This was a fresh linux Mint xfce machine
I have been battling this for a about a week. I’m trying to learn Java on Netbeans IDE and so naturally I get the combo file straight from Oracle. Which is a package of the JDK and the Netbeans IDE together in a tar file located here.
located
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
file name
JDK 8u25 with NetBeans 8.0.1
after installing them (or so I thought) I would make/compile a simple program like «hello world» and that would spit out a jar file that you would be able to run in a terminal. Keep in mind that the program ran in the Netbeans IDE.
I would end up with this error: java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError:
Even though I ran the file from oracle website I still had the old version of the Java runtime which was not compatible to run my jar file which was compiled with the new java runtime.
After messing with stuff that was mostly over my head from setting Paths to editing .bashrc with no remedy.
I came across a solution that was easy enough for even me. I have come across something that auto installs java and configures it on your system and it works with the latest 1.8.*
One of the steps is adding a PPA wasn’t sure about this at first but seems ok as it has worked for me
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install oracle-java8-installer
domenic@domenic-AO532h ~ $ java -version
java version «1.8.0_25»
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_25-b17)
Java HotSpot(TM) Server VM (build 25.25-b02, mixed mode)
I think it also configures the browser java as well.
I hope this helps others.
Если вы сталкивались с ошибками Exception in thread “main”, то в этой статье я расскажу что это значит и как исправить ее на примерах.
При работе в среде Java, типа Eclipse или Netbeans, для запуска java-программы, пользователь может не столкнуться с этой проблемой, потому что в этих средах предусмотрен качественный запуск с правильным синтаксисом и правильной командой.
Здесь мы рассмотрим несколько общих java-исключений(Exceptions) в основных исключениях потоков, которые вы можете наблюдать при запуске java-программы с терминала.
Это исключение происходит, когда ваш класс java компилируется из другой версии JDK и вы пытаетесь запустить его из другой версии java. Рассмотрим это на простом примере:
package com.journaldev.util;
public class ExceptionInMain {
public static void main() {
System.out.println(10);
}
}
Когда создаётся проект в Eclipse, он поддерживает версию JRE, как в Java 7, но установлен терминал Jawa 1.6. Из-за настройки Eclipse IDE JDK, созданный файл класса компилируется с Java 1.7.
Теперь при попытке запустить эту версию с терминала, программа выдает следующее сообщение исключения.
pankaj@Pankaj:~/Java7Features/bin$java com/journaldev/util/ExceptionInMain Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: com/journaldev/util/ExceptionInMain : Unsupported major.minor version 51.0 at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass1(Native Method) at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClassCond(ClassLoader.java:631) at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass(ClassLoader.java:615) at java.security.SecureClassLoader.defineClass(SecureClassLoader.java:141) at java.net.URLClassLoader.defineClass(URLClassLoader.java:283) at java.net.URLClassLoader.access$000(URLClassLoader.java:58) at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:197) at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method) at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:190) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:306) at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:301) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:247)
Если запустить версию Java1.7, то это исключение не появится. Смысл этого исключения – это невозможность компилирования java-файла с более свежей версии на устаревшей версии JRE.
Исключение java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError
Существует два варианта. Первый из них – когда программист предоставляет полное имя класса, помня, что при запуске Java программы, нужно просто дать имя класса, а не расширение.
Обратите внимание: если написать: .class в следующую команду для запуска программы – это вызовет ошибку NoClassDefFoundError. Причина этой ошибки — когда не удается найти файл класса для выполнения Java.
pankaj@Pankaj:~/CODE/Java7Features/bin$java com/journaldev/util/ExceptionInMain.class Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: com/journaldev/util/ExceptionInMain/class Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.journaldev.util.ExceptionInMain.class at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:202) at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method) at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:190) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:306) at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:301) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:247)
Второй тип исключения происходит, когда Класс не найден.
pankaj@Pankajs-MacBook-Pro:~/CODE/Java7Features/bin/com/journaldev/util$java ExceptionInMain Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: ExceptionInMain (wrong name: com/journaldev/util/ExceptionInMain) at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass1(Native Method) at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass(ClassLoader.java:791) at java.security.SecureClassLoader.defineClass(SecureClassLoader.java:142) at java.net.URLClassLoader.defineClass(URLClassLoader.java:449) at java.net.URLClassLoader.access$100(URLClassLoader.java:71) at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:361) at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355) at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method) at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:423) at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:356) at sun.launcher.LauncherHelper.checkAndLoadMain(LauncherHelper.java:480)
Обратите внимание, что класс ExceptionInMain находится в пакете com.journaldev.util, так что, когда Eclipse компилирует этот класс, он размещается внутри /com/journaldev/util. Следовательно: класс не найден. Появится сообщение об ошибке.
