switch)# interface vlan 100
nfvis(config-switch-if)# ip address dhcp
nfvis(config-switch-if)# commit
nfvis(config-switch-if)# end
switch renew dhcp
switch renew dhcp vlan vlan-id
Syntax Description
|
vlan |
Specifies the VLAN ID. |
Command Default
None
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
|
3.7.1 |
This command was introduced. |
Usage Guidelines
This command does not enable the DHCP client on an interface. If the DHCP client is not enabled on the specified interface,
this command returns an error message. To enable the DHCP client on an interface, use the ip address dhcp command.
Examples
The following example renews an IP address on VLAN 19 that was acquired from a DHCP server:
nfvis# switch renew dhcp vlan 19
ip
default-gateway
To define a
default gateway (device), use the
ip default-gateway command in switch configuration
mode. To delete the default gateway, use the
no form of this command.
ip default-gateway ip-address
no ip default-gateway
Syntax Description
|
ip-address |
Specifies |
Command Default
No default gateway
is defined.
Command Modes
Switch configuration (config-switch)
Command History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.5.1 |
This |
Usage Guidelines
None
Examples
The following
example defines the default gateway 209.165.201.1.
nfvis(config-switch)# ip default-gateway 209.165.201.1
nfvis(config-switch)# commit
nfvis(config-switch)# end
show switch ip
interface
To display the
usability status of configured IP interfaces, use the
show switch
ip interface command in privileged EXEC mode.
show switch ip interface
Syntax Description
| This command has no arguments. |
Command Default
None
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.6.1 |
This command |
Examples
The following is a
sample output of the
show switch
ip interface command:
nfvis# show switch ip interface
IF ADMIN OPER
IP ADDRESS NAME STATUS STATUS TYPE
----------------------------------------------
172.25.213.10 VLAN2 Up Up Static
arp
To add a permanent
entry to the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache, use the
arp command in switch configuration mode. To remove an
entry from the ARP cache, use the
no form of this
command.
arp ip-address vlan vlan-id mac-address
no arp ip-address
Syntax Description
|
ip-address |
Specifies |
|
vlan vlan-id |
the VLAN ID. You can enter a value from one of the following ranges:
|
|
mac-address |
Specifies |
Command Default
None
Command Modes
Switch configuration (config-switch)
Command History
| Release
|
Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.6.1 |
This command |
Usage Guidelines
The software uses
ARP cache entries to translate 32-bit IP addresses into 48-bit hardware (MAC)
addresses. Because most hosts support dynamic address resolution, static ARP
cache entries generally do not need to be specified.
Examples
The following
example adds IP address 198.133.219.232 and MAC address 00:00:0c:40:0f:bc to
the ARP table:
nfvis(config-switch)# arp 198.133.219.232 vlan 100 00:00:0c:40:0f:bc
nfvis(config-switch)# commit
nfvis(config-switch)# end
arp timeout
To set the time
interval during which an entry remains in the ARP cache, use the
arp
timeout command in switch configuration mode. To restore the default
configuration, use the
no form of this
command.
arp timeout seconds
no arp timeout
Syntax Description
|
seconds |
Specifies |
Command Default
The default ARP
timeout is 60000 seconds, if IP Routing is enabled, and 300 seconds if IP
Routing is disabled.
Command Modes
Switch configuration (config-switch)
Command History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.6.1 |
This command |
Usage Guidelines
None
Examples
The following
example configures the ARP timeout to 12000 seconds:
nfvis(config-switch)# arp timeout 12000
nfvis(config-switch)# commit
nfvis(config-switch)# end
switch clear
arp-cache
To delete all
dynamic entries from the ARP cache, use the
switch clear arp-cache command in privileged EXEC
mode.
switch clear arp-cache
Syntax Description
|
This |
Command Default
None
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#).
Command History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.5.1 |
This |
Examples
The following
example deletes all dynamic entries from the ARP cache:
nfvis# switch clear arp-cache
show switch arp
table
To display entries in the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table, use the show switch arp table command in privileged EXEC mode.
show switch arp table
Syntax Description
| This command does not have any arguments. |
Command Default
None
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC (#)
Command History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
| 3.5.1 |
This command |
Examples
The following is a sample output of the show switch arp table command:
nfvis# show switch arp table
IP ADDR VLAN INTERFACE HW ADDRESS STATUS
--------------------------------------------------------------
192.0.2.4 VLAN2363 te1/2 00:50:22:00:2A:A4 dynamic
192.0.2.5 VLAN2364 te1/0 00:a6:ca:d6:30:c3 dynamic
192.0.2.6 VLAN2365 te1/1 00:50:22:00:2A:A5 dynamic
Join
- Home
- Networking
- Cisco
- How-tos


to enable IT peers to see that you are a professional.
2 Minute Read
-
Spice
-
Reply (9)
-
Subscribe
-
Share
Opens a new window
-
Facebook
Opens a new window -
Twitter
Opens a new window -
Reddit
Opens a new window -
LinkedIn
Opens a new window
-


to enable IT peers to see that you are a professional.