Подробнее узнать об ошибке java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError.
Исключение java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: main
Это исключение происходит, когда вы пытаетесь запустить класс, который не имеет метод main. В Java.7, чтобы сделать его более ясным, изменяется сообщение об ошибке:
pankaj@Pankaj:~/CODE/Java7Features/bin$ java com/journaldev/util/ExceptionInMain Error: Main method not found in class com.journaldev.util.ExceptionInMain, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args) Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException
Всякий раз, когда происходит исключение из метода main – программа выводит это исключение на консоль.
В первой части сообщения поясняется, что это исключение из метода main, вторая часть сообщения указывает имя класса и затем, после двоеточия, она выводит повторно сообщение об исключении.
Например, если изменить первоначальный класс появится сообщение System.out.println(10/0); Программа укажет на арифметическое исключение.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at com.journaldev.util.ExceptionInMain.main(ExceptionInMain.java:6)
Методы устранения исключений в thread main
Выше приведены некоторые из распространенных исключений Java в потоке main, когда вы сталкиваетесь с одной из следующих проверок:
- Эта же версия JRE используется для компиляции и запуска Java-программы.
- Вы запускаете Java-класс из каталога классов, а пакет предоставляется как каталог.
- Ваш путь к классу Java установлен правильно, чтобы включить все классы зависимостей.
- Вы используете только имя файла без расширения .class при запуске.
- Синтаксис основного метода класса Java правильный.
Introduction: Early-Stage Runtime Errors
Runtime errors occur when a program is being executed and, in the case of compiled languages, after the program has been successfully compiled. Runtime errors are, therefore, harder to detect and prevent than compile-time errors [1]. In Java, some of these runtime errors (namely throwable objects which are not exceptions) are triggered at a very early stage, while the program is basically starting up. Namely, there is a process of dynamic loading, linking, and initializing of classes and interfaces by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that occurs at the very beginning of execution of any Java application [2]. This allows for a certain category of errors to be captured and dealt with before the program effectively starts.
This category of high level runtime errors in Java is represented by classes which are direct descendants of the java.lang.Error class [3], including the java.lang.LinkageError class which denotes errors occurring during the aforementioned startup process [4]. An instance of the Error class (or any of its subclasses) is a throwable object that a program is not expected or advised to handle, but instead, should cause immediate termination of the program. This is because most of these errors occur as a result of abnormal conditions, often so severe that it is impossible to know or control what further execution of the program might do. LinkageError instances in particular indicate critical class-related errors triggered during the class linking phase of the startup process, usually as a consequence of some post-compilation changes in the bytecode or the Java environment.
What is the UnsupportedClassVersionError Error and Why Does it Happen?
The java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError class extends java.lang.ClassFormatError which is thrown whenever the JVM attempts to read a class file and determines that the file is malformed or otherwise cannot be interpreted as a class file [5][6]. As per Java’s error class hierarchy (Figure 1), an instance of UnsupportedClassVersionError is also a LinkageError which means that the error is identified during the JVM class linking process.
The specific issue that the UnsupportedClassVersionError error raises is the detection of a class file which had been compiled with a newer version of Java than the one used to run it. For instance, if a specific .class file has been compiled with Java Development Kit (JDK) 15, trying to run it with Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 8 will trigger the UnsupportedClassVersionError error. This almost invariably happens when someone attempts to run a program with a JDK or a JRE version that is incompatible with, i.e., lower than the Java version in which the code was compiled.
How to Fix the UnsupportedClassVersionError Error
The solution to the UnsupportedClassVersionError error generally boils down to two options:
- Run the code with a newer version of Java/JRE, or
- Recompile the code with an older Java/JDK compiler.
As a variant of #2, recompiling the code can also be done by specifying the “target” or “release” parameter of a newer Java/JDK compiler to an earlier version of Java, to produce backward-compatible bytecode.
Before recompiling any code, it is important to know the runtime version of both the already compiled code and the environment in which it needs to run on. The message accompanying the UnsupportedClassVersionError error provides this information in the form of class file versions, which can be mapped directly to a specific Java version, using the values from the table below.
| Java SE (JDK) | Major Version | Release Date |
| 17 | 61 | September 2021 |
| 16 | 60 | March 2021 |
| 15 | 59 | September 2020 |
| 14 | 58 | March 2020 |
| 13 | 57 | September 2019 |
| 12 | 56 | March 2019 |
| 11 | 55 | September 2018 |
| 10 | 54 | March 2018 |
| 9 | 53 | September 2017 |
| 8 | 52 | March 2014 |
| 7 | 51 | July 2011 |
| 6 | 50 | December 2006 |
| 5.0 | 49 | September 2004 |
| 1.4 | 48 | February 2002 |
| 1.3 | 47 | May 2000 |
| 1.2 | 46 | December 1998 |
| 1.1 | 45 | February 1997 |
| 1.01 | 45 | May 1996 |
UnsupportedClassVersionError Error Example
Below is an example of the UnsupportedClassVersionError error, indicating that the class com.rollbar.ExampleApp was compiled with Java 17 (class file version 61) but executed with Java 8 (class file version 52).
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: com/rollbar/ExampleApp
has been compiled by a more recent version of the Java Runtime (class file version 61.0),
this version of the Java Runtime only recognizes class file versions up to 52.0Using a newer Java version
The most straightforward solution is to update the JRE on the machine on which the code is running. Executing the commands echo %JAVA_HOME% and java -version inside a terminal should point to the existing Java installation directory and its version number. This can be particularly useful to pinpoint which version is in use when multiple JREs are installed on the same machine. From there, downloading and updating the JAVA_HOME variable to point to the newer Java version (e.g. Java 17) [7] will fix the UnsupportedClassVersionError error.
Recompiling by Targeting an Older Java Version
If the program needs to be compatible with older versions of Java as a business requirement, compiling it accordingly would be the most sensible solution. This can be accomplished either by using an older JDK compiler, or by specifying the target version on a newer JDK compiler. Using the terminal command javac -target 8 com/rollbar/ExampleApp.java by specifying the targeted JDK version with the -target or alternatively the -release flag, will instruct the compiler to produce bytecode compatible with that version (Java 8 in this example).
This solution should work universally across different JDKs and compilers, so long as the target version is the same or older than that of the compiler, and given that the source code syntax is compatible with the target version. In instances where this isn’t the case, refactoring the code before compiling it might be necessary.
Working with IDEs
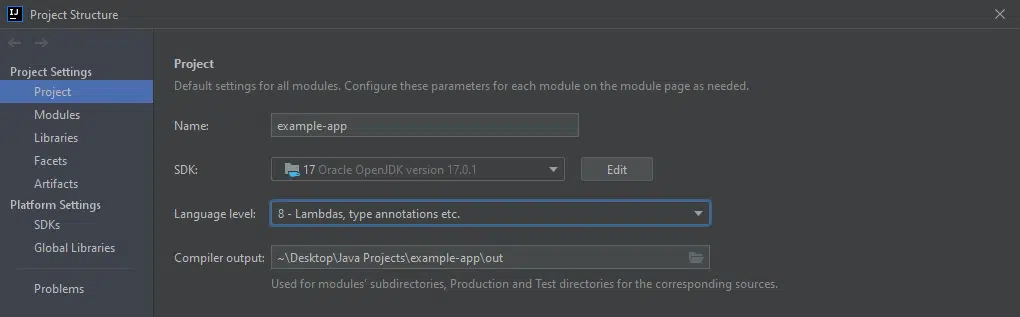
All major IDEs have configuration settings where one can specify which JDK and JRE versions to use, down to a project level. Newer IDEs even allow downloading newer versions directly through their graphical user interfaces which makes setting up a Java project a breeze, even if just for recompiling it. For this specific purpose, a setting normally called “Project language level” or “Compiler compliance level” can be tweaked, the project rebuilt/recompiled, and the aforementioned UnsupportedClassVersionError error resolved without ever leaving the IDE. An example for where to find this setting in JetBrains IDEs is shown below.
Maven Projects
When dealing with Maven projects, which the majority of both small and large enterprise Java programs are, it is possible to control the Java version targeted by the compilation process from the Maven configuration, i.e. Maven Project Object Model (POM) file. The relevant settings are shown in the Figure below.
Note that while it is possible to control the source and target versions independently, it is recommended to set them to equal values, as backward compatibility of the compiled bytecode cannot be guaranteed [8].
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
...
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
...