- General Networking |
- IT Jobs / Careers |
- Cisco |
- Training & Development |
- Spiceworks General Support
Sign Up
Load More
By default, Cisco switches forward Ethernet frames without any configuration. This means that you can buy a Cisco switch, plug in the right cables to connect various devices to the switch, power it on, and the switch will work properly.
However, to perform switch management over the network or use protocols such as SNMP, the switch will need to have an IP address. The IP address is configured under a logical interface, known as the management domain or VLAN. Usually, the default VLAN 1 acts like the switch’s own NIC for connecting into a LAN to send IP packets. Here are the steps to configure an IP address under VLAN 1:
- enter the VLAN 1 configuration mode with the interface vlan 1 global configuration command.
- assign an IP address with the ip address IP_ADDRESS SUBNET_MASK interface subcommand.
- enable the VLAN 1 interface with the no shutdown interface subcommand.
- (Optional) use the ip default-gateway IP_ADDRESS global configuration command to configure the default gateway.
- (Optional) Add the ip name-server IP_ADDRESS global configuration command to configure the DNS server.
Here is a simple example network:
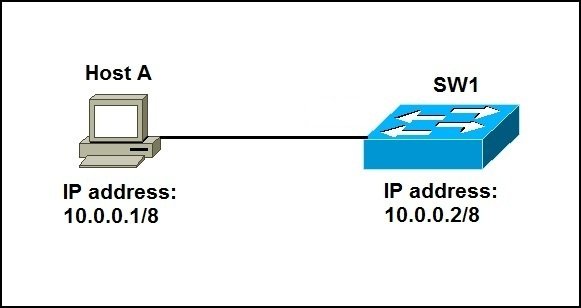
We have a simple network of a host and a switch. We can assign the switch with an IP address to enable IP communication between the two devices:
SW1(config)#int vlan 1 SW1(config-if)# SW1(config-if)# SW1(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 SW1(config-if)#no shutdown SW1(config-if)# %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Vlan1, changed state to up %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan1, changed state to up
To verify the IP address set on a switch, we can use the show int vlan 1 command:
SW1#show int vlan 1 Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is CPU Interface, address is 0030.a3e8.6b3c (bia 0030.a3e8.6b3c) Internet address is 10.0.0.2/8 ....
We can verify that the host can reach the switch using its IP address by pinging it from Host A:
C:>ping 10.0.0.2 Pinging 10.0.0.2 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 10.0.0.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255 Reply from 10.0.0.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=255 ...
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training:

Получаем информацию об IP и MAC адресах устройства, подключенного к коммутатору Cisco.
Шаг 1.
Смотрим MAC-адреса порта:
c4948
Unicast Entries
vlan mac address type protocols port
-------+---------------+--------+---------------------+--------------------
2003 5254.0028.6a01 dynamic ip GigabitEthernet1/41
2003 5254.0046.7761 dynamic ip GigabitEthernet1/41
2003 5254.007b.59cd dynamic ip,other GigabitEthernet1/41
2003 5254.0088.5ab1 dynamic ip,other GigabitEthernet1/41
2003 5254.00c8.959f dynamic ip GigabitEthernet1/41
2003 5254.00e8.823c dynamic ip,other GigabitEthernet1/41
2003 5254.00e8.88c3 dynamic ip GigabitEthernet1/41
2003 d8d3.8562.26f0 dynamic ip,other GigabitEthernet1/41
Multicast Entries
vlan mac address type ports
-------+---------------+-------+--------------------------------------------
2003 ffff.ffff.ffff system Gi1/4,Gi1/17,Gi1/25,Gi1/27,Gi1/30,Gi1/41
Gi1/45,Po1
На данном этапе мы получим список MAC-адресов, которые используются на указанном порту.
Шаг 2.
Теперь, используя полученную на предыдущем шаге информацию, узнаем IP-адрес по каждому MAC-адресу. Для этого на основном коммутаторе сети (в моем случае им выступает Nexus 7000), смотрим ARP базу:
Nexus7k
188.64.XXX.XXX 00:06:31 5254.0028.6a01 Vlan2003