</project>Conclusion
The UnsupportedClassVersionError error is a critical Java runtime error thrown during the class linking phase at the very beginning of a program’s execution. This error occurs when attempting to run some code, usually a full-fledged pre-compiled program, on a platform that has a JRE older than the one the code was compiled on. Resolving the UnsupportedClassVersionError error involves either updating the JRE on the target machine or, if backward compatibility is needed, recompiling the program to target the older JRE. Modern IDEs make this process easy with their built-in tools and configuration settings, which is not to say that the same cannot be accomplished without them, as has been explained in this article.
Track, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar
Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring and triaging, making fixing Java errors easier than ever. Sign Up Today!
References
[1] Rollbar, 2021. How to Fix «Illegal Start of Expression» in Java. Rollbar Editorial Team. [Online]. Available: https://rollbar.com/blog/how-to-fix-illegal-start-of-expression-in-java/. [Accessed Jan. 8, 2022]
[2] Oracle, 2021. Chapter 5. Loading, Linking, and Initializing. Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. [Online]. Available: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jvms/se17/html/jvms-5.html. [Accessed Jan. 8, 2022]
[3] Oracle, 2021. Error (Java SE 17 & JDK 17). Oracle and/or its affiliates. [Online]. Available: https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/17/docs/api/java.base/java/lang/Error.html. [Accessed Jan. 8, 2022]
[4] Oracle, 2021. LinkageError (Java SE 17 & JDK 17). Oracle and/or its affiliates. [Online]. Available: https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/17/docs/api/java.base/java/lang/LinkageError.html. [Accessed Jan. 8, 2022]
[5] Oracle, 2021. ClassFormatError (Java SE 17 & JDK 17). Oracle and/or its affiliates. [Online]. Available: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/9/docs/api/java/lang/ClassFormatError.html. [Accessed Jan. 8, 2022]
[6] Oracle, 2021. UnsupportedClassVersionError (Java SE 17 & JDK 17). Oracle and/or its affiliates. [Online]. Available: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/9/docs/api/java/lang/UnsupportedClassVersionError.html. [Accessed Jan. 8, 2022]
[7] Oracle, 2011. Installing the JDK Software and Setting JAVA_HOME. Oracle and/or its affiliates. [Online]. Available: https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E21454_01/html/821-2531/inst_jdk_javahome_t.html. [Accessed Jan. 8, 2022]
[8] E. Punzalan, 2019. Apache Maven Compiler Plugin – Setting the -source and -target of the Java Compiler. The Apache Software Foundation. [Online]. Available: https://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-compiler-plugin/examples/set-compiler-source-and-target.html. [Accessed Jan. 8, 2022]
Автор оригинала: Amy DeGregorio.
1. введение
В этом коротком уроке мы узнаем, что вызывает ошибку Java во время выполнения java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Неподдерживаемая основная.второстепенная версия и как это исправить.
Дальнейшее чтение:
Не удалось найти или загрузить основную ошибку класса
Причины и предотвращение java.lang.Ошибка проверки
2. Взгляните на ошибку
Давайте начнем с рассмотрения примера ошибки:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: com/baeldung/MajorMinorApp has been compiled by a more recent version of the Java Runtime (class file version 55.0), this version of the Java Runtime only recognizes class file versions up to 52.0
Эта ошибка говорит нам о том, что наш класс был скомпилирован на более высокой версии Java, чем версия, с которой мы пытались его запустить. Более конкретно, в данном случае мы скомпилировали наш класс с Java 11 и попытались запустить его с Java 8.
2.1. Номера версий Java
Для справки, давайте быстро взглянем на номера версий Java. Это пригодится в случае, если нам понадобится загрузить соответствующую версию Java.
Основные и второстепенные номера версий хранятся в байт-коде класса в байтах шесть и семь.
Давайте посмотрим, как основные номера версий соотносятся с версиями Java:
- 45 1.1
- 46 1.2
- 47 1.3
- 48 1.4
- 49 5
- 50 6
- 51 7
- 52 8
- 53 9
- 54 10
- 55 11
- 56 12
- 57 13
3. Исправьте ошибку с помощью командной строки
Теперь давайте обсудим, как мы можем устранить эту ошибку при запуске Java из командной строки.
В зависимости от вашей ситуации у нас есть два способа устранить эту ошибку: скомпилировать наш код для более ранней версии Java или запустить наш код на более новой версии Java .
Окончательное решение зависит от вашей ситуации. Если нам нужно использовать стороннюю библиотеку, которая уже была скомпилирована на более высоком уровне, нашим лучшим вариантом, вероятно, является запуск нашего приложения с использованием более новой версии Java. Если мы упаковываем приложение для распространения, возможно, лучше всего скомпилировать его до более старой версии.
3.1. Переменная среды JAVA_HOME
Давайте начнем с проверки того, как установлена наша переменная JAVA_HOME . Это подскажет нам, какой JDK используется, когда мы запускаем javac из нашей командной строки:
echo %JAVA_HOME% C:AppsJavajdk8-x64
Если мы готовы полностью перейти на более новую JDK , мы можем загрузить более новую версию и убедиться, что наши ПУТЬ и Переменные среды JAVA_HOME установлены соответствующим образом .
3.2. Запуск нового JRE
Возвращаясь к нашему примеру, давайте посмотрим, как мы можем устранить ошибку, запустив ее на более поздней версии Java. Предполагая, что у нас есть Java 11 JRE в C:Appsjdk-11.0.2 , мы можем запустить ваш код с помощью команды java , упакованной вместе с ним:
C:Appsjdk-11.0.2binjava com.baeldung.MajorMinorApp Hello World!
3.3. Компиляция С более старым JDK
Если мы пишем приложение, которое хотим запустить до определенной версии Java, нам нужно скомпилировать код для этой версии.
Мы можем сделать это одним из трех способов: используя более старый JDK для компиляции нашего кода; используя -bootclasspath , -исходный и -целевой параметры команды javac (JDK 8 и старше); или используя параметр –release (JDK 9 и новее).
Давайте начнем с использования более старого JDK, аналогично тому, как мы использовали более новую JRE для запуска нашего кода:
C:AppsJavajdk1.8.0_31binjavac com/baeldung/MajorMinorApp.java
Можно просто использовать -исходный код и -целевой , но это все равно может привести к созданию файлов классов, несовместимых со старой Java.
Чтобы обеспечить совместимость, мы можем указать -bootclasspath на rt.jar целевого JRE:
javac -bootclasspath "C:AppsJavajdk1.8.0_31jrelibrt.jar" -source 1.8 -target 1.8 com/baeldung/MajorMinorApp.java
Вышесказанное относится в основном к JDK 8 и ниже. В JDK 9 параметр –release был добавлен для замены -источника и -цели . Опция –выпуск поддерживает целевые объекты 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, и 11.
Давайте используем –release для таргетинга Java 8:
javac --release 8 com/baeldung/MajorMinorApp.java
Теперь мы можем запускать наш код на Java 8 или выше JRE.
4. Среда разработки Eclipse
Теперь, когда мы понимаем ошибку и общий подход к ее исправлению, давайте возьмем то, что мы узнали, и посмотрим, как мы можем применить ее при работе в среде разработки Eclipse.
4.1. Изменение JRE
Предполагая , что у нас уже есть Eclipse, настроенный на разные версии Java, давайте изменим JRE нашего проекта.
Давайте перейдем к вашим Свойствам проекта , затем Пути сборки Java , а затем на вкладку Библиотеки . Оказавшись там, мы выберем JRE и нажмем Редактировать :
Теперь давайте выберем Альтернативный JRE и укажем на нашу установку Java 11:
На этом этапе наше приложение будет работать с Java 11.
4.2. Изменение уровня компилятора
Теперь давайте посмотрим, как мы можем изменить нашу цель на более низкий уровень Java.
Во-первых, давайте вернемся к нашим Свойствам проекта , затем Компилятору Java , а затем проверим Включить настройки для конкретного проекта :
Здесь мы можем настроить компиляцию вашего проекта для более ранних версий Java и настроить другие параметры соответствия:
5. ИДЕЯ IntelliJ
Мы также можем контролировать версию Java, которую мы используем для компиляции и запуска в IntelliJ IDEA.
5.1. Добавление JDK
Прежде чем мы это сделаем, мы посмотрим, как добавить дополнительные JDK. Давайте перейдем в Файл -> Структура проекта -> Настройки платформы -> SDKs :
Давайте щелкнем значок плюса в средней колонке, выберем JDK из раскрывающегося списка и выберем наше местоположение JDK:
5.2. Изменение JRE
Сначала мы рассмотрим, как использовать IDEA для запуска нашего проекта на более новой JRE.
Давайте перейдем в Выполнить -> Редактировать конфигурации… и измените наш JRE на 11:
Теперь, когда мы запускаем наш проект, он будет работать с Java 11 JRE.
5.3. Изменение уровня компилятора
Если мы распространяем наше приложение для работы на более низком ИЛИ, нам необходимо настроить уровень компилятора для более старой версии Java.
Давайте перейдем в Файл -> Структура проекта… -> Настройки проекта -> Проект и изменим наш SDK проекта и Уровень языка проекта :
Теперь мы можем создать ваш проект, и созданные файлы классов будут работать на Java 8 и выше.
6. Maven
Когда мы создаем и упаковываем файл в Maven , мы можем контролировать версию Java, на которую мы нацелены.
При использовании Java 8 или более поздней версии мы устанавливаем источник и цель для плагина компилятора.
Давайте установим источник и цель, используя свойства плагина компилятора:
В качестве альтернативы мы можем установить источник и цель в плагине компилятора:
maven-compiler-plugin
1.8
1.8
С –отпустите опция добавлена в Java 9, мы также можем настроить ее с помощью Maven.
Давайте используем свойство плагина компилятора для установки выпуска :
Или мы можем настроить плагин компилятора напрямую:
7. Заключение
В этой статье мы узнали, что вызывает java.lang.Ошибка UnsupportedClassVersionError: Неподдерживаемая основная.второстепенная версия сообщение об ошибке и способы ее исправления.
- Cause of the
java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError - Fix the
java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError

This tutorial demonstrates the Exception in thread main java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError error in Java.
Cause of the java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError
The UnsupportedClassVersionError is a sub-class of the ClassFormatError exception, which is thrown when JVM tries to read a class and finds that the class file is malformed or the file cannot be interpreted as a class. Here is the hierarchy of the UnsupportedClassVersionError exception:
Java.Lang.Object
Java.Lang.Throwable
Java.Lang.Error
Java.Lang.LinkageError
Java.Lang.ClassFormatError
Java.Lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError
The UnsupportedClassVersionError exception is specific to detecting a class file run by a lower version of Java before and now run by a newer version.
For example, suppose a Java file was run by JDK 12 and now by a newer JRE 8. In that case, it will throw the UnsupportedClassVersionError exception, or if we compile the class using Java version 1.8 and compile it using Java 1.7, it will throw the same error.
Let’s try an example in a class compiled by the newer version of Java and then run by an older version. See example:
public class Unsupported_Class_Version_Error{
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Hello this is Delftstack.com");
}
}
The code above will throw the UnsupportedClassVersionError as shown below:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Unsupported_Class_Version_Error : Unsupported major.minor version 52.0
at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass1(Native Method)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass(ClassLoader.java:800)
at java.security.SecureClassLoader.defineClass(SecureClassLoader.java:142)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.defineClass(URLClassLoader.java:449)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.access$100(URLClassLoader.java:71)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:361)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:425)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:358)
at sun.launcher.LauncherHelper.checkAndLoadMain(LauncherHelper.java:482)
The output shows the error because the code is compiled at Java 1.8 and executed at Java 1.7. That is why Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Unsupported_Class_Version_Error : Unsupported major.minor version 52.0 will be thrown.
Fix the java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError
There are two conditions for this error, so the solution lies in these two conditions:
- Run the code with the latest JDK and JRE.
- Compile the code with the older version of JDK to match the runtime JDK.
- One simple solution is to use the Java Cross Compilation. If the Production Environment JDK is lower than the Build Environment, we can generate a class file with a lower version using cross-compilation.
The following command will be used to create a class file for the code above:
javac -target 1.7 Unsupported_Class_Version_Error.java
As mentioned above, the solution is to build the application with the same versions at compile and runtime, or at least the compile-time version is lower than the runtime version.
The error above shows the Major Minor versions problem. Major Minor versions are the versions of JRE; for example, for JRE 8, the Major version is 52.0.
We must ensure no Major Minor version problems occur while compiling and executing the Java Class file. The list for the versions of JRE which are compatible with the class are:
Java SE 17 = 61,
Java SE 16 = 60,
Java SE 15 = 59,
Java SE 14 = 58,
Java SE 13 = 57,
Java SE 12 = 56,
Java SE 11 = 55,
Java SE 10 = 54,
Java SE 9 = 53,
Java SE 8 = 52,
Java SE 7 = 51,
Java SE 6.0 = 50,
Java SE 5.0 = 49,
JDK 1.4 = 48,
JDK 1.3 = 47,
JDK 1.2 = 46,
JDK 1.1 = 45